read
Read data from GPS receiver
Syntax
Description
[
returns matrices of measurements from the GPS. This is a non blocking read which
returns N data points in matrix format, where
N is specified by lla,groundSpeed,course,dops,gpsReceiverTime,timestamp,overrun] = read(gps)SamplesPerRead
property and matrix is specified using
OutputFormat property of the gpsdev
object.
Examples
Read data from the GPS receiver connected to the host computer on a specific serial port.
Required Hardware
To run this example, you need:
UBlox Neo-6M GPS module
GPS antenna
USB to UART module
USB cable
Connecting wires
Hardware Connection
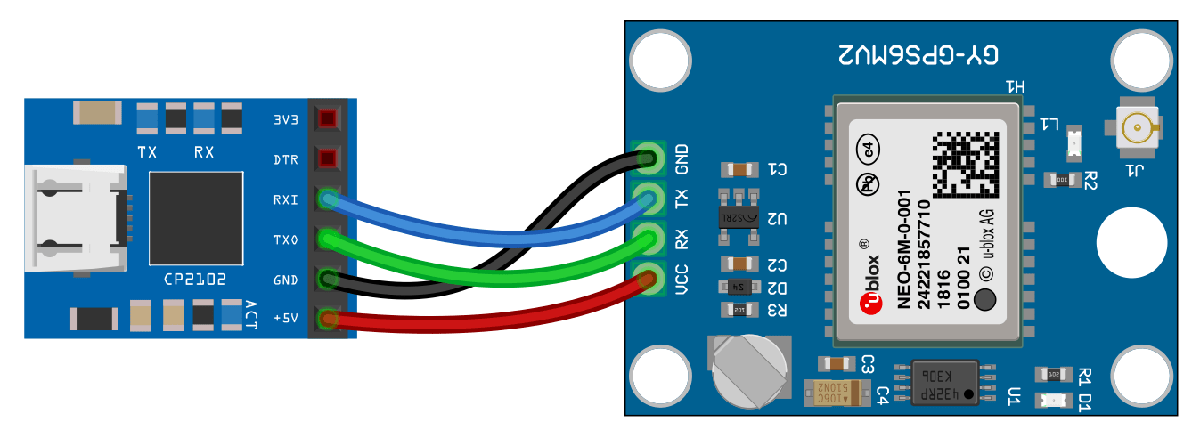
Connect the pins on the UBlox Neo-6M GPS module to the pins on your USB to UART module. The connections are:
VCC - +5V
RX - TXO
TX - RXI
GND - GND
Connect the GPS antenna to the GPS module. Connect the USB to UART module to the host computer with a USB cable. GPS Fix can be easily acquired in locations that have a clear view of the sky. Wait for the GPS module to acquire satellite signals (Fix). This can be verified by checking the Fix LED (D1) of your GPS module.
Create GPS Object
Create a gpsdev object for the GPS receiver connected to a specific port. Specify the output format of the data as a timetable.
gps = gpsdev('COM4','OutputFormat',"timetable")
gps =
gpsdev with properties:
SerialPort: COM4
BaudRate: 9600 (bits/s)
SamplesPerRead: 1
ReadMode: "latest"
SamplesRead: 0
Show all properties all functions
Read the GPS Data
Read the GPS data and return them as a timetable.
[tt,overruns] = read(gps)
tt=1×5 timetable
Time LLA GroundSpeed Course DOPs GPSReceiverTime
________________________ _________________________ ___________ ______ ____________________ ________________________
22-Mar-2021 15:31:15.190 17.47 78.343 449.6 0.25619 NaN 9.31 1.48 9.19 22-Mar-2021 10:01:14.000
overruns = 0
Display number of samples read and the samples available in the host buffer.
gps.SamplesRead
ans = 1
gps.SamplesAvailable
ans = 0
Release the GPS object to configure the non tunable properties. The release function also clears the buffer and resets the SamplesRead and SamplesAvailable properties.
release(gps)
Specify the number of samples per read to 2. Read the GPS data.
