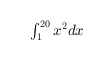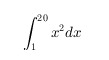ConstantLine のプロパティ
定数直線の外観と動作
定数直線とは、直交座標軸の指定された x 値または y 値を通って描画される直線です。関数 xline および yline は垂直の定数直線と水平の定数直線をそれぞれ作成します。ConstantLine プロパティ値を変更することによって、定数直線の外観と動作を変更できます。
xl = xline(4); xl.LineWidth = 2;
位置
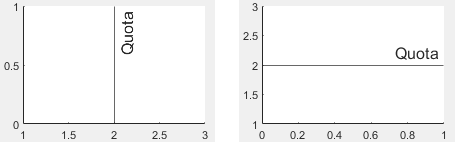
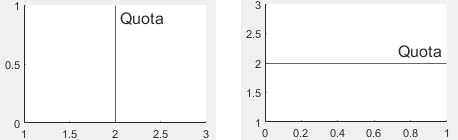
定数直線の x 軸上または y 軸上の位置。スカラーとして指定します。この値は数値、categorical 値、datetime 値または、duration 値として指定できます。
例
x = 5.5 の定数直線を作成します。その後、値を 7 に変更します。
xl = xline(5.5); xl.Value = 7;
交差する軸。垂直線または水平線をそれぞれ 'x' または 'y' として指定します。x 軸と交差する定数直線は垂直線で、y 軸と交差する定数直線は水平線です。
R2024a 以降
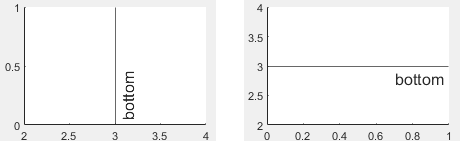
レイヤー位置。"bottom" または "top" として指定します。値が "bottom" の場合、座標軸のラインやマーカーなどの他の項目の下に ConstantLine オブジェクトが表示されます。値が "top" の場合、他の項目の上に ConstantLine オブジェクトが表示されます。
ConstantLine オブジェクトを関数 uistack に渡しても、その重なり順序に影響はなく、座標軸の Children プロパティが並べ替えられることもありません。
ラベル
ライン ラベル。文字ベクトル、文字ベクトルの cell 配列、string 配列、または数値配列として指定します。複数行のラベルを作成するには、string 配列、または文字ベクトルの cell 配列を使用します。
例: "cutoff frequency"
例: ["One row of text","A second row of text"]
例: {'One row of text','A second row of text'}
上付き文字、下付き文字、ギリシャ文字、数学記号などの特殊文字を含めるには、TeX マークアップを使用します。サポートされるマークアップの一覧については、Interpreter プロパティを参照してください。
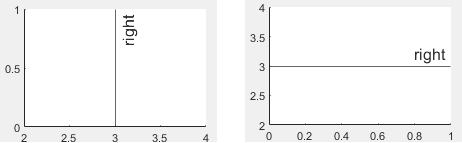
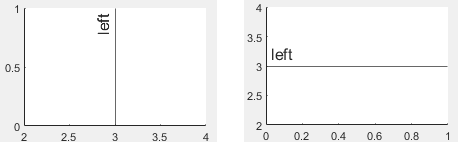
ラインに対するラベルの水平方向の配置。次の表のいずれかのオプションとして指定します。
| オプション | 説明 | |
|---|---|---|
'right' | ラインの右側。
| |
'left' | ラインの左側。
| |
'center' | ラインの中心。垂直線では、ラベルでラインが分割されます。
| |
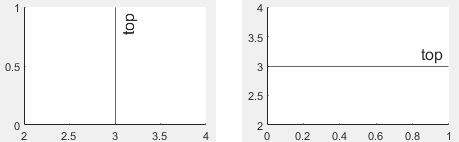
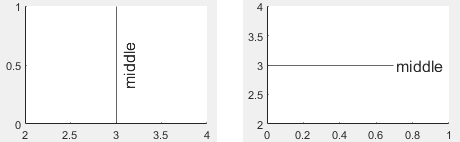
ラインに対するラベルの垂直方向の配置。次の表のいずれかのオプションとして指定します。
| オプション | 説明 | |
|---|---|---|
'top' | ラインの上方。
| |
'middle' | ラインの中央。水平線では、ラベルでラインが分割されます。
| |
'bottom' | ラインの下方。
| |
ラベルの向き。'aligned' または 'horizontal' として指定します。例を表に示します。
| 向き | 説明 | |
|---|---|---|
'aligned' | ラベルの向きはラインの向きと同じです。
| |
'horizontal' | ラインの向きに関係なく、ラベルは水平です。
| |
テキスト インタープリター。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
'tex'— TeX マークアップのサブセットを使用して文字を解釈します。'latex'— LaTeX マークアップを使用して文字を解釈します。'none'— リテラル文字を表示します。
TeX マークアップ
MATLAB® では、既定で TeX マークアップのサブセットをサポートしています。TeX マークアップを使用して、上付き文字や下付き文字の追加、フォントのタイプや色の変更、テキストへの特殊文字の挿入を行うことができます。
修飾子の効果はテキストの末尾まで適用されます。上付き文字と下付き文字は例外であり、次の 1 文字または中かっこで囲まれた文字にのみ適用されます。インタープリターを "tex" に設定した場合にサポートされる修飾子は次のとおりです。
