timeseries2timetable
説明
TT = timeseries2timetable( は ts)timeseries オブジェクトを timetable に変換します。
tsがtimeseriesオブジェクトの場合、TTは 1 つの変数をもつ timetable です。tsがtimeseriesオブジェクトの配列の場合、TTはts内のtimeseriesオブジェクトと同数の変数をもつ timetable です。ts内のすべてのtimeseriesオブジェクトのサンプル時間は同じでなければなりません。いずれかの
timeseriesオブジェクトがイベントをもつ場合、この関数はイベントをイベント テーブルに変換し、そのイベント テーブルをTTに付加します。イベントが重複すると、イベント テーブルの行が重複します。 (R2024b 以降)
例
10 秒間隔でサンプリングされた 5 つの乱数をもつ timeseries オブジェクトを作成します。
ts = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40])
timeseries
Common Properties:
Name: 'unnamed'
Time: [5x1 double]
TimeInfo: [1x1 tsdata.timemetadata]
Data: [5x1 double]
DataInfo: [1x1 tsdata.datametadata]
More properties, Methods
ts 内の時間およびデータを表示します。
ts.Time
ans = 5×1
0
10
20
30
40
ts.Data
ans = 5×1
0.8147
0.9058
0.1270
0.9134
0.6324
ts を timetable に変換します。
TT = timeseries2timetable(ts)
TT=5×1 timetable
Time Data
______ _______
0 sec 0.81472
10 sec 0.90579
20 sec 0.12699
30 sec 0.91338
40 sec 0.63236
timeseries オブジェクトの配列を作成します。サンプル時間と同じベクトルを使用しますが、時系列を異なる名前にします。関数 rand を使用して、異なるデータ値の配列を作成します。
ts1 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_1"); ts2 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_2"); ts3 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_3"); ts = [ts1 ts2 ts3]
1×3 timeseries array with properties:
Events
Name
UserData
Data
DataInfo
Time
TimeInfo
Quality
QualityInfo
IsTimeFirst
TreatNaNasMissing
Length
すべての timeseries オブジェクトのデータを 1 つの timetable に結合します。配列内の各時系列は 1 つの変数を timetable に提供します。
TT = timeseries2timetable(ts)
TT=5×3 timetable
Time Series_1 Series_2 Series_3
______ ________ ________ ________
0 sec 0.81472 0.09754 0.15761
10 sec 0.90579 0.2785 0.97059
20 sec 0.12699 0.54688 0.95717
30 sec 0.91338 0.95751 0.48538
40 sec 0.63236 0.96489 0.80028
複数の timeseries オブジェクトを timetable に変換します。
ts1 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_1"); ts2 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_2"); ts3 = timeseries(rand(5,1),[0 10 20 30 40],"Name","Series_3"); TT = timeseries2timetable(ts1,ts2,ts3)
TT=5×3 timetable
Time Series_1 Series_2 Series_3
______ ________ ________ ________
0 sec 0.81472 0.09754 0.15761
10 sec 0.90579 0.2785 0.97059
20 sec 0.12699 0.54688 0.95717
30 sec 0.91338 0.95751 0.48538
40 sec 0.63236 0.96489 0.80028
3 つの都市交差点の車両交通量データをもつ 3 つの timeseries オブジェクトを読み込みます。
load trafficCounts.mat count1 count2 count3
最初の timeseries オブジェクトのプロパティを表示します。これらのプロパティには、交通量データ、データが収集された時刻、および 2 つのイベントが格納されています。イベントは tsdata.event オブジェクトです。
count1
timeseries
Common Properties:
Name: 'Intersection1'
Time: [15x1 double]
TimeInfo: [1x1 tsdata.timemetadata]
Data: [15x1 double]
DataInfo: [1x1 tsdata.datametadata]
Events: [1x2 tsdata.event]
More properties, Methods
count1 に付加されている最初のイベントを表示します。
count1.Events(1)
EventData: []
Name: 'AMCommute'
Time: 8
Units: 'hours'
StartDate: ''
2 番目のイベントを表示します。イベントは、朝と夕方の通勤時間を示しています。
count1.Events(2)
EventData: []
Name: 'PMCommute'
Time: 18
Units: 'hours'
StartDate: ''
3 つの timeseries オブジェクトからデータをプロットします。サブプロットで時系列を表示するタイル表示チャート レイアウトを作成するために、tiledlayout 関数を使用します。チャートには、3 つの時系列に関連付けられたイベントを示す赤い点が表示されます。
tiledlayout(3,1) nexttile plot(count1) nexttile plot(count2) nexttile plot(count3)
