RGB-D カメラでの Visual SLAM
この例では、RGB-D イメージ データを処理して、屋内環境マップを作成し、カメラの軌跡を推定する方法を説明します。次に、MATLAB® Coder™ を使用して、コード生成をサポートするようにコードを変更する方法を示します。この例では、特徴ベースで RGB-D カメラをサポートするバージョンの ORB-SLAM2 [1] アルゴリズムを使用します。
Visual simultaneous localization and mapping (vSLAM) とは、環境地図作成を行うのと同時に、周囲に対するカメラの位置と向きを計算する処理を意味します。
vSLAM は単眼カメラを使用して実行できます。しかし、深度を正確に計算できず、推定軌跡が不明で、時間の経過とともにドリフトが発生します。最初のフレームから三角形分割できないように初期マップを作成するためには、単眼カメラの複数のビューを使用しなければなりません。より適切で信頼性の高い解決策は、1 つの RGB カラー イメージと 1 つの深度イメージで構成される RGB-D カメラを使用することです。
コード生成には MATLAB Coder のライセンスが必要です。
処理パイプラインの概要
RGB-D vSLAM のパイプラインは、単眼の Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mappingの例にある単眼 vSLAM のパイプラインと非常によく似ています。主な違いは、"地図の初期化" 段階で、2 フレームのカラー イメージではなく、1 つのカラー イメージと 1 つの深度イメージで構成されるイメージのペアから 3 次元マップ点が作成されることです。
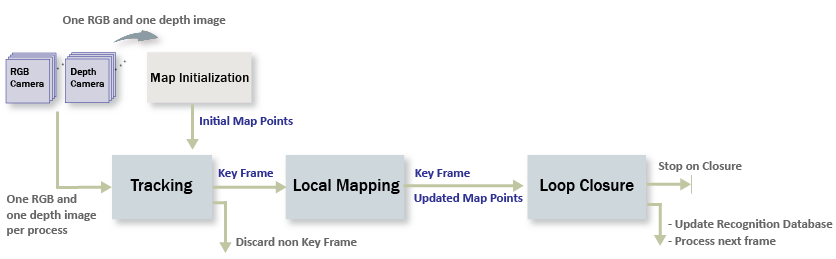
地図の初期化: 初期の 3 次元ワールド ポイントは、カラー イメージから ORB 特徴点を抽出し、深度イメージから 3 次元ワールド位置を計算することで構築できます。カラー イメージは最初のキー フレームとして保存されます。
トラッキング: マップが初期化された後は、カラー イメージの特徴を最後のキー フレームの特徴とマッチングすることにより、新しい RGB-D イメージごとにカメラ姿勢が推定されます。
局所地図作成: 現在のカラー イメージがキー フレームとして識別された場合、深度イメージから新しい 3 次元マップ点が計算されます。この段階で、カメラ姿勢と 3 次元点を調整することにより、バンドル調整を使用して再投影誤差を最小化します。
ループ閉じ込み: bag-of-features アプローチを使用して、キー フレームごとにそれまでのすべてのキー フレームと比較することで、ループを検出します。ループ閉じ込みが検出されると姿勢グラフが最適化され、すべてのキー フレームのカメラ姿勢を調整します。
入力イメージ シーケンスのダウンロードと確認
この例で使用するデータは TUM RGB-D ベンチマーク [2] のものです。Web ブラウザーを使用するか、次のコードを実行することで、データを一時フォルダーにダウンロードできます。
baseDownloadURL = "https://cvg.cit.tum.de/rgbd/dataset/freiburg3/rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_long_office_household.tgz"; dataFolder = fullfile(tempdir, 'tum_rgbd_dataset', filesep); options = weboptions('Timeout', Inf); tgzFileName = [dataFolder, 'fr3_office.tgz']; folderExists = exist(dataFolder, 'dir'); % Create a folder in a temporary directory to save the downloaded file if ~folderExists mkdir(dataFolder); disp('Downloading fr3_office.tgz (1.38 GB). This download can take a few minutes.') websave(tgzFileName, baseDownloadURL, options); % Extract contents of the downloaded file disp('Extracting fr3_office.tgz (1.38 GB) ...') untar(tgzFileName, dataFolder); end imageFolder = [dataFolder, 'rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_long_office_household/'];
2 つのimageDatastoreオブジェクトを作成して、カラー イメージと深度イメージをそれぞれ保存します。
imgFolderColor = [imageFolder,'rgb/']; imgFolderDepth = [imageFolder,'depth/']; imdsColor = imageDatastore(imgFolderColor); imdsDepth = imageDatastore(imgFolderDepth);
カラー イメージと深度イメージが、データセット内で非同期的に生成されることに注意してください。したがって、タイム スタンプに基づいてカラー イメージを深度イメージに関連付ける必要があります。
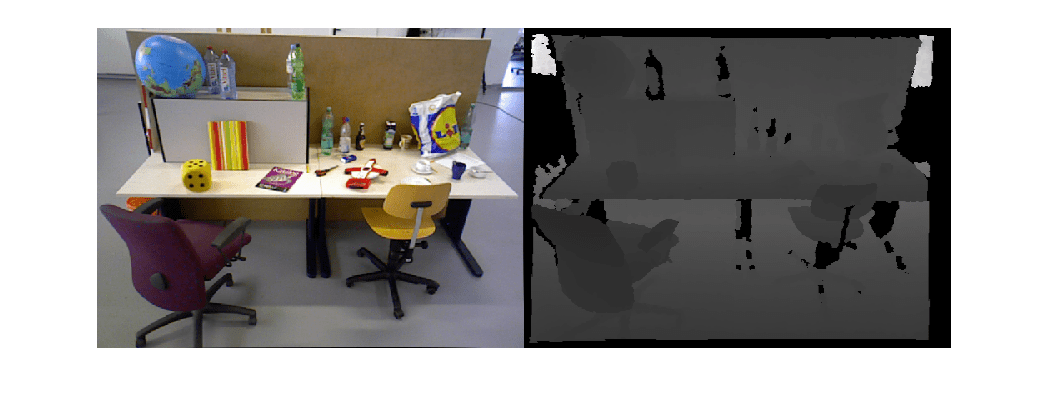