| 修飾子 | 説明 | 例 |
|---|---|---|
^{ } | 上付き文字 | "text^{superscript}" |
_{ } | 下付き文字 | "text_{subscript}" |
\bf | 太字フォント | "\bf text" |
\it | イタリック フォント | "\it text" |
\sl | 斜体フォント (通常はイタリック フォントと同じ) | "\sl text" |
\rm | 標準フォント | "\rm text" |
\fontname{ | フォント名 — | "\fontname{Courier} text" |
\fontsize{ | フォント サイズ — | "\fontsize{15} text" |
\color{ | フォントの色 — red、green、yellow、magenta、blue、black、white、gray、darkGreen、orange、lightBlue の色のいずれかに置き換えます。 | "\color{magenta} text" |
\color[rgb]{specifier} | フォントのカスタムの色 — | "\color[rgb]{0,0.5,0.5} text" |
次の表に、"tex" インタープリターでサポートされる特殊文字を示します。
| 文字列 | 記号 | 文字列 | 記号 | 文字列 | 記号 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α |
| υ |
| ~ |
| ∠ |
| ϕ |
| ≤ |
|
|
| χ |
| ∞ |
| β |
| ψ |
| ♣ |
| γ |
| ω |
| ♦ |
| δ |
| Γ |
| ♥ |
| ϵ |
| Δ |
| ♠ |
| ζ |
| Θ |
| ↔ |
| η |
| Λ |
| ← |
| θ |
| Ξ |
| ⇐ |
| ϑ |
| Π |
| ↑ |
| ι |
| Σ |
| → |
| κ |
| ϒ |
| ⇒ |
| λ |
| Φ |
| ↓ |
| µ |
| Ψ |
| º |
| ν |
| Ω |
| ± |
| ξ |
| ∀ |
| ≥ |
| π |
| ∃ |
| ∝ |
| ρ |
| ∍ |
| ∂ |
| σ |
| ≅ |
| • |
| ς |
| ≈ |
| ÷ |
| τ |
| ℜ |
| ≠ |
| ≡ |
| ⊕ |
| ℵ |
| ℑ |
| ∪ |
| ℘ |
| ⊗ |
| ⊆ |
| ∅ |
| ∩ |
| ∈ |
| ⊇ |
| ⊃ |
| ⌈ |
| ⊂ |
| ∫ |
| · |
| ο |
| ⌋ |
| ¬ |
| ∇ |
| ⌊ |
| x |
| ... |
| ⊥ |
| √ |
| ´ |
| ∧ |
| ϖ |
| ∅ |
| ⌉ |
| 〉 |
| | |
| ∨ |
| 〈 |
| © |
LaTeX マークアップ
LaTeX マークアップを使用するには、インタープリターを "latex" に設定します。インライン モードでは、マークアップを 1 つのドル記号 ($) で囲みます。表示モードでは、マークアップを 2 つのドル記号 ($$) で囲みます。
| LaTeX モード | 例 | 結果 |
|---|---|---|
| インライン |
"$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$" |
|
| 表示 |
"$$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$$" |
|
テキストは LaTeX の既定のフォント スタイルで表示され、FontName、FontWeight、FontAngle のプロパティは無視されます。フォント スタイルを変更するには、LaTeX マークアップを使用します。
LaTeX インタープリターで使用できるテキストの最大サイズは 1200 文字です。複数行のテキストの場合は、さらに 1 行につき 10 文字ほど文字数が少なくなります。
MATLAB では、大半の標準の LaTeX 数式モード コマンドがサポートされています。詳細については、サポートされる LaTeX コマンドを参照してください。TeX および LaTeX の使用例については、チャートのテキスト内のギリシャ文字と特殊文字を参照してください。
R2024b 以降
ラベルの色。RGB 3 成分、16 進数カラー コード、色名、または省略名として指定します。
カスタム色を使用する場合は、RGB 3 成分または 16 進数カラー コードを指定します。
RGB 3 成分は、色の赤、緑、青成分の強度を指定する 3 成分の行ベクトルです。強度値は
[0,1]の範囲でなければなりません。たとえば[0.4 0.6 0.7]のようになります。16 進数カラー コードは、ハッシュ記号 (
