drivingScenario
ドライビング シナリオの作成
説明
drivingScenario オブジェクトは、ドライビング シナリオの道路、駐車場、車両、歩行者、障壁、その他の要素が含まれた 3-D アリーナを表します。このオブジェクトを使用して、現実的な交通シナリオをモデル化し、コントローラーまたはセンサー フュージョン アルゴリズムをテストするための合成検出を生成します。
道路を追加するには、関数
roadを使用します。道路に車線を指定するには、lanespecオブジェクトを作成します。関数roadNetworkを使用して、サードパーティの道路ネットワークから道路をインポートすることもできます。駐車場を追加するには、関数
parkingLotを使用します。アクター (車、歩行者、自転車など) を追加するには、関数
actorを使用します。車両専用に設計されたプロパティを備えたアクターを追加するには、関数vehicleを使用します。障壁を追加するには、関数barrierを使用します。車両および障壁を含む、すべてのアクターは一意のアクター ID をもつ直方体 (箱の形状) でモデル化されます。シナリオをシミュレートするために、ループ内で関数
advanceを呼び出します。これにより、一度に 1 つのタイム ステップずつシミュレーションを進めます。
ドライビング シナリオ デザイナー アプリを使用してドライビング シナリオを対話的に作成することもできます。また、アプリから drivingScenario オブジェクトをエクスポートして、アプリまたは Simulink® で使用するための複数のシナリオ バリエーションを生成できます。詳細については、プログラムでのドライビング シナリオのバリエーションの作成を参照してください。
作成
説明
scenario = drivingScenario
scenario = drivingScenario(Name,Value)SampleTime、StopTime、および GeoReference の各プロパティを設定します。たとえば、drivingScenario('GeoReference',[42.3 -71.0 0]) は、シーンの地理的原点を緯度と経度の座標 (42.3, –71.0)、および高度 0 に設定します。
プロパティ
シナリオ シミュレーション ステップ間の時間間隔。正の実数スカラーとして指定します。単位は秒です。
例: 1.5
シミュレーションの終了時間。正の実数スカラーとして指定します。単位は秒です。既定の StopTime である Inf では、最初のアクターが軌跡の最後に到達すると、シミュレーションは終了します。
例: 60.0
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
シミュレーションの現在時間。非負の実数スカラーとして指定します。時間をゼロにリセットするには、関数 restart を呼び出します。単位は秒です。
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
シミュレーション状態。true または false として指定します。シミュレーションが実行中の場合、IsRunning は true です。
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
シナリオに含まれている障壁。Barrier オブジェクトの異種混合配列として指定します。障壁をドライビング シナリオに追加するには、関数 barrier を使用します。
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
シナリオに含まれている駐車場。ParkingLot オブジェクトの異種混合配列として指定します。駐車場をドライビング シナリオに追加するには、関数 parkingLot を使用します。
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
道路ネットワーク原点の地理座標。[lat, lon, alt] という形式の 3 要素数値行ベクトルとして指定します。ここで、
latは座標の緯度 (単位は度) です。lonは座標の経度 (単位は度) です。altは座標の高度 (単位はメートル) です。
これらは、GPS データで使用される標準楕円体である WGS84 準拠楕円体を基準とした値です。
ドライビング シナリオの作成時に GeoReference を設定できます。関数 roadNetwork も、道路を空のドライビング シナリオにインポートした場合にこのプロパティを設定します。
座標を指定して道路をインポートした場合、関数
roadNetworkはGeoReferenceを最初の (または唯一の) 指定された座標に設定します。領域またはマップ ファイルを指定して道路をインポートした場合、
roadNetworkはGeoReferenceをその領域またはマップの中心点に設定します。
関数 roadNetwork は、以前に設定された GeoReference の値をオーバーライドします。
ドライビング シナリオ デザイナー アプリで、マップ データをインポートし、drivingScenario オブジェクトをエクスポートすると、そのオブジェクトの GeoReference プロパティがアプリ シナリオの地理参照に設定されます。
関数 latlon2local でこれらの座標を原点として指定することで、運転ルートの地理座標をドライビング シナリオのローカル座標に変換できます。その後、シナリオの車両軌跡としてこの変換されたルートを指定できます。
ドライビング シナリオで地理座標を使用していない場合は、GeoReference は空の配列 [] になります。
