dsphdl.Upsampler
Description
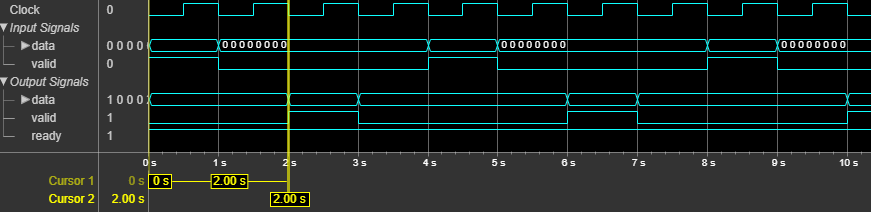
The dsphdl.Upsampler
System object™ upsamples an input signal by adding L–1 zeros between input
samples, where L is the upsampling factor. The System object supports these combinations of input and output data.
Scalar input and scalar output
Scalar input and vector output
Vector input and vector output
The System object provides an architecture suitable for HDL code generation and hardware deployment.
To upsample input data with an upsampler, follow these steps:
Create the
dsphdl.Upsamplerobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Note
You can also generate HDL code for this hardware-optimized algorithm, without creating a MATLAB® script, by using the DSP HDL IP Designer app. The app provides the same interface and configuration options as the System object.
Creation
Description
upsample = dsphdl.Upsampler
upsample = dsphdl.Upsampler(Name=Value)
Properties
Usage
Syntax
Description
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
Algorithms
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2022b