#) で始まり、3 桁または 6 桁の0からFまでの範囲の 16 進数が続く string スカラーまたは文字ベクトルです。この値は大文字と小文字を区別しません。したがって、カラー コード"#FF8800"、"#ff8800"、"#F80"、および"#f80"は等価です。
あるいは、名前を使用して一部の一般的な色を指定できます。次の表に、名前の付いた色オプション、等価の RGB 3 成分、および 16 進数カラー コードを示します。
| 色名 | 省略名 | RGB 3 成分 | 16 進数カラー コード | 外観 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | 該当なし | 該当なし | 該当なし | 色なし |
次の表に、ライト テーマとダーク テーマでのプロットの既定のカラー パレットを示します。
| パレット | パレットの色 |
|---|---|
R2025a より前: ほとんどのプロットで、これらの色が既定で使用されます。 |
|
|
|
orderedcolors 関数と rgb2hex 関数を使用すると、これらのパレットの RGB 3 成分および 16 進数カラー コードを取得できます。たとえば、"gem" パレットの RGB 3 成分を取得し、16 進数カラー コードに変換します。
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);R2023b より前: RGB = get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder") を使用して、RGB 3 成分を取得します。
R2024a より前: H = compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)) を使用して、16 進数カラー コードを取得します。
R2024b 以降
LabelColor プロパティの設定方法を制御します。次のいずれかの値として指定します。
"auto"— MATLAB はLabelColorプロパティをColorプロパティと同じ値に設定します。したがって、ラインとラベルは同じ色になります。"manual"—LabelColorプロパティの値を直接設定します。この色は変更されません。
LabelColor プロパティの値を手動で変更すると、MATLAB は LabelColorMode プロパティの値を "manual" に変更します。
色とスタイル
ラインの色。RGB 3 成分、16 進数カラー コード、色名、または省略名として指定します。
カスタム色を使用する場合は、RGB 3 成分または 16 進数カラー コードを指定します。
RGB 3 成分は、色の赤、緑、青成分の強度を指定する 3 成分の行ベクトルです。強度値は
[0,1]の範囲でなければなりません。たとえば[0.4 0.6 0.7]のようになります。16 進数カラー コードは、ハッシュ記号 (
#) で始まり、3 桁または 6 桁の0からFまでの範囲の 16 進数が続く string スカラーまたは文字ベクトルです。この値は大文字と小文字を区別しません。したがって、カラー コード"#FF8800"、"#ff8800"、"#F80"、および"#f80"は等価です。
あるいは、名前を使用して一部の一般的な色を指定できます。次の表に、名前の付いた色オプション、等価の RGB 3 成分、および 16 進数カラー コードを示します。
| 色名 | 省略名 | RGB 3 成分 | 16 進数カラー コード | 外観 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | 該当なし | 該当なし | 該当なし | 色なし |
次の表に、ライト テーマとダーク テーマでのプロットの既定のカラー パレットを示します。
| パレット | パレットの色 |
|---|---|
R2025a より前: ほとんどのプロットで、これらの色が既定で使用されます。 |
|
|
|
orderedcolors 関数と rgb2hex 関数を使用すると、これらのパレットの RGB 3 成分および 16 進数カラー コードを取得できます。たとえば、"gem" パレットの RGB 3 成分を取得し、16 進数カラー コードに変換します。
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);R2023b より前: RGB = get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder") を使用して、RGB 3 成分を取得します。
R2024a より前: H = compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)) を使用して、16 進数カラー コードを取得します。
例: 'g'
例: [0.6 0.2 0.5]
例: '#D2F9A7'