オブジェクト関数
advance | ドライビング シナリオ シミュレーションを 1 タイム ステップずつ進める |
plot | ドライビング シナリオをプロット |
plotSim3d | Plot driving scenario in Unreal Engine viewer |
record | ドライビング シナリオを実行してアクターの状態を記録 |
restart | 最初からドライビング シナリオ シミュレーションを再実行 |
updatePlots | ドライビング シナリオのプロットの更新 |
export | Export driving scenario to ASAM OpenDRIVE, ASAM OpenSCENARIO XML or RoadRunner HD Map file |
actor | Add actor to driving scenario |
actorPoses | ドライビング シナリオにおけるアクターの位置、速度、および向き |
actorProfiles | Physical and radar characteristics of actors in driving scenario |
vehicle | Add vehicle to driving scenario |
barrier | Add a barrier to a driving scenario |
chasePlot | 自己を中心とした射影パースペクティブのプロット |
trajectory | ドライビング シナリオでアクターまたは車両の軌跡を作成 |
smoothTrajectory | Create smooth, jerk-limited actor trajectory in driving scenario |
targetPoses | Target positions and orientations relative to host vehicle |
targetOutlines | Outlines of targets viewed by actor |
driving.scenario.targetsToEgo | Convert target poses from scenario to ego coordinates |
driving.scenario.targetsToScenario | Convert target poses from ego to scenario coordinates |
road | Add road to driving scenario or road group |
roadNetwork | Add road network to driving scenario |
roadBoundaries | 道路の境界を取得 |
driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo | Convert road boundaries to ego vehicle coordinates |
lanespec | Create road lane specifications |
laneMarking | Create road lane marking object |
laneMarkingVertices | Lane marking vertices and faces in driving scenario |
currentLane | Get current lane of actor |
laneBoundaries | Get lane boundaries of actor lane |
clothoidLaneBoundary | クロソイド形状の車線境界線モデル |
computeBoundaryModel | クロソイド車線境界線モデルから車線境界線の点を計算 |
laneType | Create road lane type object |
parkingLot | Add parking lot to driving scenario |
parkingSpace | Define parking space for parking lot |
insertParkingSpaces | Insert parking spaces into parking lot |
parkingLaneMarkingVertices | Parking lane marking vertices and faces in driving scenario |
addSensors | Add sensors to specific host vehicle |
例
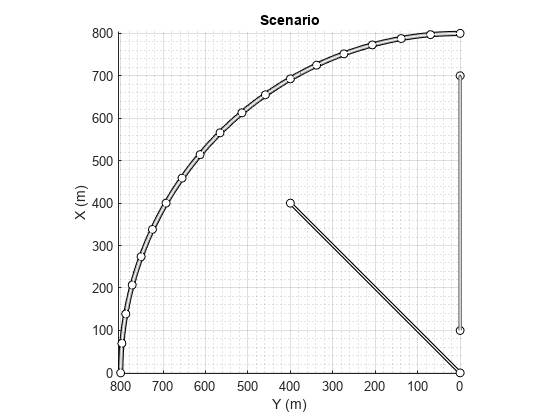
1 つの曲線道路、2 つの直線道路、2 つのアクター (車と自転車) が含まれたドライビング シナリオを作成します。どちらのアクターも 60 秒間道路に沿って移動します。
ドライビング シナリオ オブジェクトを作成します。
scenario = drivingScenario('SampleTime',0.1','StopTime',60);
半径 800 メートルの円弧に従う道路中心点を使用して、曲線道路を作成します。円弧は 0 度から開始して 90 度で終了し、5 度のインクリメントでサンプリングされます。
angs = [0:5:90]'; R = 800; roadcenters = R*[cosd(angs) sind(angs) zeros(size(angs))]; roadwidth = 10; cr = road(scenario,roadcenters,roadwidth);
