事前学習済みの ONNX YOLO v2 オブジェクト検出器のインポート
この例では、事前学習済みの ONNX™ (Open Neural Network Exchange) you only look once (YOLO) v2 [1] オブジェクト検出ネットワークをインポートし、このネットワークを使用してオブジェクトを検出する方法を説明します。ネットワークをインポートした後、GPU Coder™ を使用してこのネットワークを組み込みプラットフォームに展開したり、trainYOLOv2ObjectDetector 関数を使用してカスタム データで転移学習を行い、このネットワークに再学習させたりすることができます。
ONNX YOLO v2 ネットワークのインポート
事前学習済みの Tiny YOLO v2 ネットワークに関連するファイルをダウンロードします。
pretrainedURL = "https://ssd.mathworks.com/supportfiles/vision/deeplearning/models/yolov2/tiny_yolov2.tar"; pretrainedNetTar = "yolov2Tiny.tar"; if ~exist(pretrainedNetTar,"file") disp("Downloading pretrained network (58 MB)...") websave(pretrainedNetTar,pretrainedURL); end
ダウンロードした .tar ファイルのコンテンツを解凍します。このファイルには、Tiny YOLO v2 ネットワークが含まれています。tiny_yolov2 フォルダーから Model.onnx モデルを読み込みます。このモデルは、PASCAL VOC データセット [2] で事前学習された ONNX YOLO v2 ネットワークです。ネットワークは 20 種類の異なるクラスのオブジェクトを検出できます [3]。
onnxfiles = untar(pretrainedNetTar); pretrainedNet = fullfile("tiny_yolov2","Model.onnx");
importNetworkFromONNX 関数を使用して、ダウンロードしたネットワークをインポートします。
net = importNetworkFromONNX(pretrainedNet);
YOLO v2 オブジェクト検出器の作成
出力層の削除
既定では、importNetworkFromONNX は、ONNX ネットワークの出力テンソルを MATLAB® 出力形式に変換するカスタム出力層を追加します。ただし、yolov2ObjectDetector (Computer Vision Toolbox)オブジェクトは YOLO v2 検出ネットワークが YOLO v2 変換層で終了することを想定しているため、カスタム出力層を削除しなければなりません。YOLO v2 検出ネットワークの詳細については、YOLO v2 入門 (Computer Vision Toolbox)を参照してください。
net = removeLayers(net,"gridOutput");YOLO v2 アンカー ボックスの定義
YOLO v2 は、事前定義されたアンカー ボックスを使用してオブジェクトの位置を予測します。インポートしたネットワークで使用されているアンカー ボックスは、Tiny YOLO v2 ネットワークの構成ファイルで定義されています [4]。ONNX のアンカーは、最終畳み込み層の出力サイズ (13 x 13) に基づき定義されています。yolov2ObjectDetector でアンカーを使用するには、ネットワークの入力サイズ (416x416) に合わせてアンカー ボックスのサイズを変更しなければなりません。アンカー ボックスを [高さ 幅] の形式で指定します。
onnxAnchors = [1.08 1.19; 3.42 4.41; 6.63 11.38; 9.42 5.11; 16.62 10.52]; inputSize = net.Layers(1,1).InputSize(1:2); lastActivationSize = [13 13]; upScaleFactor = inputSize./lastActivationSize; anchorBoxesTmp = upScaleFactor.*onnxAnchors; anchorBoxes = [anchorBoxesTmp(:,2) anchorBoxesTmp(:,1)];
検出層の重みの並べ替え
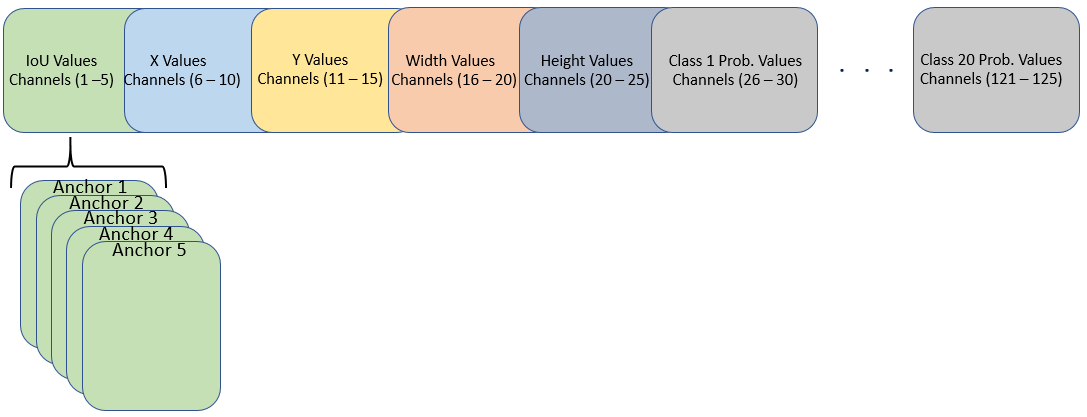
効率よく処理を行うには、インポートしたネットワークに含まれる最終畳み込み層の重みとバイアスを並べ替えて、yolov2ObjectDetector オブジェクトが必要とする配置の活性化を取得します。yolov2ObjectDetector には、最終畳み込み層の特徴マップに含まれる 125 個のチャネルを次の配置で入力する必要があります。
チャネル 1 から 5 — アンカー 5 個の IoU の値
チャネル 6 から 10 — アンカー 5 個の X の値
チャネル 11 から 15 — アンカー 5 個の Y の値
チャネル 16 から 20 — アンカー 5 個の幅の値
チャネル 21 から 25 — アンカー 5 個の高さの値
チャネル 26 から 30 — アンカー 5 個のクラス 1 の確率値
チャネル 31 から 35 — アンカー 5 個のクラス 2 の確率値
チャネル 121 から 125 — アンカー 5 個のクラス 20 の確率値
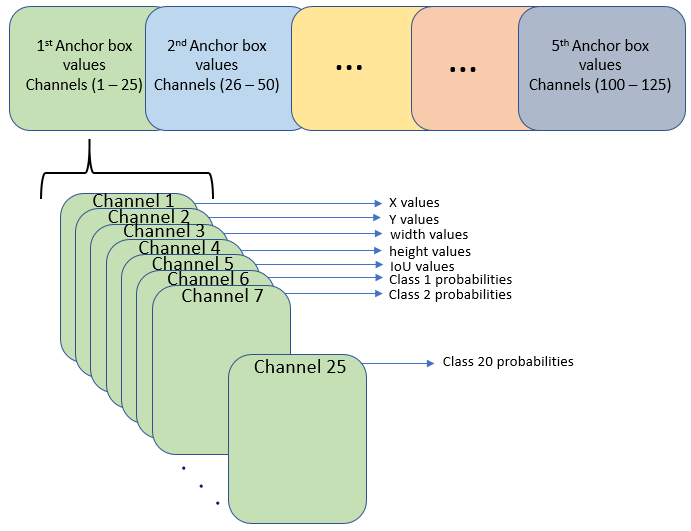
ただし、サイズが 13 x 13 の最終畳み込み層では、活性化の配置が異なります。特徴マップ内の 25 個のチャネルは、それぞれ次のように対応しています。
チャネル 1 — X の値
チャネル 2 — Y の値
チャネル 3 — 幅の値
チャネル 4 — 高さの値
チャネル 5 — IoU の値
チャネル 6 — クラス 1 の確率値
チャネル 7 — クラス 2 の確率値
チャネル 25 — クラス 20 の確率値
この例の最後にリストされている補助関数 rearrangeONNXWeights を使用して、インポートしたネットワークに含まれる最終畳み込み層の重みとバイアスを並べ替え、yolov2ObjectDetector が必要とする形式の活性化を取得します。
