isminphase
Verify that discrete-time filter System object is minimum phase
Syntax
Description
flag = isminphase(___,Arithmetic=arithType)arithType input
using either of the previous syntaxes.
For more input options, see isminphase in Signal Processing Toolbox™.
Examples
Design a Chebyshev Type I IIR filter and determine if the filter has minimum phase and is stable.
Using the fdesign.lowpass and design functions, design a Chebyshev Type I IIR filter with a passband ripple of 0.5 dB and a 3 dB cutoff frequency at 9600 Hz.
Fs = 48000; % Sampling frequency of input signal d = fdesign.lowpass('N,F3dB,Ap', 10, 9600, .5, Fs); filt = design(d,'cheby1',Systemobject=true)
filt =
dsp.SOSFilter with properties:
Structure: 'Direct form II'
CoefficientSource: 'Property'
Numerator: [5×3 double]
Denominator: [5×3 double]
HasScaleValues: true
ScaleValues: [0.3318 0.2750 0.1876 0.0904 0.0225 0.9441]
Show all properties
Using the isminphase function, determine if the filter has minimum phase.
isminphase(filt)
ans = logical
1
Verify the location of poles and zeros of the filter transfer function on the z-plane. By definition, the poles and zeros of the minimum phase filter must be on or inside the unit circle.
zplane(filt)
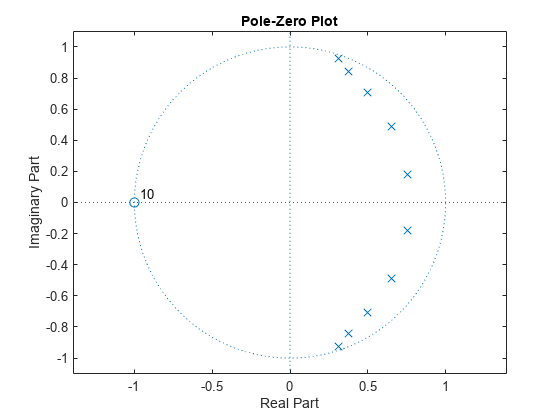
All minimum phase filters are stable. To verify if the designed filter is stable, use the isstable function.
isstable(filt)
ans = logical
1
Input Arguments
Tolerance value to determine when two numbers are close enough to be considered
equal, specified as a positive scalar. If not specified, tol
defaults to eps^(2/3).
Arithmetic used in the filter analysis, specified as 'double',
'single', or 'Fixed'. When the arithmetic
input is not specified and the filter System object is unlocked, the analysis tool assumes a double-precision filter. When the
arithmetic input is not specified and the System object is locked, the function performs the analysis based on the data type of
the locked input.
The 'Fixed' value applies to filter System objects with fixed-point
properties only.
When the 'Arithmetic' input argument is specified as
'Fixed' and the filter object has the data type of the
coefficients set to 'Same word length as input', the arithmetic
analysis depends on whether the System object is unlocked or locked.
unlocked –– The analysis object function cannot determine the coefficients data type. The function assumes that the coefficients data type is signed, has a 16-bit word length, and is auto scaled. The function performs fixed-point analysis based on this assumption.
locked –– When the input data type is
'double'or'single', the analysis object function cannot determine the coefficients data type. The function assumes that the data type of the coefficients is signed, has a 16-bit word length, and is auto scaled. The function performs fixed-point analysis based on this assumption.
To check if the System object is locked or unlocked, use the isLocked function.
When the arithmetic input is specified as 'Fixed' and the filter
object has the data type of the coefficients set to a custom numeric type, the object
function performs fixed-point analysis based on the custom numeric data type.
Output Arguments
Flag to determine if the filter has minimum phase, returned as a logical:
1–– Filter has minimum phase.0–– Filter has non minimum phase.
Data Types: logical
More About
A causal and stable discrete-time system is said to be strictly minimum-phase when all its zeros are inside the unit circle. A causal and stable LTI system is a minimum-phase system if its inverse is causal and stable as well.
Such a system is called a minimum-phase
system because it has the minimum group delay (grpdelay) of the set of systems that have the same magnitude response.
Version History
Introduced in R2013aStarting in R2024b, the isminphase analysis function supports the
dsp.VariableFIRDecimator and dsp.VariableFIRInterpolator objects.
The dsp.BiquadFilter object issues a warning and will be removed in a
future release. Use the dsp.SOSFilter object
instead. For more information on how to replace your existing code, see the
Compatibility Considerations section in the dsp.BiquadFilter reference page.
Starting in R2024b, this function supports the dsp.DCBlocker object.
Starting in R2023b, the isminphase analysis function supports the
dsp.ParallelFilter
and the dsp.Delay objects.
The dsp.BiquadFilter object will be removed in a future release. Use
the dsp.SOSFilter object
instead.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)