% Load time stamp data of color images timeColor = helperImportTimestampFile([imageFolder, 'rgb.txt']); % Load time stamp data of depth images timeDepth = helperImportTimestampFile([imageFolder, 'depth.txt']); % Align the time stamp indexPairs = helperAlignTimestamp(timeColor, timeDepth); % Select the synchronized image data imdsColor = subset(imdsColor, indexPairs(:, 1)); imdsDepth = subset(imdsDepth, indexPairs(:, 2)); % Inspect the first RGB-D image currFrameIdx = 1; currIcolor = readimage(imdsColor, currFrameIdx); currIdepth = readimage(imdsDepth, currFrameIdx); imshowpair(currIcolor, currIdepth, "montage");

地図の初期化
パイプラインではまず、3 次元ワールド ポイントをもつマップを初期化します。このステップは重要であり、SLAM の最終結果の精度に大きく影響します。初期 ORB 特徴点は、helperDetectAndExtractFeatures を使用して最初のカラー イメージから抽出されます。対応する 3 次元ワールド位置は、helperReconstructFromRGBD を使用して、特徴点のピクセル座標と深度値から計算できます。
% Set random seed for reproducibility rng(0); % Create a cameraIntrinsics object to store the camera intrinsic parameters. % The intrinsics for the dataset can be found at the following page: % https://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/file_formats focalLength = [535.4, 539.2]; % in units of pixels principalPoint = [320.1, 247.6]; % in units of pixels imageSize = size(currIcolor,[1,2]); % in pixels [mrows, ncols] depthFactor = 5e3; intrinsics = cameraIntrinsics(focalLength,principalPoint,imageSize); % Detect and extract ORB features from the color image scaleFactor = 1.2; numLevels = 8; numPoints = 1000; [currFeatures, currPoints] = helperDetectAndExtractFeatures(currIcolor, scaleFactor, numLevels, numPoints); initialPose = rigidtform3d(); [xyzPoints, validIndex] = helperReconstructFromRGBD(currPoints, currIdepth, intrinsics, initialPose, depthFactor);
場所認識データベースの初期化
ループ検出は bags-of-words アプローチを使用して行われます。次の呼び出しを行うことにより、データセットに含まれる大量のイメージ セットから抽出された ORB 記述子を使用して、bagOfFeaturesオブジェクトで表されるビジュアル ボキャブラリがオフラインで作成されます。
bag = bagOfFeatures(imds,CustomExtractor=@helperORBFeatureExtractorFunction, TreeProperties=[5, 10], StrongestFeatures=1);
ここで、imds は学習イメージを格納するimageDatastoreオブジェクトであり、helperORBFeatureExtractorFunction は ORB 特徴抽出器関数です。詳細については、bag of visual words を用いた画像検索を参照してください。
ループ閉じ込み処理により、データベースがインクリメンタルに作成されます。このデータベースはinvertedImageIndexオブジェクトで表され、bag of ORB features に基づきビジュアル ワードとイメージのマッピングを格納します。
% Load the bag of features data created offline bofData = load("bagOfFeaturesDataSLAM.mat"); % Initialize the place recognition database loopDatabase = invertedImageIndex(bofData.bof, SaveFeatureLocations=false); % Add features of the first key frame to the database currKeyFrameId = 1; addImageFeatures(loopDatabase, currFeatures, currKeyFrameId);
データの管理と可視化
カラー イメージと深度イメージの最初のペアを使用してマップを初期化した後で、imageviewsetとworldpointsetを使用して、最初のキー フレームとこれらに対応するマップ点を格納できます。