Color プロパティの設定方法を制御します。次のいずれかの値として指定します。
"auto"— MATLAB がConstantLineオブジェクトのSeriesIndexプロパティと座標軸のColorOrderプロパティを使用して、Colorプロパティ値を制御します。"manual"—ConstantLineオブジェクトを作成するときに、Colorプロパティ値を直接設定するか、関数の引数として間接的に設定します。
Color プロパティの値を手動で変更すると、MATLAB は ColorMode プロパティの値を "manual" に変更します。
ライン スタイル。次の表にリストされたオプションのいずれかとして指定します。
| ライン スタイル | 説明 | 結果として得られる線 |
|---|---|---|
"-" | 実線 |
|
"--" | 破線 |
|
":" | 点線 |
|
"-." | 一点鎖線 |
|
"none" | ラインなし | ラインなし |
LineStyle プロパティの設定方法を制御します。次のいずれかの値として指定します。
"auto"—ConstantLineオブジェクトのSeriesIndexプロパティと座標軸のLineStyleOrderプロパティを使用することにより、MATLAB がLineStyleプロパティ値を制御します。"manual"—ConstantLineオブジェクトを作成するときに、LineStyleプロパティ値を直接設定するか、関数の引数として間接的に設定します。
LineStyle プロパティの値を手動で変更すると、MATLAB は LineStyleMode プロパティの値を "manual" に変更します。
ライン幅。ポイント単位の正の値として指定します。
ラインの透明度。[0,1] の範囲のスカラーとして指定します。値 1 は不透明で、値 0 は完全に透明です。0 と 1 の間の値は半透明です。
シリーズ インデックス。正の整数または "none" として指定します。このプロパティは、ConstantLine オブジェクトの色とライン スタイルを他のオブジェクトと一致するよう再割り当てするのに役立ちます。
SeriesIndex プロパティが数値の場合、MATLAB はこの数値を使用して、関数 xline または yline を呼び出すときに色とライン スタイルを割り当てるインデックスを計算します。インデックスは座標軸の ColorOrder プロパティと LineStyleOrder プロパティに格納されている配列の行を参照します。同じ SeriesIndex 数値をもつ座標軸内のオブジェクトは同じ色 (および、該当する場合は同じライン スタイル) をもちます。
SeriesIndex の値が "none" の場合は、インデックス方式に参加しない中間色の実線に対応します。
色、ライン スタイル、またはマーカーの手動設定が SeriesIndex の動作をオーバーライドする方法
色とライン スタイルを手動で制御するには、ConstantLine オブジェクトの Color および LineStyle プロパティを設定します。
オブジェクトのこれらのプロパティを手動で設定すると、MATLAB はそのオブジェクトの色とライン スタイルの自動選択を無効にし、SeriesIndex プロパティの値に関係なく選択を保持できるようにします。ColorMode および LineStyleMode プロパティは、色とライン スタイルが手動で (ユーザーにより) 設定されているか、自動的に設定されているかを示します。これらの各モード プロパティについて、値 "manual" は手動選択を示し、"auto" は自動選択を示します。
自動選択を再度有効にするには、ColorMode、LineStyleMode、または両方のプロパティを "auto" に設定し、SeriesIndex プロパティを正の整数に設定します。
場合によっては、MATLAB は SeriesIndex プロパティを 0 に設定し、色の自動選択も無効にします。
フォント
フォント名。サポートされているフォント名または "FixedWidth" として指定します。テキストを正しく表示し印刷するには、システムでサポートされているフォントを選択しなければなりません。既定のフォントは、オペレーティング システムとロケールによって異なります。
どのロケールでもテキストが整って見える固定幅のフォントを使用するには、"FixedWidth" を使用します。固定幅フォントは、ルートの FixedWidthFontName プロパティによって決まります。ルートの FixedWidthFontName プロパティを設定すると、表示内容が新しいフォントを使用して直ちに更新されます。
フォント サイズ。正の数値として指定します。測定単位はポイントです。既定のフォント サイズは、オペレーティング システムとロケールによって異なります。
文字の太さ。'normal' または 'bold' として指定します。
