movsum
移動合計値
構文
説明
M = movsum( は局所 A,k)k 点における合計値を返します。各合計値は、長さ k のスライディング ウィンドウにわたる A の隣接要素から計算されます。k が奇数である場合、ウィンドウは現在位置にある要素を中心にして配置されます。k が偶数である場合、ウィンドウは現在の要素および直前の要素を中心にして配置されます。ウィンドウを埋めるのに十分な数の要素がない場合、ウィンドウ サイズは自動的に端点で打ち切られます。ウィンドウが打ち切られた場合、合計値はウィンドウを埋めている要素のみから取得されます。M は A と同じサイズです。
Aがベクトルである場合、movsumはベクトルAの長さに沿って演算します。Aが多次元配列の場合、movsumは、サイズが 1 に等しくないAの最初の次元に沿って演算します。Aが table または timetable の場合、movsumはAの変数に沿って演算します。 (R2025a 以降)
M = movsum(___, は、前述の任意の構文について、演算の対象とする dim)A の次元を指定します。たとえば、A が行列である場合、movsum(A,k,2) は A の列に沿って動作し、各行の k 個の要素の移動合計値を計算します。
M = movsum(___, は、nanflag)A の NaN 値を含めるか省略するかを指定します。たとえば、movsum(A,k,"omitnan") は各合計値の計算時にすべての NaN 値を無視します。既定では、movsum は NaN 値を含めます。
M = movsum(___, は、名前と値の引数を 1 つ以上使用して合計値に追加のパラメーターを指定します。たとえば、Name,Value)x が時間ベクトルである場合、movsum(A,k,"SamplePoints",x) は x を基準として A の移動合計値を計算します。
例
行ベクトルの 3 点の中心移動合計値を計算します。端点でウィンドウ内の要素数が 3 より少ない場合、使用可能な要素の合計値を取得します。
A = [4 8 6 -1 -2 -3 -1 3 4 5]; M = movsum(A,3)
M = 1×10
12 18 13 3 -6 -6 -1 6 12 9
行ベクトルの 3 点の末尾移動合計値を計算します。端点でウィンドウ内の要素数が 3 より少ない場合、movsum は使用可能な要素の合計値を取得します。
A = [4 8 6 -1 -2 -3 -1 3 4 5]; M = movsum(A,[2 0])
M = 1×10
4 12 18 13 3 -6 -6 -1 6 12
行列の各行に対して 3 点の中心移動合計値を計算します。ウィンドウは最初の行で始まり、行の終わりまで横方向にスライドし、それから 2 行目に移動して同様に繰り返します。次元引数は 2 であるため、ウィンドウは A の列を横断する方向にスライドします。
A = [4 8 6; -1 -2 -3; -1 3 4]
A = 3×3
4 8 6
-1 -2 -3
-1 3 4
M = movsum(A,3,2)
M = 3×3
12 18 14
-3 -6 -5
2 6 7
NaN 値が含まれた行ベクトルを作成します。
A = [4 8 NaN -1 -2 -3 NaN 3 4 5];
NaN 値を除外して、ベクトルの 3 点の中心移動合計値を計算します。NaN 値が含まれているウィンドウでは、movsum は NaN 以外の要素で計算します。
M = movsum(A,3,"omitnan")M = 1×10
12 12 7 -3 -6 -5 0 7 12 9
時間ベクトル t に従って、A のデータの 3 時間中心移動合計値を計算します。
A = [4 8 6 -1 -2 -3]; k = hours(3); t = datetime(16,1,1,0,0,0) + hours(0:5)
t = 1×6 datetime
01-Jan-0016 00:00:00 01-Jan-0016 01:00:00 01-Jan-0016 02:00:00 01-Jan-0016 03:00:00 01-Jan-0016 04:00:00 01-Jan-0016 05:00:00
M = movsum(A,k,"SamplePoints",t)M = 1×6
12 18 13 3 -6 -5
行ベクトルの 3 点の中心移動合計値を計算しますが、使用する要素が 3 点より少ない計算を出力から破棄します。言い換えれば、3 要素をすべて含むウィンドウから計算された合計値のみを返し、端点での計算を破棄します。
A = [4 8 6 -1 -2 -3 -1 3 4 5]; M = movsum(A,3,"Endpoints","discard")
M = 1×8
18 13 3 -6 -6 -1 6 12
魔方陣の列から table を作成します。
A = magic(3); T = array2table(A)
T=3×3 table
A1 A2 A3
__ __ __
8 1 6
3 5 7
4 9 2
movsum を使用して table の移動合計値を計算します。
M = movsum(T,3)
M=3×3 table
A1 A2 A3
__ __ __
11 6 13
15 15 15
7 14 9
指定した変数についてのみ移動合計値を計算するには、名前と値の引数 DataVariables を指定します。