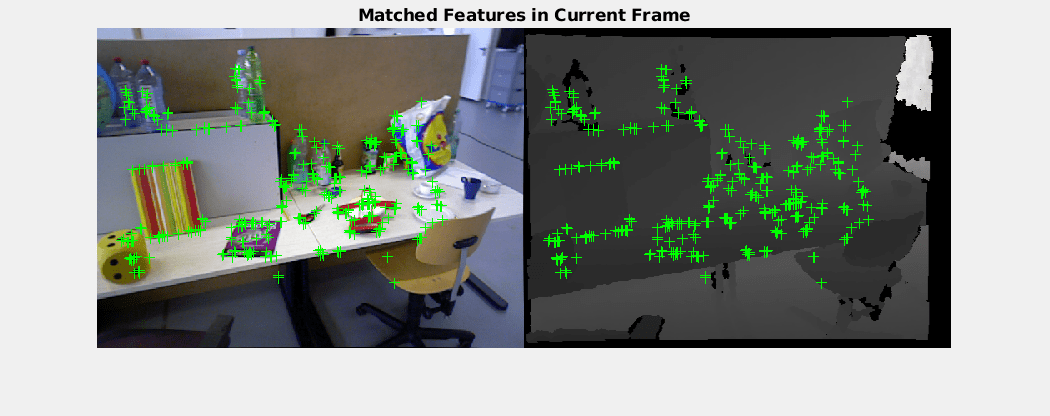
% Create an empty imageviewset object to store key frames vSetKeyFrames = imageviewset; % Create an empty worldpointset object to store 3-D map points mapPointSet = worldpointset; % Add the first key frame vSetKeyFrames = addView(vSetKeyFrames, currKeyFrameId, initialPose, Points=currPoints,... Features=currFeatures.Features); % Add 3-D map points [mapPointSet, rgbdMapPointsIdx] = addWorldPoints(mapPointSet, xyzPoints); % Add observations of the map points mapPointSet = addCorrespondences(mapPointSet, currKeyFrameId, rgbdMapPointsIdx, validIndex); % Update view direction and depth mapPointSet = updateLimitsAndDirection(mapPointSet, rgbdMapPointsIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views); % Update representative view mapPointSet = updateRepresentativeView(mapPointSet, rgbdMapPointsIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views); % Visualize matched features in the first key frame featurePlot = helperVisualizeMatchedFeaturesRGBD(currIcolor, currIdepth, currPoints(validIndex)); % Visualize initial map points and camera trajectory xLim = [-4 4]; yLim = [-3 1]; zLim = [-1 6]; mapPlot = helperVisualizeMotionAndStructure(vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet, xLim, yLim, zLim); % Show legend showLegend(mapPlot);
トラッキング
トラッキング処理はすべての RGB-D イメージを使用して行われ、新しいキー フレームを挿入するタイミングを決定します。
% ViewId of the last key frame lastKeyFrameId = currKeyFrameId; % Index of the last key frame in the input image sequence lastKeyFrameIdx = currFrameIdx; % Indices of all the key frames in the input image sequence addedFramesIdx = lastKeyFrameIdx; currFrameIdx = 2; isLoopClosed = false;
各フレームが次のように処理されます。
新しいフレームごとに ORB 特徴が抽出され、既知の対応する 3 次元マップ点をもつ最後のキー フレームの特徴とのマッチングが行われます。線形カメラ モーション モデルであると仮定した場合、最後のキー フレームの特徴点に対応する現在のフレーム内の予想される一致位置は、
vision.PointTrackerを使用して予測できます。現在のフレームにおける 3 次元から 2 次元への対応関係をもとに、
estworldposeを使用して透視 n 点アルゴリズムでカメラ姿勢を推定し、bundleAdjustmentMotionを使用して動きのみのバンドル調整を行うことでカメラ姿勢を調整します。matchFeaturesInRadiusを使用し、局所地図点を現在のフレームに投影して、その他の特徴の対応関係を探索します。そして、bundleAdjustmentMotionを使用して、再度カメラ姿勢を調整します。トラッキングの最後のステップでは、現在のフレームを新しいキー フレームにするかどうかを決定します。次の両方の条件が満たされている場合、フレームはキー フレームとなります。
最後のキー フレームから少なくとも 20 フレームが経過しているか、現在のフレームのトラッキングが 100 マップ点未満であるか、参照キー フレームでトラッキングされている点の 25% 未満であること。
現在のフレームで追跡されているマップ点が、参照キー フレームでトラッキングされている点の 90% 未満である。
現在のフレームがキー フレームになる場合、"局所地図作成" 処理に進みます。そうでない場合、次のフレームのトラッキングを開始します。