MATLAB ではフォントは、FontWeight プロパティを使用して、ユーザーのシステムで使用可能なフォントから選択します。すべてのフォントに太字があるとは限りません。そのため、太字フォントを指定しても標準フォントの太さと変わらない場合があります。
文字の傾斜。'normal' または 'italic' として指定します。
すべてのフォントに両方のフォント スタイルがあるとは限りません。そのため、イタリック フォントを指定しても標準フォントと変わらない場合があります。
凡例
凡例ラベル。文字ベクトルまたは string スカラーとして指定します。legend コマンドを呼び出すまで、凡例は表示されません。テキストを指定しない場合、legend は 'dataN' 形式を使用してラベルを設定します。
Annotation オブジェクトとして指定して、凡例にオブジェクトを含めます。Annotation オブジェクトの基となる IconDisplayStyle プロパティを次のいずれかの値に設定します。
"on"— 凡例にオブジェクトを含めます (既定)。"off"— 凡例にオブジェクトを含めません。
たとえば、obj という名前の ConstantLine オブジェクトを凡例から除外するには、IconDisplayStyle プロパティを "off" に設定します。
obj.Annotation.LegendInformation.IconDisplayStyle = "off";
あるいは、関数 legend を使用して、凡例内の項目を制御することもできます。最初の入力引数を、含めるグラフィックス オブジェクトのベクトルとして指定します。最初の入力引数に既存のグラフィックス オブジェクトを指定しない場合、それは凡例に表示されません。ただし、凡例が作成された後に座標軸に追加されたグラフィックス オブジェクトは凡例には表示されません。追加の項目を避けるには、すべてのプロットを作成した後に凡例を作成することを考慮してください。
対話機能
可視性の状態。"on" または "off"、もしくは数値または logical 1 (true) または 0 (false) として指定します。"on" の値は true と等価であり、"off" の値は false と等価です。したがって、このプロパティの値を logical 値として使用できます。値は matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として格納されます。
"on"— オブジェクトを表示します。"off"— オブジェクトを削除せずに非表示にします。非表示のオブジェクトのプロパティには引き続きアクセスできます。
コンテキスト メニュー。ContextMenu オブジェクトとして指定します。このプロパティは、オブジェクトを右クリックしたときにコンテキスト メニューを表示するために使用します。関数 uicontextmenu を使用して、コンテキスト メニューを作成します。
メモ
PickableParts プロパティが 'none' に設定されている場合または HitTest プロパティが 'off' に設定されている場合には、このコンテキスト メニューは表示されません。
選択状態。'on' または 'off'、もしくは数値または logical 1 (true) または 0 (false) として指定します。'on' の値は true と等価であり、'off' の値は false と等価です。したがって、このプロパティの値を logical 値として使用できます。値は matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として格納されます。
'on'— 選択されています。プロット編集モードでオブジェクトをクリックした場合、MATLAB はSelectedプロパティを'on'に設定します。SelectionHighlightプロパティも'on'に設定されている場合、MATLAB はオブジェクトの周囲に選択ハンドルを表示します。'off'— 選択されていません。
選択時の選択ハンドルの表示。'on' または 'off'、もしくは数値または logical 1 (true) または 0 (false) として指定します。'on' の値は true と等価であり、'off' の値は false と等価です。したがって、このプロパティの値を logical 値として使用できます。値は matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として格納されます。
'on'—Selectedプロパティが'on'に設定されているときに選択ハンドルを表示します。'off'—Selectedプロパティが'on'に設定されている場合でも選択ハンドルを表示しません。
コールバック
マウスクリック コールバック。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
関数ハンドル
関数ハンドルと追加の引数を含む cell 配列
ベース ワークスペース内で評価される有効な MATLAB コマンドまたは MATLAB 関数の文字ベクトル (非推奨)