両端の道路中央点を使用して、既定の幅をもつ 2 本の直線道路を追加します。最初の直線道路の両エッジに障壁を追加します。
roadcenters = [700 0 0; 100 0 0]; sr1 = road(scenario,roadcenters); barrier(scenario,sr1) barrier(scenario,sr1,'RoadEdge','left') roadcenters = [400 400 0; 0 0 0]; road(scenario,roadcenters);
道路の境界を取得します。
rbdry = roadBoundaries(scenario);
車と自転車をシナリオに追加します。1 つ目の直線道路の最初の位置に車を配置します。
car = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1,'Position',[700 0 0], ... 'Length',3,'Width',2,'Height',1.6);
道路を進んだ先に自転車を配置します。
bicycle = actor(scenario,'ClassID',3,'Position',[706 376 0]', ... 'Length',2,'Width',0.45,'Height',1.5);
シナリオをプロットします。
plot(scenario,'Centerline','on','RoadCenters','on'); title('Scenario');
アクターの姿勢とプロファイルを表示します。
allActorPoses = actorPoses(scenario)
allActorPoses=242×1 struct array with fields:
ActorID
Position
Velocity
Roll
Pitch
Yaw
AngularVelocity
allActorProfiles = actorProfiles(scenario)
allActorProfiles=242×1 struct array with fields:
ActorID
ClassID
Length
Width
Height
OriginOffset
MeshVertices
MeshFaces
RCSPattern
RCSAzimuthAngles
RCSElevationAngles
このシナリオには障壁があり、各障壁セグメントがアクターと見なされているため、関数 actorPoses および関数 actorProfiles は、すべての静止アクターと非静止アクターの姿勢を返します。車両や二輪車など非静止アクターの姿勢とプロファイルのみを取得するには、まず scenario.Actors.ActorID プロパティを使用して、それらの対応するアクター ID を取得します。
movableActorIDs = [scenario.Actors.ActorID];
次に、それらの ID を使用して、非静止アクターの姿勢とプロファイルのみをフィルター処理します。
movableActorPoseIndices = ismember([allActorPoses.ActorID],movableActorIDs); movableActorPoses = allActorPoses(movableActorPoseIndices)
movableActorPoses=2×1 struct array with fields:
ActorID
Position
Velocity
Roll
Pitch
Yaw
AngularVelocity
movableActorProfiles = allActorProfiles(movableActorPoseIndices)
movableActorProfiles=2×1 struct array with fields:
ActorID
ClassID
Length
Width
Height
OriginOffset
MeshVertices
MeshFaces
RCSPattern
RCSAzimuthAngles
RCSElevationAngles
ドライビング シナリオを作成し、シミュレーションの進行に伴うターゲット アウトラインの変化を示します。
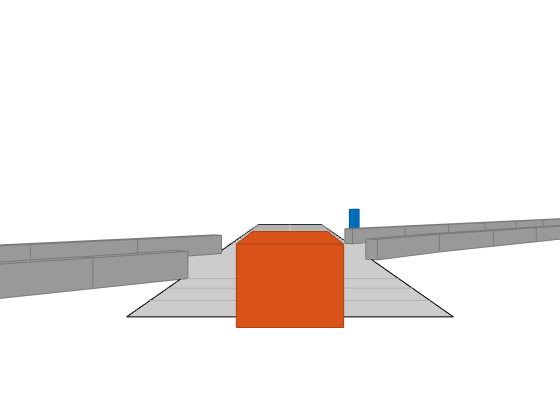
2 つの交差する直線道路で構成されたドライビング シナリオを作成します。1 つ目の道路セグメントの長さは 45 メートルです。2 つ目の直線道路は、長さが 32 メートルで、両端にジャージ障壁があり、1 つ目の道路と交差します。1 つ目の道路に沿って秒速 12.0 メートルで移動している車が、秒速 2.0 メートルで交差点を現在渡っている歩行者に近づいていきます。
scenario = drivingScenario('SampleTime',0.1,'StopTime',1); road1 = road(scenario,[-10 0 0; 45 -20 0]); road2 = road(scenario,[-10 -10 0; 35 10 0]); barrier(scenario,road1) barrier(scenario,road1,'RoadEdge','left') ped = actor(scenario,'ClassID',4,'Length',0.4,'Width',0.6,'Height',1.7); car = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1); pedspeed = 2.0; carspeed = 12.0; smoothTrajectory(ped,[15 -3 0; 15 3 0],pedspeed); smoothTrajectory(car,[-10 -10 0; 35 10 0],carspeed);