% Main loop isLastFrameKeyFrame = true; % Create and initialize the KLT tracker tracker = vision.PointTracker(MaxBidirectionalError = 5); initialize(tracker, currPoints.Location(validIndex, :), currIcolor); while currFrameIdx < numel(imdsColor.Files) currIcolor = readimage(imdsColor, currFrameIdx); currIdepth = readimage(imdsDepth, currFrameIdx); [currFeatures, currPoints] = helperDetectAndExtractFeatures(currIcolor, scaleFactor, numLevels, numPoints); % Track the last key frame % trackedMapPointsIdx: Indices of the map points observed in the current left frame % trackedFeatureIdx: Indices of the corresponding feature points in the current left frame [currPose, trackedMapPointsIdx, trackedFeatureIdx] = helperTrackLastKeyFrameKLT(tracker, currIcolor, mapPointSet, ... vSetKeyFrames.Views, currFeatures, currPoints, lastKeyFrameId, intrinsics); if isempty(currPose) || numel(trackedMapPointsIdx) < 20 currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1; continue end % Track the local map and check if the current frame is a key frame. % A frame is a key frame if both of the following conditions are satisfied: % % 1. At least 20 frames have passed since the last key frame or the % current frame tracks fewer than 120 map points. % 2. The map points tracked by the current frame are fewer than 90% of % points tracked by the reference key frame. % % localKeyFrameIds: ViewId of the connected key frames of the current frame numSkipFrames = 20; numPointsKeyFrame = 120; [localKeyFrameIds, currPose, trackedMapPointsIdx, trackedFeatureIdx, isKeyFrame] = ... helperTrackLocalMap(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, trackedMapPointsIdx, ... trackedFeatureIdx, currPose, currFeatures, currPoints, intrinsics, scaleFactor, ... isLastFrameKeyFrame, lastKeyFrameIdx, currFrameIdx, numSkipFrames, numPointsKeyFrame); % Visualize matched features updatePlot(featurePlot, currIcolor, currIdepth, currPoints(trackedFeatureIdx)); if ~isKeyFrame currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1; isLastFrameKeyFrame = false; continue else % Match feature points between the stereo images and get the 3-D world positions [xyzPoints, validIndex] = helperReconstructFromRGBD(currPoints, currIdepth, ... intrinsics, currPose, depthFactor); [untrackedFeatureIdx, ia] = setdiff(validIndex, trackedFeatureIdx); xyzPoints = xyzPoints(ia, :); isLastFrameKeyFrame = true; end % Update current key frame ID currKeyFrameId = currKeyFrameId + 1;
局所地図作成
局所地図作成はすべてのキー フレームに対して行われます。新しいキー フレームが決定されると、それをキー フレームに追加し、新しいキー フレームにおいて観測されたマップ点の属性を更新します。mapPointSet に含まれる外れ値をできるだけ少なくするには、有効なマップ点が少なくとも 3 つのキー フレームで観測されなければなりません。
現在のキー フレームにおける ORB 特徴点と、接続されたキー フレームを三角形分割することで、新しいマップ点が作成されます。matchFeatures を使用して、現在のキー フレームにおける非マッチの特徴点ごとに、接続されたキー フレームにおいて、他の非マッチの点との一致を探索します。局所バンドル調整により、現在のキー フレームの姿勢、接続されたキー フレームの姿勢、およびこれらのキー フレームで観測されたすべてのマップ点を調整します。