このプロパティは、オブジェクトをクリックしたときにコードを実行するために使用します。関数ハンドルを使用してこのプロパティを指定した場合、MATLAB はコールバックを実行するときに次の 2 つの引数をコールバック関数に渡します。
クリックしたオブジェクト — コールバック関数内から、クリックしたオブジェクトのプロパティにアクセスします。
イベント データ — 空の引数です。この引数が使用されないことを示すために、関数定義の中でこの引数をチルダ文字 (
~) に置換します。
関数ハンドルを使用してコールバック関数を定義する方法についての詳細は、グラフィックス オブジェクトのコールバックの作成を参照してください。
メモ
PickableParts プロパティが 'none' に設定されている場合または HitTest プロパティが 'off' に設定されている場合には、このコールバックは実行されません。
オブジェクト作成関数。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
関数ハンドル。
最初の要素が関数ハンドルである cell 配列。cell 配列内のその後の要素はコールバック関数に渡される引数です。
有効な MATLAB 式を含む文字ベクトル (非推奨)。MATLAB は、この式をベース ワークスペースで評価します。
コールバックを関数ハンドル、cell 配列、または文字ベクトルとして指定する方法の詳細については、グラフィックス オブジェクトのコールバックの作成を参照してください。
このプロパティは、MATLAB がオブジェクトを作成するときに実行されるコールバック関数を指定します。MATLAB は CreateFcn コールバックを実行する前に、すべてのプロパティ値を初期化します。CreateFcn プロパティを指定しない場合、MATLAB は既定の作成関数を実行します。
既存のコンポーネントに CreateFcn プロパティを設定しても効果はありません。
このプロパティを関数ハンドルまたは cell 配列として指定した場合、コールバック関数の最初の引数を使用して、作成中のオブジェクトにアクセスできます。それ以外の場合は、関数 gcbo を使用してオブジェクトにアクセスします。
オブジェクト削除関数。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
関数ハンドル。
最初の要素が関数ハンドルである cell 配列。cell 配列内のその後の要素はコールバック関数に渡される引数です。
有効な MATLAB 式を含む文字ベクトル (非推奨)。MATLAB は、この式をベース ワークスペースで評価します。
コールバックを関数ハンドル、cell 配列、または文字ベクトルとして指定する方法の詳細については、グラフィックス オブジェクトのコールバックの作成を参照してください。
このプロパティは、MATLAB がオブジェクトを削除するときに実行されるコールバック関数を指定します。MATLAB は、オブジェクトのプロパティを破棄する前に DeleteFcn コールバックを実行します。DeleteFcn プロパティを指定しない場合、MATLAB は既定の削除関数を実行します。
このプロパティを関数ハンドルまたは cell 配列として指定した場合、コールバック関数の最初の引数を使用して、削除されるオブジェクトにアクセスできます。それ以外の場合は、関数 gcbo を使用してオブジェクトにアクセスします。
コールバック実行制御
コールバックの割り込み。'on' または 'off'、もしくは数値または logical 1 (true) または 0 (false) として指定します。'on' の値は true と等価であり、'off' の値は false と等価です。したがって、このプロパティの値を logical 値として使用できます。値は matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として格納されます。
このプロパティは実行中のコールバックが割り込み可能かどうかを決定します。次の 2 つのコールバックの状態について考慮する必要があります。
"実行中" コールバックは、現在実行しているコールバックです。
"割り込み" コールバックは、実行中のコールバックに割り込もうとするコールバックです。
MATLAB は、コールバック キューを処理するコマンドを実行するたびにコールバックの割り込み動作を判別します。これらのコマンドには、drawnow、figure、uifigure、getframe、waitfor、pause があります。
実行中コールバックにこれらのコマンドが含まれていない場合、割り込みは発生しません。MATLAB は、実行中コールバックの実行を先に終了させ、その後に割り込みコールバックを実行します。
実行中コールバックにこれらのいずれかのコマンドが含まれている場合、実行中コールバックを所有するオブジェクトの Interruptible プロパティに応じて割り込みが発生するかどうかが決まります。
