LinearGauge
Linear gauge UI component
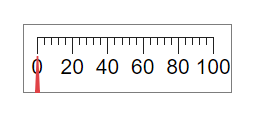
Description
A linear gauge UI component represents a measurement instrument that displays a
measurement in an app. Use the LinearGauge object to modify the appearance
and behavior of a linear gauge after you create it.
Creation
Create a linear gauge in an app using the uigauge function, specifying the gauge style as
"linear".
Properties
Gauge
Location of the gauge needle, specified as any numeric value.
If the value is less than the minimum
Limitsproperty value, then the needle points to a location immediately before the beginning of the scale.If the value is more than the maximum
Limitsproperty value, then the needle points to a location immediately after the end of the scale.
Changing the Limits property value has
no effect on the Value property setting.
Example: 60
Minimum and maximum gauge scale values, specified as a two-element numeric array. The first value in the array must be less than the second value.
If you change Limits such that the Value property
is less than the new lower limit, or more than the new upper limit,
then the gauge needle points to a location off the scale.
For example, suppose Limits is [0
100] and the Value property is 20.
If the Limits changes to [50 100],
then the needle points to a location off the scale, slightly less
than 50.
Data Types: double
Orientation of the gauge, specified as 'horizontal' or
'vertical'.
Scale colors, specified as one of the following arrays:
A 1-by-
nstring array of color options, such as["blue" "green" "red"].An
n-by-3 array of RGB triplets, such as[0 0 1;1 1 0].A 1-by-
ncell array containing RGB triplets, hexadecimal color codes, or named color options. For example,{'#EDB120','#7E2F8E','#77AC30'}.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Each color of the ScaleColors array corresponds to a colored
section of the gauge. Set the ScaleColorLimits property to map the
colors to specific sections of the gauge.
If you do not set the ScaleColorLimits property, MATLAB® distributes the colors equally over the range of the gauge.
Scale color limits, specified as a n-by-2 array of numeric values. For every row in the array, the first element must be less than the second element.
When applying colors to the gauge, MATLAB applies the colors starting with the first color in the
ScaleColors array. Therefore, if two rows in
ScaleColorLimits array overlap, then the color applied later
takes precedence.
The gauge does not display any portion of the ScaleColorLimits
that fall outside of the Limits property.
If the ScaleColors and ScaleColorLimits
property values are different sizes, then the gauge shows only the colors that have
matching limits. For example, if the ScaleColors array has three
colors, but the ScaleColorLimits has only two rows, then the gauge
displays the first two color/limit pairs only.
Ticks
Major tick mark locations, specified as a vector of numeric values or an empty vector. If you do not want to show major tick marks, specify this property as an empty vector.
Tick locations that are outside the range of the Limits property
do not display.
MATLAB removes duplicate tick values. However, if a major tick falls on the same value as a minor tick, only the major tick displays.
Setting the MajorTicks property sets the
MajorTicksMode property to 'manual'.
Major tick creation mode, specified as one of the following:
'auto'— MATLAB determines the placement of major ticks.'manual'— You specify theMajorTicksvalue array.
Major tick labels, specified as a cell array of character vectors, string array, or
1-D categorical array. If you do not want to show tick labels, specify this property as
an empty cell array. If you want to remove a label from a specific tick mark, specify an
empty character vector or empty string scalar for the corresponding element in the
MajorTickLabels array. If you specify this property as a
categorical array, MATLAB uses the values in the array, not the full set of categories.
If the length of the MajorTickLabels array is different from the
length of the MajorTicks vector, MATLAB ignores the extra entries of the longer array. If there are extra labels,
they are ignored. If there are extra tick marks, they display without labels.
Setting MajorTickLabels changes the
MajorTickLabelsMode value to 'manual'.
Note
Setting MajorTickLabels when
MajorTicksMode is 'auto' might lead to
unexpected results. To avoid this behavior, set MajorTicksMode
to 'manual' and manually specify the value of
MajorTicks before setting
MajorTickLabels.
Major tick labels mode, specified as one of the following:
'auto'— MATLAB specifies the major tick labels.'manual'— You specify the major tick labels using theMajorTickLabelsproperty.
Minor tick mark locations, specified as a vector of numeric values or an empty vector. If you do not want to show minor tick marks, specify this property as an empty vector.
Tick locations that are outside the range of the Limits property
do not display.
MATLAB removes duplicate tick values. However, if a minor tick falls on the same value as a major tick, only the major tick displays.
Setting the MinorTicks property value sets the
MinorTicksMode property value to 'manual'.
Minor tick creation mode, specified as one of the following:
'auto'— MATLAB determines the placement of minor ticks. MATLAB does not generate minor ticks for major ticks that are beyond scale limits. If theLimitsproperty value changes, then MATLAB updates minor ticks to populate the full scale range (theMinorTicksproperty is updated accordingly).'manual'— You specify theMinorTicksproperty numeric array. TheMinorTicksproperty value does not change size or content on its own.