% Add the new key frame [mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames] = helperAddNewKeyFrame(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, ... currPose, currFeatures, currPoints, trackedMapPointsIdx, trackedFeatureIdx, localKeyFrameIds); % Remove outlier map points that are observed in fewer than 3 key frames if currKeyFrameId == 2 triangulatedMapPointsIdx = []; end [mapPointSet, trackedMapPointsIdx] = ... helperCullRecentMapPointsRGBD(mapPointSet, trackedMapPointsIdx, triangulatedMapPointsIdx, ... rgbdMapPointsIdx); % Add new map points computed from disparity [mapPointSet, rgbdMapPointsIdx] = addWorldPoints(mapPointSet, xyzPoints); mapPointSet = addCorrespondences(mapPointSet, currKeyFrameId, rgbdMapPointsIdx, ... untrackedFeatureIdx); % Create new map points by triangulation minNumMatches = 10; minParallax = 1; [mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, triangulatedMapPointsIdx, rgbdMapPointsIdx] = helperCreateNewMapPointsStereo( ... mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, currKeyFrameId, intrinsics, scaleFactor, minNumMatches, minParallax, ... untrackedFeatureIdx, rgbdMapPointsIdx); % Update view direction and depth mapPointSet = updateLimitsAndDirection(mapPointSet, [triangulatedMapPointsIdx; rgbdMapPointsIdx], ... vSetKeyFrames.Views); % Update representative view mapPointSet = updateRepresentativeView(mapPointSet, [triangulatedMapPointsIdx; rgbdMapPointsIdx], ... vSetKeyFrames.Views); % Local bundle adjustment [mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, triangulatedMapPointsIdx, rgbdMapPointsIdx] = ... helperLocalBundleAdjustmentStereo(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, ... currKeyFrameId, intrinsics, triangulatedMapPointsIdx, rgbdMapPointsIdx); % Visualize 3-D world points and camera trajectory updatePlot(mapPlot, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet); % Set the feature points to be tracked [~, index2d] = findWorldPointsInView(mapPointSet, currKeyFrameId); setPoints(tracker, currPoints.Location(index2d, :));
ループ閉じ込み
ループ閉じ込みの検出ステップでは、局所地図作成処理で処理された現在のキー フレームを受け取り、ループを検出して閉じようと試みます。evaluateImageRetrieval を使用し、データベース内のイメージをクエリすることで、現在のキー フレームと視覚的に似ているループ候補が特定されます。候補キー フレームが最後のキー フレームと接続されておらず、隣接するキー フレームの 3 つがループ候補であれば、その候補キー フレームは有効です。
有効なループ候補が見つかると、estgeotform3dを使用して、ループ候補フレームと現在のキー フレームの間の相対姿勢を計算します。相対姿勢はrigidtform3dオブジェクトに保存されている 3 次元剛体変換を表します。そして、ループの接続を相対姿勢と共に追加し、mapPointSet と vSetKeyFrames を更新します。