Interruptibleの値が'off'の場合、割り込みは発生しません。代わりに、割り込みコールバックを所有するオブジェクトのBusyActionプロパティに応じて、割り込みコールバックが破棄されるかコールバック キューに追加されるかが決まります。Interruptibleの値が'on'の場合、割り込みが発生します。MATLAB は、コールバック キューの次回処理時に、実行中コールバックの実行を停止し、割り込みコールバックを実行します。割り込みコールバックが完了した後、MATLAB は実行中だったコールバックの実行を再開します。
メモ
コールバックの割り込みと実行は、以下の状況では動作が異なります。
割り込みコールバックが
DeleteFcn、CloseRequestFcnまたはSizeChangedFcnコールバックの場合、Interruptibleプロパティの値にかかわらず割り込みが発生します。実行中のコールバックが関数
waitforを現在実行している場合、Interruptibleプロパティの値にかかわらず割り込みが発生します。割り込みコールバックが
Timerオブジェクトで所有されている場合、Interruptibleプロパティの値にかかわらずスケジュールに従ってコールバックが実行されます。
コールバック キューイング。'queue' または 'cancel' として指定します。BusyAction プロパティは MATLAB による割り込みコールバックの実行の処理方法を決定します。次の 2 つのコールバックの状態について考慮する必要があります。
"実行中" コールバックは、現在実行しているコールバックです。
"割り込み" コールバックは、実行中のコールバックに割り込もうとするコールバックです。
BusyAction プロパティによってコールバック キューイングの動作が決まるのは、次の両方の条件を満たす場合のみです。
これらの条件に当てはまる場合、割り込みコールバックを所有するオブジェクトの BusyAction プロパティに応じて MATLAB による割り込みコールバックの処理方法が決まります。BusyAction プロパティは次の値を取ることができます。
'queue'— 割り込みコールバックをキューに入れ、実行中のコールバックが終了した後に処理されるようにします。'cancel'— 割り込みコールバックを実行しません。
マウス クリック キャプチャ機能。次の値の 1 つとして指定します。
'visible'— 表示されている場合にマウス クリックをキャプチャします。Visibleプロパティが'on'に設定されていなければならず、ConstantLineオブジェクトの色が定義されている部分をクリックしなければなりません。関連付けられている色のプロパティが'none'に設定されている部分をクリックすることはできません。ConstantLineオブジェクトがクリックに応答するか、先祖がクリックに応答するかは、HitTestプロパティが決定します。'all'— 表示状態に関係なくマウス クリックをキャプチャします。Visibleプロパティを'on'または'off'に設定でき、ConstantLineオブジェクトの色が設定されていない部分をクリックできます。ConstantLineオブジェクトがクリックに応答するか、先祖がクリックに応答するかは、HitTestプロパティが決定します。'none'— マウス クリックをキャプチャしません。ConstantLineオブジェクトをクリックすると、Figure ウィンドウの現在のビュー内でその下にあるオブジェクトまでクリックが渡されます。HitTestプロパティは無効になります。
キャプチャしたマウス クリックへの応答。'on' または 'off'、もしくは数値または logical 1 (true) または 0 (false) として指定します。'on' の値は true と等価であり、'off' の値は false と等価です。したがって、このプロパティの値を logical 値として使用できます。値は matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として格納されます。
'on'—ConstantLineオブジェクトのButtonDownFcnコールバックをトリガーします。ContextMenuプロパティが定義されている場合は、コンテキスト メニューを呼び出します。'off'—ConstantLineオブジェクトの先祖のうち、次のいずれかの条件を満たす最も近い先祖のコールバックをトリガーします。HitTestプロパティが、'on'に設定されている。PickablePartsプロパティが、先祖によるマウス クリックのキャプチャを有効にする値に設定されている。
メモ
PickableParts プロパティは、ConstantLine オブジェクトがマウス クリックをキャプチャできるかどうかを決定します。キャプチャできない場合、HitTest プロパティは無効です。
