MIL-188 QAM Demodulator Baseband
MIL-STD-188-110 B/C 標準固有の直交振幅復調
ライブラリ:
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
AM
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
Standard-Compliant
説明
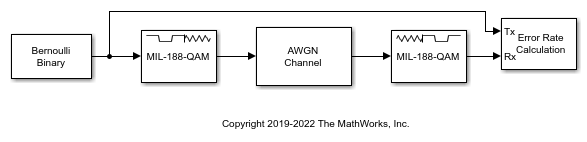
MIL-188 QAM Demodulator Baseband ブロックは、MIL-STD-188-110規格固有の直交振幅変調 (QAM) を使用して入力信号を復調します。MIL-STD-188 準拠の復調の詳細については、MIL-STD-188-110 QAM 硬復調およびMIL-STD-188-110 QAM 軟復調を参照してください。
このアイコンには、利用可能な ![]() のすべての端子を使用したブロックが表示されています。
のすべての端子を使用したブロックが表示されています。
例
端子
入力
出力
パラメーター
ブロックの特性
データ型 |
|
多次元信号 |
|
可変サイズの信号 |
|
詳細
ヒント
MIL-188 QAM Demodulator Baseband ブロックをより高速に実行するには、[シミュレーション実行方法] パラメーターを以下のように設定します。
コード生成(硬判定復調を使用する場合)。インタープリター型実行(軟判定復調を使用する場合)。
参照
[1] MIL-STD-188-110B & C: "Interoperability and Performance Standards for Data Modems." Department of Defense Interface Standard, USA.
拡張機能
バージョン履歴
R2018b で導入