weights = net.Layers(end,1).Weights; bias = net.Layers(end,1).Bias; layerName = net.Layers(end,1).Name; numAnchorBoxes = size(onnxAnchors,1); [modWeights,modBias] = rearrangeONNXWeights(weights,bias,numAnchorBoxes);
並べ替えた重みとバイアスを使用して、インポートしたネットワークに含まれる最終畳み込み層の重みとバイアスを新しい畳み込み層の重みとバイアスに置き換えます。
filterSize = size(modWeights,[1 2]); numFilters = size(modWeights,4); modConvolution8 = convolution2dLayer(filterSize,numFilters, ... Name=layerName,Bias=modBias,Weights=modWeights); net = replaceLayer(net,"convolution8",modConvolution8);
YOLO v2 変換層の追加
yolov2ObjectDetector オブジェクトでは、ネットワークが YOLO v2 変換層で終了する必要があります。この層を作成し、最後の畳み込み層に接続します。
classNames = tinyYOLOv2Classes; yolov2Transform = yolov2TransformLayer(numAnchorBoxes,Name="yolov2Transform"); net = addLayers(net,yolov2Transform); net = connectLayers(net,layerName,"yolov2Transform"); net.OutputNames = {'yolov2Transform'};
インポートしたネットワークに含まれる ScalingLayer は、yolov2ObjectDetector によって実行される前処理演算を複製し、インポートされたネットワークから ScalingLayer を削除します。
yoloScaleLayerIdx = find( ... arrayfun(@(x)isa(x,"nnet.cnn.layer.ScalingLayer"), ... net.Layers)); if ~isempty(yoloScaleLayerIdx) for i = 1:size(yoloScaleLayerIdx,1) layerNames{i} = net.Layers(yoloScaleLayerIdx(i,1),1).Name; end net = removeLayers(net,layerNames); net = connectLayers(net,"image","convolution"); end
yolov2ObjectDetector オブジェクトの作成
ネットワークの未設定の学習可能なパラメーターと状態値を初期化します。
net = initialize(net);
YOLO v2 オブジェクト検出器を yolov2ObjectDetector オブジェクトとして作成します。
yolov2Detector = yolov2ObjectDetector(net,classNames,anchorBoxes)
yolov2Detector =
yolov2ObjectDetector with properties:
Network: [1×1 dlnetwork]
InputSize: [416 416 3]
TrainingImageSize: [416 416]
AnchorBoxes: [5×2 double]
ClassNames: [20×1 categorical]
ReorganizeLayerSource: ''
LossFactors: [5 1 1 1]
ModelName: ''
インポートした YOLO v2 検出器を使用したオブジェクトの検出
テスト イメージを読み取り、チャネルを BGR 形式に変換します。
I = imread("highway.png");
Ibgr = cat(3,I(:,:,3),I(:,:,2),I(:,:,1));インポートした検出器を使用して、テスト イメージ内のオブジェクトを検出します。結果を表示します。
[bboxes,scores,labels] = detect(yolov2Detector,Ibgr);
detectedImg = insertObjectAnnotation(I,"rectangle",bboxes,scores);
imshow(detectedImg)
サポート関数
function [modWeights,modBias] = rearrangeONNXWeights(weights,bias,numAnchorBoxes) % rearrangeONNXWeights rearranges the weights and biases of an imported YOLO % v2 network as required by yolov2ObjectDetector. numAnchorBoxes is a scalar % value containing the number of anchors that are used to reorder the weights and % biases. This function performs these operations: % * Extract the weights and biases related to IoU, boxes, and classes. % * Reorder the extracted weights and biases as expected by yolov2ObjectDetector. % * Combine and reshape them back to the original dimensions. weightsSize = size(weights); biasSize = size(bias); sizeOfPredictions = biasSize(3)/numAnchorBoxes; % Reshape