checkPathValidity
Check validity of planned vehicle path
Description
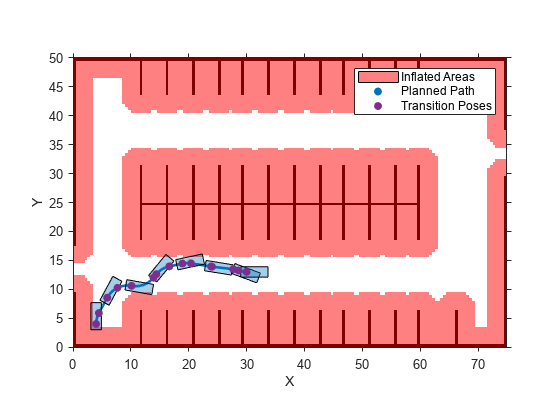
isValid = checkPathValidity(refPath,costmap)refPath, against
the vehicle costmap. Use this function to test if a path is valid within a changing
environment.
A path is valid if the following conditions are true:
The path has at least one pose.
The path is collision-free and within the limits of
costmap.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
To check if a vehicle path is valid, the checkPathValidity function
discretizes the path. Then, the function checks that the poses at the discretized points
are collision-free. The threshold for a collision-free pose depends on the resolution at
which checkPathValidity discretizes.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018a