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
削除状態。matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState 型の on/off logical 値として返されます。
MATLAB は、DeleteFcn コールバックが実行を開始すると、BeingDeleted プロパティを 'on' に設定します。コンポーネント オブジェクトが存在しなくなるまで BeingDeleted プロパティは 'on' に設定されたままです。
クエリや変更の前にオブジェクトが削除されようとしていないか確認するために BeingDeleted プロパティの値をチェックします。
親/子
親。Axes オブジェクトとして指定します。
このオブジェクトには子がありません。このプロパティは設定できません。
親の Children プロパティ内でのオブジェクト ハンドルの可視性。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
"on"— オブジェクト ハンドルは常に表示されます。"off"— オブジェクト ハンドルは常に非表示です。このオプションは、他の関数による意図しない変更を防止するために役立ちます。HandleVisibilityを"off"に設定すると、その関数の実行中にハンドルが一時的に非表示になります。"callback"— オブジェクト ハンドルはコールバック内から、あるいはコールバックにより呼び出される関数から参照できます。しかし、コマンド ラインから呼び出される関数からは参照できません。このオプションを使用すると、コマンド ラインからのオブジェクトへのアクセスがブロックされますが、コールバック関数からのアクセスは許可されます。
オブジェクトが親の Children プロパティ内にリストされない場合、オブジェクト階層の検索またはハンドル プロパティのクエリによってオブジェクト ハンドルを取得する関数は、そのオブジェクト ハンドルを返しません。こうした関数の例としては、関数 get、findobj、gca、gcf、gco、newplot、cla、clf、および close などが挙げられます。
非表示のオブジェクト ハンドルは有効なままです。ルートの ShowHiddenHandles プロパティを "on" に設定すると、HandleVisibility プロパティの設定にかかわらず、すべてのオブジェクト ハンドルがリストされます。
識別子
このプロパティは読み取り専用です。
グラフィックス オブジェクトのタイプ。'constantline' として返されます。プロット階層内にある特定のタイプのすべてのオブジェクトを検出するためにこのプロパティを使用できます。たとえば findobj を使用してタイプを検索します。
オブジェクト識別子。文字ベクトルまたは string スカラーとして指定します。オブジェクトの識別子として機能する一意の Tag 値を指定できます。コードの他の部分からオブジェクトにアクセスする必要がある場合、関数 findobj を使用して Tag 値に基づいてオブジェクトを検索できます。
ユーザー データ。任意の MATLAB 配列として指定します。たとえば、スカラー、ベクトル、行列、cell 配列、文字配列、table、または構造体を指定できます。このプロパティを使用して、任意のデータをオブジェクトに保存します。
App Designer を使用している場合は、UserData プロパティを使用する代わりに、アプリでパブリック プロパティまたはプライベート プロパティを作成してデータを共有します。詳細については、App Designer アプリ内でのデータの共有を参照してください。
バージョン履歴
R2018b で導入LabelColor プロパティを設定して、ラインのテキスト ラベルの色を制御します。
ConstantLine オブジェクトをプロットの他の要素の上または下に移動するには、Layer プロパティを "top" または "bottom" に設定します。
ConstantLine オブジェクトの SeriesIndex プロパティを設定し、オブジェクトの色やライン スタイルがどのように変化するかを制御します。このプロパティの値を変更することは、座標軸内の異なるオブジェクトの色やライン スタイルを一致させる場合に便利です。
UIContextMenu プロパティの設定や取得は推奨されていません。代わりに、ContextMenu プロパティを使用してください。これは、UIContextMenu プロパティと同じタイプの入力を受け入れ、同じように動作します。
UIContextMenu プロパティを削除する予定はありませんが、関数 set、get、または properties を ConstantLine オブジェクトで呼び出す際にリストされなくなりました。
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)