% Check loop closure after some key frames have been created if currKeyFrameId > 20 % Minimum number of feature matches of loop edges loopEdgeNumMatches = 120; % Detect possible loop closure key frame candidates [isDetected, validLoopCandidates] = helperCheckLoopClosureT(vSetKeyFrames, currKeyFrameId, ... loopDatabase, currIcolor, loopEdgeNumMatches); if isDetected % Add loop closure connections maxDistance = 0.1; [isLoopClosed, mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames] = helperAddLoopConnectionsStereo(... mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, validLoopCandidates, currKeyFrameId, ... currFeatures, currPoints, loopEdgeNumMatches, maxDistance); end end % If no loop closure is detected, add current features into the database if ~isLoopClosed addImageFeatures(loopDatabase, currFeatures, currKeyFrameId); end % Update IDs and indices lastKeyFrameId = currKeyFrameId; lastKeyFrameIdx = currFrameIdx; addedFramesIdx = [addedFramesIdx; currFrameIdx]; %#ok<AGROW> currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1; end % End of main loop
Loop edge added between keyframe: 4 and 86 Loop edge added between keyframe: 2 and 86 Loop edge added between keyframe: 3 and 87 Loop edge added between keyframe: 4 and 87 Loop edge added between keyframe: 5 and 87 Loop edge added between keyframe: 6 and 88 Loop edge added between keyframe: 4 and 88 Loop edge added between keyframe: 7 and 96 Loop edge added between keyframe: 7 and 97 Loop edge added between keyframe: 6 and 97
最後に、vSetKeyFrames の Essential グラフ全体に対して姿勢グラフの最適化を適用し、ドリフトを修正します。Essential グラフは、Covisibility グラフの接続のうち、一致数が minNumMatches よりも少ない接続を削除することで、内部的に作成されます。姿勢グラフの最適化後、最適化された姿勢を使用してマップ点の 3 次元での位置を更新します。
% Optimize the poses minNumMatches = 50; vSetKeyFramesOptim = optimizePoses(vSetKeyFrames, minNumMatches, Tolerance=1e-16); % Update map points after optimizing the poses mapPointSet = helperUpdateGlobalMap(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, vSetKeyFramesOptim); updatePlot(mapPlot, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet); % Plot the optimized camera trajectory optimizedPoses = poses(vSetKeyFramesOptim); plotOptimizedTrajectory(mapPlot, optimizedPoses) % Update legend showLegend(mapPlot);
グラウンド トゥルースとの比較
最適化されたカメラの軌跡をグラウンド トゥルースと比較して、精度を評価できます。ダウンロードしたデータには、各フレームのカメラ姿勢のグラウンド トゥルースが格納された groundtruth.txt ファイルが含まれています。データは MAT ファイル形式で保存されています。軌跡の平方根平均二乗誤差 (RMSE) の推定を計算することもできます。
% Load ground truth gTruthData = load("orbslamGroundTruth.mat"); gTruth = gTruthData.gTruth; % Plot the actual camera trajectory plotActualTrajectory(mapPlot, gTruth(indexPairs(addedFramesIdx, 1)), optimizedPoses); % Show legend showLegend(mapPlot);
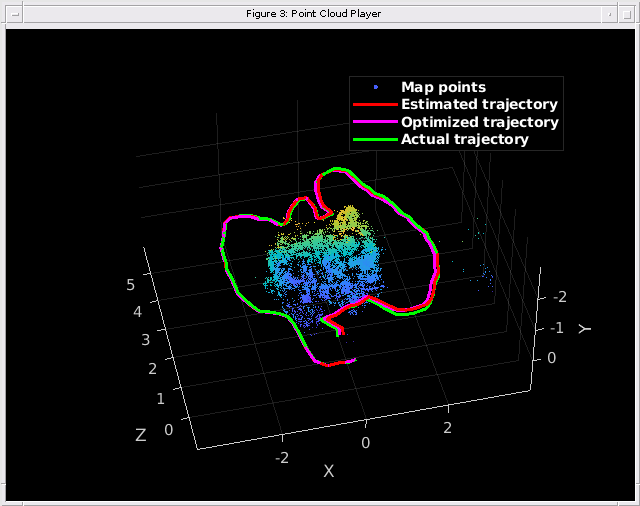