車両の自己を中心とした追跡プロットを作成します。
chasePlot(car,'Centerline','on')
空の鳥瞰図プロットを作成し、アウトライン プロッターおよび車線境界線プロッターを追加します。次に、シミュレーションを実行します。各シミュレーション ステップは以下のとおりです。
追跡プロットを更新して、道路の境界およびターゲット アウトラインを表示する。
鳥瞰図プロットを更新して、更新した道路の境界およびターゲット アウトラインを表示する。プロットのパースペクティブは常に、自車が基準となっています。
bepPlot = birdsEyePlot('XLim',[-50 50],'YLim',[-40 40]); outlineplotter = outlinePlotter(bepPlot); laneplotter = laneBoundaryPlotter(bepPlot); legend('off') while advance(scenario) rb = roadBoundaries(car); [position,yaw,length,width,originOffset,color] = targetOutlines(car); [bposition,byaw,blength,bwidth,boriginOffset,bcolor,barrierSegments] = targetOutlines(car,'Barriers'); plotLaneBoundary(laneplotter,rb) plotOutline(outlineplotter,position,yaw,length,width, ... 'OriginOffset',originOffset,'Color',color) plotBarrierOutline(outlineplotter,barrierSegments,bposition,byaw,blength,bwidth, ... 'OriginOffset',boriginOffset,'Color',bcolor) pause(0.01) end


3 車線の道路に沿って走行している自車とターゲット車両が含まれたドライビング シナリオを作成します。Vision Detection Generator を使用して車線境界線を検出します。
scenario = drivingScenario;
車線指定を使用して 3 車線の道路を作成します。
roadCenters = [0 0 0; 60 0 0; 120 30 0];
lspc = lanespec(3);
road(scenario,roadCenters,'Lanes',lspc);
自車が 30 m/s で中央車線を追従するように指定します。
egovehicle = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1);
egopath = [1.5 0 0; 60 0 0; 111 25 0];
egospeed = 30;
smoothTrajectory(egovehicle,egopath,egospeed);
ターゲット車両が 40 m/s で自車の前を走行し、自車の近くで車線を変更するように指定します。
targetcar = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1);
targetpath = [8 2; 60 -3.2; 120 33];
targetspeed = 40;
smoothTrajectory(targetcar,targetpath,targetspeed);
自車の後ろからのシナリオの 3-D ビューの追跡プロットを表示します。
chasePlot(egovehicle)

車線とオブジェクトを検出する Vision Detection Generator を作成します。センサーのピッチは 1 度下を指します。
visionSensor = visionDetectionGenerator('Pitch',1.0); visionSensor.DetectorOutput = 'Lanes and objects'; visionSensor.ActorProfiles = actorProfiles(scenario);
シミュレーションを実行します。
鳥瞰図プロットおよび関連プロッターを作成します。
センサー カバレッジ領域を表示します。
車線区分線を表示します。
道路上のターゲットのグラウンド トゥルース姿勢を取得します。
60 m 前までの最適な車線境界線の点を取得します。
最適なターゲット姿勢および車線境界線から検出を生成します。
ターゲットのアウトラインを表示します。
オブジェクト検出が有効な場合はオブジェクト検出を表示します。
車線検出が有効な場合は車線境界線を表示します。