the weights with regard to the size of the predictions and anchors. reshapedWeights = reshape(weights,prod(weightsSize(1:3)),sizeOfPredictions,numAnchorBoxes); % Extract the weights related to IoU, boxes, and classes. weightsIou = reshapedWeights(:,5,:); weightsBoxes = reshapedWeights(:,1:4,:); weightsClasses = reshapedWeights(:,6:end,:); % Combine the weights of the extracted parameters as required by % yolov2ObjectDetector. reorderedWeights = cat(2,weightsIou,weightsBoxes,weightsClasses); permutedWeights = permute(reorderedWeights,[1 3 2]); % Reshape the new weights to the original size. modWeights = reshape(permutedWeights,weightsSize); % Reshape the biases with regared to the size of the predictions and anchors. reshapedBias = reshape(bias,sizeOfPredictions,numAnchorBoxes); % Extract the biases related to IoU, boxes, and classes. biasIou = reshapedBias(5,:); biasBoxes = reshapedBias(1:4,:); biasClasses = reshapedBias(6:end,:); % Combine the biases of the extracted parameters as required by yolov2ObjectDetector. reorderedBias = cat(1,biasIou,biasBoxes,biasClasses); permutedBias = permute(reorderedBias,[2 1]); % Reshape the new biases to the original size. modBias = reshape(permutedBias,biasSize); end function classes = tinyYOLOv2Classes() % Return the class names corresponding to the pretrained ONNX tiny YOLO v2 % network. % % The tiny YOLO v2 network is pretrained on the Pascal VOC data set, % which contains images from 20 different classes. classes = ["aeroplane","bicycle","bird","boat","bottle","bus","car", ... "cat","chair","cow","diningtable","dog","horse","motorbike", ... "person","pottedplant","sheep","sofa","train","tvmonitor"]; classes = categorical(classes); end
参考文献
[1] Redmon, Joseph, and Ali Farhadi. "YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger." In 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 6517–25. Honolulu, HI: IEEE, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.690.
[2] "Tiny YOLO v2." https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/validated/vision/object_detection_segmentation/tiny-yolov2.
[3] Everingham, Mark, Luc Van Gool, Christopher K. I. Williams, John Winn, and Andrew Zisserman."The Pascal Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge."International Journal of Computer Vision 88, no. 2 (June 2010):303–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4.
[4] "yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg" https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/blob/master/cfg/yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg.
参考
関数
importONNXNetwork|convolution2dLayer|replaceLayer|removeLayers|connectLayers|findPlaceholderLayers|detect(Computer Vision Toolbox) |trainYOLOv2ObjectDetector(Computer Vision Toolbox) |addLayers
オブジェクト
yolov2ObjectDetector(Computer Vision Toolbox)