onehotdecode
説明
A = onehotdecode(B,classes,featureDim)B 内の各確率ベクトルを、classes で指定されたラベルのうち確率が最も高いクラス ラベルに復号化します。featureDim は、確率ベクトルの定義に使用される次元を指定します。この関数は、ベクトル内で最も高い値がある位置と、classes 内でそれに対応する位置にあるクラス ラベルをマッチングさせて、確率ベクトルをクラス ラベルに復号化します。A 内の各確率ベクトルは、確率ベクトル内で最も高い値に対応する classes の値に置き換えられます。
例
ラベルのセットを確率ベクトルに符号化し、それらを復号化してラベルに戻します。
色の種類を指定する categorical ラベルのベクトルを作成します。
colorsOriginal = ["red","blue","red","green","yellow","blue"]; colorsOriginal = categorical(colorsOriginal)
colorsOriginal = 1×6 categorical
red blue red green yellow blue
categorical ベクトルのクラスを調べます。
classes = categories(colorsOriginal)
classes = 4×1 cell
{'blue' }
{'green' }
{'red' }
{'yellow'}
関数 onehotencode を使用して、ラベルを確率ベクトルに one-hot 符号化します。各行がクラスに対応し、各列が確率ベクトルに対応するように、最初の次元にラベルを符号化します。
colorsEncoded = onehotencode(colorsOriginal,1)
colorsEncoded = 4×6
0 1 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
関数 onehotdecode を使用して、確率ベクトルを復号化します。
colorsDecoded = onehotdecode(colorsEncoded,classes,1)
colorsDecoded = 1×6 categorical
red blue red green yellow blue
復号化されたラベルは元のラベルと一致します。
ダミー変数を作成し、元のデータに復号化します。
色の種類を指定して、カテゴリカル データの列ベクトルを作成します。
colorsOriginal = ["red";"blue";"red";"green";"yellow";"blue"]; colorsOriginal = categorical(colorsOriginal)
colorsOriginal = 6×1 categorical
red
blue
red
green
yellow
blue
categorical ベクトルのクラスを調べます。
classes = categories(colorsOriginal);
関数 dummyvar を使用して、色の種類のそれぞれにダミー変数を作成します。
dummyColors = dummyvar(colorsOriginal)
dummyColors = 6×4
0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0
関数 onehotdecode を使用して、2 番目の次元のダミー変数を復号化します。
colorsDecoded = onehotdecode(dummyColors,classes,2)
colorsDecoded = 6×1 categorical
red
blue
red
green
yellow
blue
復号化された変数は、元の色の種類と一致します。
確率ベクトルのセットを各観測値に対する最も確率の高いクラスに復号化します。
10 個のランダムな確率ベクトルのセットを作成します。このベクトルは、観測値が 5 個のクラスのいずれかに属する確率を表します。
numObs = 10; numClasses = 5; prob = rand(numObs,numClasses); tot = sum(prob,2); prob = prob./tot
prob = 10×5
0.2938 0.0568 0.2365 0.2546 0.1582
0.3895 0.4174 0.0154 0.0137 0.1641
0.0427 0.3217 0.2854 0.0931 0.2573
0.2878 0.1529 0.2943 0.0145 0.2505
0.2640 0.3341 0.2834 0.0405 0.0780
0.0422 0.0614 0.3280 0.3564 0.2120
0.1078 0.1632 0.2876 0.2689 0.1725
0.1940 0.3249 0.1392 0.1125 0.2293
0.2356 0.1949 0.1613 0.2338 0.1745
0.3345 0.3326 0.0593 0.0119 0.2616
5 つのクラスのセットを定義します。
classes = ["Red","Yellow","Green","Blue","Purple"];
関数 onehotdecode を使用して、最も確率の高いクラスに確率を復号化します。確率ベクトルは 2 番目の次元 (各列が一意のクラスに対応) に符号化されているため、符号化された確率を含む次元を 2 と指定します。最も確率の高いクラスを string ベクトルとして取得します。
result = onehotdecode(prob,classes,2,"string")result = 10×1 string
"Red"
"Yellow"
"Yellow"
"Green"
"Yellow"
"Blue"
"Green"
"Yellow"
"Red"
"Red"
予測クラス スコアを予測ラベルに復号化します。
fisheriris データ セットを読み込みます。150 本のアヤメについて 4 つの測定値が含まれる数値行列 X を作成します。対応するアヤメの種類が含まれる categorical ラベルのベクトル S を作成します。
load fisheriris
X = meas;
S = categorical(species);関数 onehotencode を使用して、ラベルを確率ベクトルに one-hot 符号化します。確率ベクトルを 2 番目の次元に符号化します。
Y = onehotencode(S,2);
単純な線形分類器の近似係数を計算します。
B = X\Y
B = 4×3
0.0834 0.2117 -0.1481
0.2533 -0.3059 0.1412
-0.2270 0.1888 0.0181
-0.0635 -0.5749 0.5873
近似係数からクラス スコアを予測し、スコアが範囲 [0,1] に収まっていることを確認します。
scores = X*B; scores = min(1,max(0,scores));
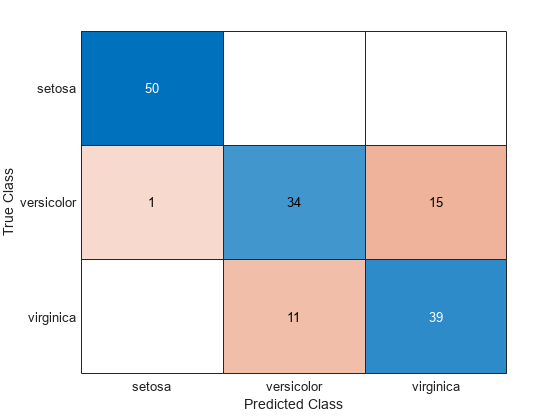
関数 onehotdecode を使用して、予測クラス スコアを予測ラベルに復号化します。その後、混同チャートを作成して、真のラベル S を予測ラベル label と比較します。
label = onehotdecode(scores,categories(S),2); confusionchart(S,label)
入力引数
復号化する確率ベクトル。数値配列として指定します。
B の値は 0 と 1 の範囲内でなければなりません。B 内の確率ベクトルに NaN 値が含まれる場合、この関数は、確率が最も高く、値が NaN ではないクラスにその観測値を復号化します。観測値に NaN 値のみが含まれる場合、この関数は、classes に含まれる最初のクラス ラベルにその観測値を復号化します。
データ型: single | double
クラス。文字ベクトルの cell 配列、string ベクトル、数値ベクトル、または 2 次元の文字配列として指定します。
データ型: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | string | cell | char
復号化されたラベルのデータ型。文字ベクトルまたは string スカラーとして指定します。
typename の有効な値は、'categorical'、'string'、および 'single' や 'int64' などの数値型です。数値型を指定する場合、classes は数値ベクトルでなければなりません。
例: 'double'
データ型: char | string
出力引数
復号化されたクラス ラベル。categorical 配列、string 配列、または数値配列として返されます。
バージョン履歴
R2021b で導入
参考
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)