bep = birdsEyePlot('XLim',[0 60],'YLim',[-35 35]); caPlotter = coverageAreaPlotter(bep,'DisplayName','Coverage area', ... 'FaceColor','blue'); detPlotter = detectionPlotter(bep,'DisplayName','Object detections'); lmPlotter = laneMarkingPlotter(bep,'DisplayName','Lane markings'); lbPlotter = laneBoundaryPlotter(bep,'DisplayName', ... 'Lane boundary detections','Color','red'); olPlotter = outlinePlotter(bep); plotCoverageArea(caPlotter,visionSensor.SensorLocation,... visionSensor.MaxRange,visionSensor.Yaw, ... visionSensor.FieldOfView(1)); while advance(scenario) [lmv,lmf] = laneMarkingVertices(egovehicle); plotLaneMarking(lmPlotter,lmv,lmf) tgtpose = targetPoses(egovehicle); lookaheadDistance = 0:0.5:60; lb = laneBoundaries(egovehicle,'XDistance',lookaheadDistance,'LocationType','inner'); [obdets,nobdets,obValid,lb_dets,nlb_dets,lbValid] = ... visionSensor(tgtpose,lb,scenario.SimulationTime); [objposition,objyaw,objlength,objwidth,objoriginOffset,color] = targetOutlines(egovehicle); plotOutline(olPlotter,objposition,objyaw,objlength,objwidth, ... 'OriginOffset',objoriginOffset,'Color',color) if obValid detPos = cellfun(@(d)d.Measurement(1:2),obdets,'UniformOutput',false); detPos = vertcat(zeros(0,2),cell2mat(detPos')'); plotDetection(detPlotter,detPos) end if lbValid plotLaneBoundary(lbPlotter,vertcat(lb_dets.LaneBoundaries)) end end


この例では、関数 addSensors を使用してドライビング シナリオにセンサーを追加し、個々のセンサー入力に基づいてグラウンド トゥルース ターゲット姿勢を取得します。次に、グラウンド トゥルース ターゲット姿勢を処理して検出にし、それらを可視化します。
ドライビング シナリオおよび鳥瞰図プロットの設定
自車および 2 台のターゲット車両が含まれるドライビング シナリオを作成します。一方のターゲット車両は自車の前方にあり、もう一方は自車の左側にあります。
[scenario, egovehicle] = helperCreateDrivingScenario;
自車の前方に取り付けるビジョン センサーを構成します。
visionSensor = visionDetectionGenerator(SensorIndex=1,SensorLocation=[4.0 0],Height=1.1,Pitch=1.0,DetectorOutput="Objects only");自車の左側に取り付ける超音波センサーを構成します。
leftUltrasonic = ultrasonicDetectionGenerator(SensorIndex=2,MountingLocation=[0.5 1 0.2],MountingAngles=[90 0 0],FieldOfView=[70 35],UpdateRate=100);
ドライビング シナリオを可視化する鳥瞰図プロットを作成します。
[detPlotter,lmPlotter,olPlotter,lulrdPlotter,luldetPlotter,bepAxes] = helperCreateBEP(visionSensor,leftUltrasonic);

センサーの追加とドライビング シナリオのシミュレート
関数 addSensors を使用して、ビジョン センサーと超音波センサーの両方をドライビング シナリオに追加します。目的の車両のアクター ID を指定することにより、関数 addSensors を使用してドライビング シナリオ内の任意の車両にセンサーを追加できます。この例では、自車のアクター ID を指定します。
addSensors(scenario,{visionSensor,leftUltrasonic},egovehicle.ActorID);ドライビング シナリオをシミュレートします。それぞれのセンサー ID を関数 targetPoses への入力として指定することにより、個々のセンサーに基づいて別々のターゲット姿勢が取得されることに注意してください。この構文では、指定したセンサーの範囲のみでターゲットのグラウンド トゥルース姿勢が返されます。その後、グラウンド トゥルース姿勢をそれぞれのセンサー モデルに渡して検出を生成し、それらを可視化します。