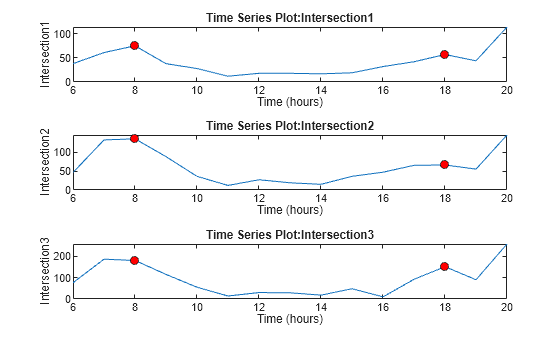
3 つの timeseries オブジェクトを 1 つの timetable に変換します。行時間の形式を hh:mm 形式に設定します。イベントは 3 つの時系列で同じ時刻に発生するため、timetable には 08:00 と 18:00 の両方に 3 つのイベントのラベルがあります。
TT = timeseries2timetable(count1,count2,count3);
TT.Time.Format = "hh:mm"TT=15×3 timetable with 6 events
Time Intersection1 Intersection2 Intersection3
_____ _____________ _____________ _____________
06:00 38 46 76
07:00 61 132 186
<3 events> 08:00 75 135 180
09:00 38 88 115
10:00 28 36 55
11:00 12 12 14
12:00 18 27 30
13:00 18 19 29
14:00 17 15 18
15:00 19 36 48
16:00 32 47 10
17:00 42 65 92
<3 events> 18:00 57 66 151
19:00 44 55 90
20:00 114 145 257
この変換では、イベント オブジェクトもイベント テーブルに変換されます。イベント テーブルは timetable に付加されます。イベント テーブルでは、2 つの時刻に 3 つの同一イベントがあることが示されています。
TT.Properties.Events
ans = 6×1 eventtable
Event Labels Variable: EventLabels
Event Lengths Variable: <instantaneous>
Time EventLabels
_____ ___________
8 hr "AMCommute"
8 hr "AMCommute"
8 hr "AMCommute"
18 hr "PMCommute"
18 hr "PMCommute"
18 hr "PMCommute"
繰り返しイベントがあるイベント テーブルをクリーニングできます。1 つの方法は、unique 関数を使用することです。
ET = TT.Properties.Events; ET = unique(ET)
ET = 2×1 eventtable
Event Labels Variable: EventLabels
Event Lengths Variable: <instantaneous>
Time EventLabels
_____ ___________
8 hr "AMCommute"
18 hr "PMCommute"
クリーニングしたイベント テーブルを timetable に付加します。timetable を表示します。
TT.Properties.Events = ET
TT=15×3 timetable with 2 events
Time Intersection1 Intersection2 Intersection3
_____ _____________ _____________ _____________
06:00 38 46 76
07:00 61 132 186
AMCommute 08:00 75 135 180
09:00 38 88 115
10:00 28 36 55
11:00 12 12 14
12:00 18 27 30
13:00 18 19 29
14:00 17 15 18
15:00 19 36 48
16:00 32 47 10
17:00 42 65 92
PMCommute 18:00 57 66 151
19:00 44 55 90
20:00 114 145 257
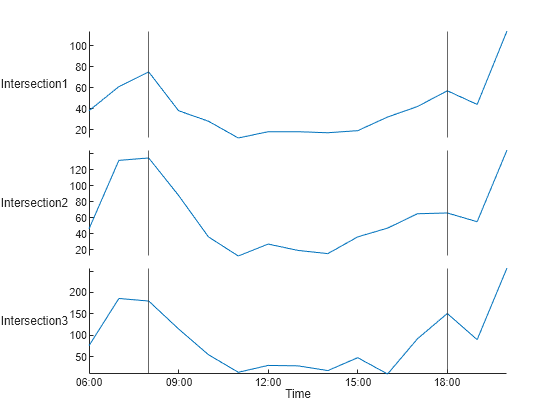
timetable 内の交通量データのチャートを作成します。最初に、新しい Figure ウィンドウを作成して、tiledlayout によって作成されたサブプロットを再利用しないようにします。次に、timetable からのデータをプロットするために、stackedplot を使用します。stackedplot 関数は、各 timetable 変数をサブプロットにプロットし、イベントが発生した時刻に黒の垂直線を表示します。
figure stackedplot(TT)
入力引数
入力時系列。timeseries オブジェクトの配列として指定します。
この関数は ts のプロパティの一部を使用して、timetable でデータを代入するかプロパティを設定します。timeseries プロパティごとに、table は出力 timetable で結果を記述します。
入力 | 出力 timetable の結果 |
|---|---|
| 対応する timetable 変数の名前を指定します。
|
| 対応する timetable 変数に代入されるデータを指定します。 |
| 対応する timetable 変数の |
| 対応する timetable 変数の |
| サンプル時間を timetable の行時間に変換します。行時間のベクトルは、入力の |
| 行時間の単位を指定します。timetable 行時間のベクトルが |
| 行時間の形式を設定します。 |
| timetable の |
| timetable の |
|
|
| データを再配向する必要があるかどうかを判別します。 |
| timetable の |
| イベントをイベント テーブルのエントリに変換し、イベント テーブルを timetable に付加します。 (R2024b 以降) 入力時系列からのイベントが重複すると、イベント テーブルの行が重複します。 |
| 警告。 |
|
|
バージョン履歴
R2021a で導入イベントをもつ timeseries オブジェクトをイベント テーブルをもつ timetable に変換できます。timeseries2timetable が timeseries オブジェクトを timetable に変換すると、関連付けられたすべての tsdata.event オブジェクトもイベント テーブルに変換されます。次に、関数はイベント テーブルを timetable に付加します。
R2024b より前では、timeseries オブジェクトを timetable に変換するときに、timeseries2timetable はイベントを無視していました。
ts2timetable 関数の名前が timeseries2timetable に変更されました。この関数の動作は同じままで、コード内の既存の ts2timetable のインスタンスは引き続き想定どおりに機能します。ts2timetable への既存の参照のサポートを削除する予定はありません。
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)