Font and Color
Font name, specified as a system supported font name. The default font depends on the specific operating system and locale.
If the specified font is not available, then MATLAB uses the best match among the fonts available on the system where the app is running.
Example: 'Arial'
Font size, specified as a positive number. The units of measurement are pixels. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale.
Example: 14
Font weight, specified as one of these values:
'normal'— Default weight as defined by the particular font'bold'— Thicker character outlines than'normal'
Not all fonts have a bold font weight. For fonts that do not, specifying
'bold' results in the normal font weight.
Font angle, specified as 'normal' or 'italic'.
Not all fonts have an italic font angle. For fonts that do not, specifying
'italic' results in the normal font angle.
Font color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, or one of the options listed in the table.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Background color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, or one of the color options listed in the table.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Interactivity
State of visibility, specified as 'on' or 'off',
or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Display the object.'off'— Hide the object without deleting it. You still can access the properties of an invisible UI component.
To make your app start faster, set the Visible property to
'off' for all UI components that do not need to appear at
startup.
Operational state of gauge, specified as 'on' or 'off',
or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
If you set this property to
'on', then the appearance of the gauge indicates that the gauge is operational.If you set this property to
'off', then the appearance of the gauge appears dimmed, indicating that the gauge is not operational.
Tooltip, specified as a character vector, cell array of character vectors, string array, or 1-D categorical array. Use this property to display a message when the user hovers the pointer over the component at run time. The tooltip displays even when the component is disabled. To display multiple lines of text, specify a cell array of character vectors or a string array. Each element in the array becomes a separate line of text. If you specify this property as a categorical array, MATLAB uses the values in the array, not the full set of categories.
Context menu, specified as a ContextMenu object created using the uicontextmenu function. Use this property to display a context menu when
you right-click on a component.
Position
Gauge location and size, specified as the vector, [left bottom width
height]. This table describes each element in the vector.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
left | Distance from the inner left edge of the parent container to the outer left edge of the gauge |
bottom | Distance from the inner bottom edge of the parent container to the outer bottom edge of the gauge |
width | Distance between the right and left outer edges of the gauge |
height | Distance between the top and bottom outer edges of the gauge |
All measurements are in pixel units.
The Position values are relative to the
drawable area of the parent container. The drawable area is the area
inside the borders of the container and does not include the area occupied by decorations such
as a menu bar or title.
Example: [100 100 100 20]
Inner location and size of the gauge, specified as [left bottom width
height]. Position values are relative to the parent container. All
measurements are in pixel units. This property value is identical to the
Position property.
This property is read-only.
Outer location and size of the gauge, returned as [left bottom width
height]. Position values are relative to the parent container. All
measurements are in pixel units. This property value is identical to the
Position property.
Layout options, specified as a
GridLayoutOptions object. This property specifies options for
components that are children of grid layout containers. If the component is not a
child of a grid layout container (for example, it is a child of a figure or panel),
then this property is empty and has no effect. However, if the component is a child of
a grid layout container, you can place the component in the desired row and column of
the grid by setting the Row and Column
properties on the GridLayoutOptions object.
For example, this code places a linear gauge in the third row and second column of its parent grid.
g = uigridlayout([4 3]);
gauge = uigauge(g,'linear');
gauge.Layout.Row = 3;
gauge.Layout.Column = 2;To make the gauge span multiple rows or columns, specify the
Row or Column property as a two-element
vector. For example, this gauge spans columns 2 through
3:
gauge.Layout.Column = [2 3];
Callbacks
Object creation function, specified as one of these values:
Function handle.
Cell array in which the first element is a function handle. Subsequent elements in the cell array are the arguments to pass to the callback function.
Character vector containing a valid MATLAB expression (not recommended). MATLAB evaluates this expression in the base workspace.
For more information about specifying a callback as a function handle, cell array, or character vector, see Callbacks in App Designer.
This property specifies a callback function to execute when MATLAB creates the object. MATLAB initializes all property values before executing the CreateFcn callback. If you do not specify the CreateFcn property, then MATLAB executes a default creation function.
Setting the CreateFcn property on an existing component has no effect.
If you specify this property as a function handle or cell array, you can access the object that is being created using the first argument of the callback function. Otherwise, use the gcbo function to access the object.
Object deletion function, specified as one of these values:
Function handle.
Cell array in which the first element is a function handle. Subsequent elements in the cell array are the arguments to pass to the callback function.
Character vector containing a valid MATLAB expression (not recommended). MATLAB evaluates this expression in the base workspace.
For more information about specifying a callback as a function handle, cell array, or character vector, see Callbacks in App Designer.