legend(bepAxes,'show') lookaheadDistance = 0:0.5:60; while advance(scenario) lb = laneBoundaries(egovehicle,'XDistance',lookaheadDistance,'LocationType','inner'); [lmv,lmf] = laneMarkingVertices(egovehicle); % Get ground-truth poses of targets in the range of vision and ultrasonic sensors separately tgtposeVision = targetPoses(scenario,visionSensor.SensorIndex); tgtposeUltrasonic = targetPoses(scenario,leftUltrasonic.SensorIndex); % Obtain detections based on targets only in range [obdets,obValid] = visionSensor(tgtposeVision,scenario.SimulationTime); [lobdets,lobValid] = leftUltrasonic(tgtposeUltrasonic,scenario.SimulationTime); helperPlotBEPVision(egovehicle,lmv,lmf,obdets,obValid,detPlotter,lmPlotter,olPlotter) helperPlotBEPUltrasonic(lobdets,lobValid,leftUltrasonic,lulrdPlotter,luldetPlotter) end

補助関数
helperCreateDrivingScenario は、道路および車両のプロパティを指定することにより、ドライビング シナリオを作成します。
function [scenario, egovehicle] = helperCreateDrivingScenario scenario = drivingScenario; roadCenters = [-120 30 0;-60 0 0;0 0 0; 60 0 0; 120 30 0; 180 60 0]; lspc = lanespec(3); road(scenario,roadCenters,Lanes=lspc); % Create an ego vehicle that travels in the center lane at a velocity of 30 m/s. egovehicle = vehicle(scenario,ClassID=1); egopath = [1.5 0 0; 60 0 0; 111 25 0]; egospeed = 30; smoothTrajectory(egovehicle,egopath,egospeed); % Add a target vehicle that travels ahead of the ego vehicle at 30.5 m/s in the right lane, and changes lanes close to the ego vehicle. ftargetcar = vehicle(scenario,ClassID=1); ftargetpath = [8 2; 60 -3.2; 120 33]; ftargetspeed = 40; smoothTrajectory(ftargetcar,ftargetpath,ftargetspeed); % Add a second target vehicle that travels in the left lane at 32m/s. ltargetcar = vehicle(scenario,ClassID=1); ltargetpath = [-5.0 3.5 0; 60 3.5 0; 111 28.5 0]; ltargetspeed = 30; smoothTrajectory(ltargetcar,ltargetpath,ltargetspeed); end
helperCreateBEP は、ドライビング シナリオ シミュレーションを可視化するための鳥瞰図プロットを作成します。
function [detPlotter, lmPlotter, olPlotter, lulrdPlotter,luldetPlotter,bepAxes] = helperCreateBEP(visionSensor,leftUltrasonic) figureName = "BEP"; Figure = findobj('Type','Figure',Name=figureName); if isempty(Figure) screenSize = double(get(groot,'ScreenSize')); Figure = figure(Name=figureName); Figure.Position = [screenSize(3)*0.17 screenSize(4)*0.15 screenSize(3)*0.4 screenSize(4)*0.6]; Figure.NumberTitle = 'off'; Figure.MenuBar = 'none'; Figure.ToolBar = 'none'; end clf(Figure); bepAxes = axes(Figure); grid(bepAxes,'on'); legend(bepAxes,'hide'); bep = birdsEyePlot(Parent=bepAxes,XLim=[-20 60],YLim=[-35 35]); caPlotterV = coverageAreaPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Vision Coverage area",FaceColor="b"); caPlotterU = coverageAreaPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Ultrasonic Coverage area",FaceColor="m"); detPlotter = detectionPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Object detections"); lmPlotter = laneMarkingPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Lane markings"); olPlotter = outlinePlotter(bep); plotCoverageArea(caPlotterV,visionSensor.SensorLocation,... visionSensor.MaxRange,visionSensor.Yaw, ... visionSensor.FieldOfView(1)); plotCoverageArea(caPlotterU,leftUltrasonic.MountingLocation(1:2),... leftUltrasonic.DetectionRange(3),leftUltrasonic.MountingAngles(1), ... leftUltrasonic.FieldOfView(1)); lulrdPlotter = rangeDetectionPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Left Ultrasonic Ranges",LineStyle="-"); luldetPlotter = detectionPlotter(bep,DisplayName="Point-On-Target (Left Ultrasonic)",MarkerFaceColor="k"); end
helperPlotBEPVision は、自車のアウトライン、車線およびビジョン検出を鳥瞰図プロット上にプロットします。
function helperPlotBEPVision(egovehicle,lmv,lmf,obdets,obValid,detPlotter, lmPlotter, olPlotter) plotLaneMarking(lmPlotter,lmv,lmf) [objposition,objyaw,objlength,objwidth,objoriginOffset,color] = targetOutlines(egovehicle); plotOutline(olPlotter,objposition,objyaw,objlength,objwidth, ... OriginOffset=objoriginOffset,Color=color) if obValid detPos = cellfun(@(d)d.Measurement(1:2),obdets,UniformOutput=false); detPos = vertcat(zeros(0,2),cell2mat(detPos')'); plotDetection(detPlotter,detPos) end end
helperPlotBEPUltrasonic は、超音波領域の測定値と点をターゲット上にプロットします。
function helperPlotBEPUltrasonic(lobdets,lobValid,leftUltrasonic,lulrdPlotter,luldetPlotter) if ~isempty(lobdets) && lobValid lranges = lobdets{1}.Measurement; plotRangeDetection(lulrdPlotter,lranges,leftUltrasonic.FieldOfView(1),leftUltrasonic.MountingLocation,leftUltrasonic.MountingAngles) plotDetection(luldetPlotter,lobdets{1}.ObjectAttributes{1}.PointOnTarget(1:2)') end end
アルゴリズム
ドライビング シナリオでアクターの運動を指定するには、アクターの軌跡を定義するか、運動を手動で指定できます。
関数 trajectory および smoothTrajectory により、一連のウェイポイント、およびアクターがウェイポイント間を移動する速さ (speed) に基づいて、アクターの姿勢プロパティが決定されます。アクターの姿勢プロパティは位置、速度 (velocity)、ロール、ピッチ、ヨー、および角速度です。このアプローチでは、運動は速さ (speed) ではなく速度 (velocity) で定義されます。これは、軌跡によって運動の方向が定義されるからです。
関数 smoothTrajectory によってさらに、ウェイポイント、速さ (speed)、縦方向の最大加加速度に基づいて、ウェイポイント間におけるアクターの加速度が決定されます。
アクターは、関数 advance が呼び出されるたびに軌跡に沿って移動します。シミュレーション中はいつでも、アクターの姿勢プロパティを手動で更新できます。ただし、これらのプロパティは、次に advance が呼び出されたときに更新された値で上書きされます。
アクターの運動を手動で指定した場合、速度 (velocity) または角速度プロパティを設定しても、関数 advance の連続呼び出しでアクターは自動的に移動しません。そのため、シミュレーションのタイム ステップごとに、独自の運動モデルを使用して位置、速度 (velocity)、その他の姿勢パラメーターを更新する必要があります。
バージョン履歴
R2017a で導入
参考
アプリ
オブジェクト
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)