M2 = movsum(T,3,DataVariables=["A2" "A3"])
M2=3×3 table
A1 A2 A3
__ __ __
8 6 13
3 15 15
4 14 9
値を置き換える代わりに table に移動合計値を追加するには、ReplaceValues を false として指定します。
M3 = movsum(T,3,ReplaceValues=false)
M3=3×6 table
A1 A2 A3 A1_movsum A2_movsum A3_movsum
__ __ __ _________ _________ _________
8 1 6 11 6 13
3 5 7 15 15 15
4 9 2 7 14 9
入力引数
入力データ。ベクトル、行列、多次元配列、table または timetable として指定します。
データ型: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | table | timetable
ウィンドウの長さ。数値または duration スカラーとして指定します。k が正の整数値スカラーである場合、中心合計値には現在位置の要素とその周囲の要素が含まれます。
たとえば、movsum(A,3) は局所 3 点における合計値の配列を計算します。
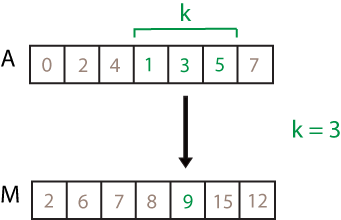
方向指定ウィンドウの長さ。2 つの要素を含む数値または duration 行ベクトルとして指定します。kb と kf が正の整数値スカラーの場合、計算は kb+kf+1 個の要素に対して行われます。この計算には、現在位置にある要素、その前にある kb 個の要素、その後にある kf 個の要素が含まれます。
たとえば、movsum(A,[2 1]) は局所 4 点における合計値の配列を計算します。
![movsum(A,[2 1]) computation. The elements in the sample window are 4, 1, 3, and 5, so the resulting local sum is 13.](movsum_windowing.png)
演算の対象の次元。正の整数のスカラーとして指定します。次元を指定しない場合、既定値はサイズが 1 でない最初の配列次元です。
次元 dim は movsum が沿って動作する次元、つまり指定されたウィンドウがスライドする方向を示します。
m 行 n 列の入力行列 A を考えます。
movsum(A,k,1)は、Aの各列についてk要素の移動合計値を計算し、m行n列の行列を返します。
movsum(A,k,2)は、Aの各行についてk要素の移動合計値を計算し、m行n列の行列を返します。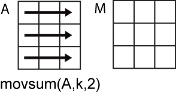
A が table または timetable の場合、dim を指定することはできません。movsum 関数は、常に table および timetable の変数に沿って演算を行います。 (R2025a 以降)
欠損値の条件。次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
"includemissing"または"includenan"— 各合計値の計算時にAのNaN値を含めます。ウィンドウ内のいずれかの要素がNaNの場合、Mの対応する要素はNaNです。"includemissing"と"includenan"の動作は同じです。"omitmissing"または"omitnan"—AのNaN値を無視し、点の数を減らして各合計値を計算します。ウィンドウ内のすべての要素がNaNの場合、Mの対応する要素は 0 です。"omitmissing"と"omitnan"の動作は同じです。
名前と値の引数
オプションの引数のペアを Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN として指定します。ここで、Name は引数名で、Value は対応する値です。名前と値の引数は他の引数の後に指定しなければなりませんが、ペアの順序は重要ではありません。
R2021a より前では、コンマを使用して名前と値をそれぞれ区切り、Name を引用符で囲みます。
例: M = movsum(A,k,"Endpoints","fill")
端点付近のウィンドウの処理方法。次のオプションのいずれかとして指定します。
| 値 | 説明 |
|---|---|
"shrink" | 入力の端点付近のウィンドウのサイズを縮小し、既存の要素のみを含めます。 |
"discard" | 既存な要素とウィンドウが完全にオーバーラップしない場合、合計値を出力しません。
|
"fill" | 存在しない要素を NaN に置き換えます。 |
| 数値または logical スカラー | 存在しない要素を指定した数値または論理値に置き換えます。 |
合計値を計算するためのサンプル点。ベクトルとして指定します。サンプル点は A のデータの位置を表します。サンプル点は等間隔でサンプリングされている必要はありません。既定では、サンプル点ベクトルは [1 2 3 ... ] です。
移動ウィンドウはサンプル点を基準として定義されます。サンプル点は並べ替えられていなければならず、また一意の要素を含んでいなければなりません。たとえば、t が入力データに対応する時間のベクトルである場合、movsum(rand(1,10),3,"SamplePoints",t) には t(i)-1.5 から t(i)+1.5 までの時間間隔を表すウィンドウがあります。