This property specifies a callback function to execute when MATLAB deletes the object. MATLAB executes the DeleteFcn callback before destroying the
properties of the object. If you do not specify the DeleteFcn
property, then MATLAB executes a default deletion function.
If you specify this property as a function handle or cell array, you can access the
object that is being deleted using the first argument of the callback function.
Otherwise, use the gcbo function to access the
object.
Callback Execution Control
Callback interruption, specified as 'on' or 'off', or as
numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
This property determines if a running callback can be interrupted. There are two callback states to consider:
The running callback is the currently executing callback.
The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
MATLAB determines callback interruption behavior whenever it executes a command that
processes the callback queue. These commands include drawnow, figure, uifigure, getframe, waitfor, and pause.
If the running callback does not contain one of these commands, then no interruption occurs. MATLAB first finishes executing the running callback, and later executes the interrupting callback.
If the running callback does contain one of these commands, then the
Interruptible property of the object that owns the running
callback determines if the interruption occurs:
If the value of
Interruptibleis'off', then no interruption occurs. Instead, theBusyActionproperty of the object that owns the interrupting callback determines if the interrupting callback is discarded or added to the callback queue.If the value of
Interruptibleis'on', then the interruption occurs. The next time MATLAB processes the callback queue, it stops the execution of the running callback and executes the interrupting callback. After the interrupting callback completes, MATLAB then resumes executing the running callback.
Note
Callback interruption and execution behave differently in these situations:
If the interrupting callback is a
DeleteFcn,CloseRequestFcn, orSizeChangedFcncallback, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.If the running callback is currently executing the
waitforfunction, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.If the interrupting callback is owned by a
Timerobject, then the callback executes according to schedule regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.
Callback queuing, specified as 'queue' or 'cancel'. The BusyAction property determines how MATLAB handles the execution of interrupting callbacks. There are two callback states to consider:
The running callback is the currently executing callback.
The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
The BusyAction property determines callback queuing behavior only
when both of these conditions are met:
Under these conditions, the BusyAction property of the
object that owns the interrupting callback determines how MATLAB handles the interrupting callback. These are possible values of the
BusyAction property:
'queue'— Puts the interrupting callback in a queue to be processed after the running callback finishes execution.'cancel'— Does not execute the interrupting callback.
This property is read-only.
Deletion status, returned as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
MATLAB sets the BeingDeleted property to
'on' when the DeleteFcn callback begins
execution. The BeingDeleted property remains set to
'on' until the component object no longer exists.
Check the value of the BeingDeleted property to verify that the object is not about to be deleted before querying or modifying it.
Parent/Child
Parent container, specified as a Figure object or
one of its child containers: Tab, Panel, ButtonGroup, or
GridLayout. If no container is specified,
MATLAB calls the uifigure function to create a new Figure object that serves as the parent container.
Visibility of the object handle, specified as 'on', 'callback',
or 'off'.
This property controls the visibility of the object in its parent's
list of children. When an object is not visible in its parent's list
of children, it is not returned by functions that obtain objects by
searching the object hierarchy or querying properties. These functions
include get, findobj, clf,
and close. Objects are valid
even if they are not visible. If you can access an object, you can
set and get its properties, and pass it to any function that operates
on objects.
| HandleVisibility Value | Description |
|---|---|
'on' | The object is always visible. |
'callback' | The object is visible from within callbacks or functions invoked by callbacks, but not from within functions invoked from the command line. This option blocks access to the object at the command-line, but allows callback functions to access it. |
'off' | The object is invisible at all times. This option is useful
for preventing unintended changes to the UI by another function. Set
the HandleVisibility to 'off' to
temporarily hide the object during the execution of that function.
|
Identifiers
This property is read-only.
Type of graphics object, returned as 'uilineargauge'.
Object identifier, specified as a character vector or string scalar. You can specify a unique Tag value to serve as an identifier for an object. When you need access to the object elsewhere in your code, you can use the findobj function to search for the object based on the Tag value.
User data, specified as any MATLAB array. For example, you can specify a scalar, vector, matrix, cell array, character array, table, or structure. Use this property to store arbitrary data on an object.
If you are working in App Designer, create public or private properties in the app to share data instead of using the UserData property. For more information, see Share Data Within App Designer Apps.
Examples
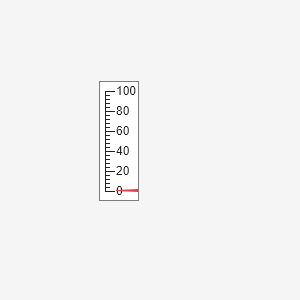
Create a vertical linear gauge in a UI figure.
fig = uifigure("Position",[100 100 300 300]); lg = uigauge(fig,"linear","Orientation","vertical");
Version History
Introduced in R2016aThe default FontColor property value in the light theme has changed slightly. Starting in R2025a, the default value is [0.1294 0.1294 0.1294]. Previously, the default value was [0 0 0].
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)