% Evaluate tracking accuracy errorMetrics = compareTrajectories(optimizedPoses.AbsolutePose, gTruth(indexPairs(addedFramesIdx, 1))); disp(['Absolute RMSE for key frame location (m): ', num2str(errorMetrics.AbsoluteRMSE(2))]);
Absolute RMSE for key frame location (m): 0.051219
深度イメージからの緻密な再構成
調整されたカメラの姿勢をもとに、関連する深度イメージ内のすべての有効なイメージ ポイントを 3 次元空間に再投影して、緻密な再構成を実行できます。
% Create an array of pointCloud objects to store the world points constructed % from the key frames ptClouds = repmat(pointCloud(zeros(1, 3)), numel(addedFramesIdx), 1); % Ignore image points at the boundary offset = 40; [X, Y] = meshgrid(offset:2:imageSize(2)-offset, offset:2:imageSize(1)-offset); for i = 1: numel(addedFramesIdx) Icolor = readimage(imdsColor, addedFramesIdx(i)); Idepth = readimage(imdsDepth, addedFramesIdx(i)); [xyzPoints, validIndex] = helperReconstructFromRGBD([X(:), Y(:)], ... Idepth, intrinsics, optimizedPoses.AbsolutePose(i), depthFactor); colors = zeros(numel(X), 1, 'like', Icolor); for j = 1:numel(X) colors(j, 1:3) = Icolor(Y(j), X(j), :); end ptClouds(i) = pointCloud(xyzPoints, Color=colors(validIndex, :)); end % Concatenate the point clouds pointCloudsAll = pccat(ptClouds); figure pcshow(pointCloudsAll,VerticalAxis="y", VerticalAxisDir="down"); xlabel('X') ylabel('Y') zlabel('Z')

コード生成
コード生成では ImageDatastore オブジェクトがサポートされないため、入力イメージを読み取り、cell 配列に保存します。
for i = 1:numel(imdsColor.Files) imagesColor{i,1} = im2gray(readimage(imdsColor,i)); end for i = 1:numel(imdsDepth.Files) imagesDepth{i,1} = readimage(imdsDepth,i); end
関数 helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen を使用して、ホスト コンピューターに展開するための C++ コードを生成します。MATLAB Coder の要件を満たすには、アルゴリズムを可視化のためのコードから分離するよう、コードを再構成する必要があります。関数 helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen は、地図の初期化、追跡、局所地図作成、およびループ閉じ込みのアルゴリズム プロセスをカプセル化します。この関数は、イメージの 2 つの cell 配列 (imagesColor と imagesDepth) を入力として受け取り、3 次元worldpointset、推定カメラ姿勢、およびすべてのキー フレームのインデックスを出力します。
コンパイル命令 %#codegen (MATLAB Coder)コマンドを使用して、関数 helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen を MEX ファイルにコンパイルします。既定では、生成された MEX ファイルの名前は、元の MATLAB 関数に接尾辞 "_mex" を付加した helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen_mex となります。MEX ファイルをカスタム ファイル名で保存するには、-o オプションを使用します。-report オプションを指定して、コンパイル レポートを生成できます。このレポートには元の MATLAB コードと、C コードの生成時に作成された関連ファイルが含まれています。MATLAB Coder が生成ファイルを保存できるように、一時ディレクトリを作成することもできます。MEX ファイル生成に関連するその他のオプションについては、codegen ページのoptions (MATLAB Coder)を参照してください。
cpuConfig = coder.config("mex"); cpuConfig.TargetLang = "C++"; % Generate C++ code codegen -config cpuConfig helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen -args {imagesColor,imagesDepth}
Code generation successful.