サンプル点ベクトルのデータ型が datetime または duration である場合、移動ウィンドウの長さの型は duration でなければなりません。
サンプル点の間隔が不均一で、Endpoints を指定する場合、その値は "shrink" でなければなりません。
R2025a 以降
演算の対象とする table または timetable 変数。次の表のオプションのいずれかとして指定します。
DataVariablesを指定しない場合、movsumはすべての変数について演算を行います。この動作は既定の動作です。DataVariablesを指定した場合、movsumは指定された変数のみについて演算を行います。DataVariablesで指定されていないその他の変数は、変更されずに出力に渡されます。
| インデックス方式 | 指定する値 | 例 |
|---|---|---|
変数名 |
|
|
変数インデックス |
|
|
関数ハンドル |
|
|
変数の型 |
|
|
R2025a 以降
値置換インジケーター。A が table または timetable の場合に、次の値のいずれかとして指定します。
trueまたは1— 出力 table または出力 timetable で、入力 table または入力 timetable の変数をmovsumからの出力値を含む変数に置き換えます。falseまたは0— 出力 table または出力 timetable にmovsumからの出力値を含む変数を追加します。
入力データがベクトル、行列、または多次元配列の場合、ReplaceValues はサポートされません。
拡張機能
この関数は tall 配列を制限付きでサポートしています。
名前と値の引数
SamplePoints、DataVariables、およびReplaceValuesはサポートされません。table および timetable の入力はサポートされていません。
詳細については、tall 配列を参照してください。
使用上の注意および制限:
コード生成では、この関数のスパース行列入力はサポートされません。
名前と値の引数
DataVariablesおよびReplaceValuesはサポートされません。table および timetable の入力はサポートされていません。
この関数はスレッドベースの環境を完全にサポートしています。詳細については、スレッドベースの環境での MATLAB 関数の実行を参照してください。
movsum 関数は GPU 配列入力をサポートしますが、次の使用上の注意および制限があります。
名前と値の引数
SamplePoints、DataVariables、およびReplaceValuesはサポートされません。table および timetable の入力はサポートされていません。
詳細については、GPU での MATLAB 関数の実行 (Parallel Computing Toolbox)を参照してください。
使用上の注意および制限:
名前と値の引数
DataVariablesおよびReplaceValuesはサポートされません。table および timetable の入力はサポートされていません。
詳細については、分散配列を使用した MATLAB 関数の実行 (Parallel Computing Toolbox)を参照してください。
バージョン履歴
R2016a で導入演算対象の数値データを含む table および timetable を入力として指定できます。既定では、movsum は table または timetable のすべての変数について演算を行います。ただし、どの変数を演算の対象とするかを指定できます。出力 table または出力 timetable に movsum からの出力値を新しい変数として追加することもできます。
"includemissing" オプションまたは "omitmissing" オプションを使用して、各合計値の計算時に入力配列の欠損値を含めるか省略します。これらのオプションの動作はそれぞれ、"includenan" オプションおよび "omitnan" オプションと同じです。
関数 movsum で、サンプル点がある場合に行列に対して計算する際のパフォーマンスが向上しています。
たとえば、以下のコードでは、対応するサンプル点をもつ 300 行 300 列の行列の移動合計値を計算しています。このコードは、以前のリリースよりパフォーマンスが約 3 倍高速化しました。
function timingMovsum A = randn(300); t = sort(rand(300,1)); tic for k = 1:2000 movsum(A,0.1,"SamplePoints",t); end toc end
おおよその実行時間は以下のとおりです。
R2022b: 1.04 秒
R2023a: 0.34
このコードの時間測定では、Windows® 10、Intel® Xeon® CPU E5-1650 v4 (3.60 GHz) を使用するテスト システムで、関数 timingMovsum を呼び出しました。
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)