サポート関数
この例には、以下の補助関数が個別のファイルとして含まれています。
"helperDetectAndExtractFeatures" — イメージから ORB 特徴を検出して抽出します。
"helperReconstructFromRGBD" — カラー イメージと深度イメージからシーンを再構成します。
"helperCullRecentMapPointsRGBD" — 最近追加されたマップ点をカリングします。
"helperAddLoopConnectionsStereo" — 現在のキー フレームと有効なループ候補キー フレームの間の接続を追加します。
"helperAddNewKeyFrame" — キー フレーム セットにキー フレームを追加します。
"helperCheckLoopClosureT" — 特徴データベースから視覚的に似たイメージを取得して、ループ候補となるキー フレームを検出します。
"helperCreateNewMapPointsStereo" — 現在のキー フレームと、接続されたキー フレームの間の一致した特徴点を三角形分割して、新しいマップ点を作成します。
"helperLocalBundleAdjustmentStereo" — 現在のキー フレームの姿勢と周囲のシーンのマップを調整します。
"helperORBFeatureExtractorFunction" — bagOfFeatures で使用される ORB 特徴抽出を実装します。
"helperRGBDVisualSLAMCodegen" — RGB-D Visual SLAM のコード生成アルゴリズムが含まれます。
"helperTrackLastKeyFrameKLT" — KLT トラッカーを使用して最後のキー フレームを追跡し、現在のカメラ姿勢を推定します。
"helperTrackLocalMap" — 局所地図を追跡して、カメラ姿勢を調整します。
"helperVisualizeMatchedFeaturesRGBD" — フレーム内のマッチした特徴を表示します。
"helperVisualizeMatchedFeatures" — マップ点とカメラの軌跡を表示します。
"helperVisualizeRGBDVisualSlam" — RGB-D vSLAM のコード生成結果を表示します。
この例では、以下の補助関数も使用します。
"helperImportTimestampFile" — タイムスタンプ ファイルをインポートします。
function timestamp = helperImportTimestampFile(filename) % Input handling dataLines = [4 Inf]; %% Set up the Import Options and import the data opts = delimitedTextImportOptions("NumVariables",2); % Specify range and delimiter opts.DataLines = dataLines; opts.Delimiter = " "; % Specify column names and types opts.VariableNames = ["VarName1","Var2"]; opts.SelectedVariableNames = "VarName1"; opts.VariableTypes = ["double","string"]; % Specify file level properties opts.ExtraColumnsRule = "ignore"; opts.EmptyLineRule = "read"; opts.ConsecutiveDelimitersRule = "join"; opts.LeadingDelimitersRule = "ignore"; % Specify variable properties opts = setvaropts(opts,"Var2","WhitespaceRule","preserve"); opts = setvaropts(opts,"Var2","EmptyFieldRule","auto"); % Import the data data = readtable(filename,opts); % Convert to output type timestamp = table2array(data); end
helperAlignTimestamp — カラー イメージと深度イメージのタイムスタンプを揃えます。
function indexPairs = helperAlignTimestamp(timeColor,timeDepth) idxDepth = 1; indexPairs = zeros(numel(timeColor),2); for i = 1:numel(timeColor) for j = idxDepth:numel(timeDepth) if abs(timeColor(i)-timeDepth(j)) < 1e-4 idxDepth = j; indexPairs(i,:) = [i,j]; break elseif timeDepth(j)-timeColor(i) > 1e-3 break end end end indexPairs = indexPairs(indexPairs(:,1)>0,:); end
helperEstimateTrajectoryError — 追従誤差を計算します。
function rmse = helperEstimateTrajectoryError(gTruth,cameraPoses) locations = vertcat(cameraPoses.AbsolutePose.Translation); gLocations = vertcat(gTruth.Translation); scale = median(vecnorm(gLocations,2,2))/median(vecnorm(locations,2,2)); scaledLocations = locations*scale; rmse = sqrt(mean(sum((scaledLocations-gLocations).^2,2))); disp(["Absolute RMSE for key frame trajectory (m): ",num2str(rmse)]); end
helperUpdateGlobalMap — 姿勢グラフの最適化後にマップ点の 3 次元位置を更新します。
function mapPointSet = helperUpdateGlobalMap(mapPointSet,vSetKeyFrames,vSetKeyFramesOptim) posesOld = vSetKeyFrames.Views.AbsolutePose; posesNew = vSetKeyFramesOptim.Views.AbsolutePose; positionsOld = mapPointSet.WorldPoints; positionsNew = positionsOld; indices = 1:mapPointSet.Count; % Update world location of each map point based on the new absolute pose of % the corresponding major view for i = 1: mapPointSet.Count majorViewIds = mapPointSet.RepresentativeViewId(i); tform = rigidtform3d(posesNew(majorViewIds).A/posesOld(majorViewIds).A); positionsNew(i,:) = transformPointsForward(tform,positionsOld(i,:)); end mapPointSet = updateWorldPoints(mapPointSet,indices,positionsNew); end
参考文献
[1] Mur-Artal, Raul, and Juan D. Tardós. “ORB-SLAM2: An Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo, and RGB-D Cameras.” IEEE Transactions on Robotics 33, no. 5 (October 2017): 1255–62. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103.
[2] Sturm, Jürgen, Nikolas Engelhard, Felix Endres, Wolfram Burgard, and Daniel Cremers. “A Benchmark for the Evaluation of RGB-D SLAM Systems.” In 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 573–80, 2012.https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2012.6385773.