gps.SamplesPerRead = 2; read(gps)
ans=2×5 timetable
Time LLA GroundSpeed Course DOPs GPSReceiverTime
________________________ _________________________ ___________ ______ ____________________ ________________________
22-Mar-2021 15:31:17.178 17.47 78.343 450 0.063791 NaN 9.32 1.48 9.2 22-Mar-2021 10:01:16.000
22-Mar-2021 15:31:17.178 17.47 78.343 450 0.063791 NaN 9.32 1.48 9.2 22-Mar-2021 10:01:16.000
Display number of samples read and the samples available in the host buffer.
gps.SamplesRead
ans = 1
gps.SamplesAvailable
ans = 0
Clean Up
When the connection is no longer needed, clear the associated object.
delete(gps);
clear gps;Read data from the GPS receiver connected to the host computer using serialport object.
Required Hardware
To run this example, you need:
UBlox Neo-6M GPS module
GPS antenna
USB to UART module
USB cable
Connecting wires
Hardware Connection

Connect the pins on the UBlox Neo-6M GPS module to the pins on your USB to UART module. The connections are:
VCC - +5V
RX - TXO
TX - RXI
GND - GND
Connect the GPS antenna to the GPS module. Connect the USB to UART module to the host computer with a USB cable. GPS Fix can be easily acquired in locations that have a clear view of the sky. Wait for the GPS module to acquire satellite signals (Fix). This can be verified by checking the Fix LED (D1) of your GPS module.
Create GPS Object
Connect to the GPS receiver using serialport object. Specify the port name and the baud rate. Specify the output format of the data as matrix.
s = serialport('COM4',9600); gps = gpsdev(s,'OutputFormat',"matrix")
gps =
gpsdev with properties:
SerialPort: COM4
BaudRate: 9600 (bits/s)
SamplesPerRead: 1
ReadMode: "latest"
SamplesRead: 0
Show all properties all functions
Read the GPS Data
Read the GPS data and return them as matrices.
[lla,speed,course,dops,gpsReceiverTime,timestamp,overruns] = read(gps)
lla = 1×3
NaN NaN NaN
speed = NaN
course = NaN
dops = 1×3
NaN NaN NaN
gpsReceiverTime = datetime
NaT
timestamp = datetime
22-Mar-2021 03:41:00.274
overruns = 1
Display number of samples read and the samples available in the host buffer.
gps.SamplesRead
ans = 1
gps.SamplesAvailable
ans = 0
Flush all GPS data accumulated in the buffers and reset the SamplesRead and SamplesAvailable properties.
flush(gps)
Display number of samples read and the samples available in the host buffer.
gps.SamplesRead
ans = 0
gps.SamplesAvailable
ans = 0
Clean Up
When the connection is no longer needed, clear the associated object.
delete(gps); clear gps; clear s;
Input Arguments
The GPS sensor, specified as a gpsdev object.
Output Arguments
GPS data, returned as a timetable. The
timetable returned has the following fields:
LLA (Latitude, Longitude, Altitude)
Ground Speed
Course over ground
Dilution of Precisions(DOPs), VDOP,HDOP,PDOP
GPS Receiver Time
Time — System time when the data is read, in
datetimeordurationformat
Data Types: timetable
Position of the GPS receiver in the geodetic latitude, longitude, and altitude (LLA), returned as a real finite N-by-3 array. Latitude and longitude are in degrees with North and East being positive. Altitude is in meters.
Data Types: double
Speed over ground, returned as a real finite N-by-1 vector.
Data Types: double
Course over ground relative to true north, returned as a real finite N-by-1 vector of values between 0 and 2pi radians.
Data Types: double
Dilution of precisions, returned as a real finite
N-by-3 matrix of the form
[PDOP,HDOP,VDOP].
Data Types: double
UTC time, returned as a N-by-1 vector.
Data Types: datetime
Time at which GPS data is read, returned as a real finite
N-by-1 vector. This is the system time. If the
TimeFormat is datetime, the
timestamp will be datetime. If the
TimeFormat is a duration, the
timestamp will be duration
datetime— Displays the date and time at which the data is read.duration— Displays the time elapsed in seconds after the first call of thereadfunction or the last execution of thereleasefunction.
Note
If the SamplesPerRead is greater than 1, an
extrapolation is done on the time value. Hence it might not be
precise.
Data Types: datetime | duration
The number of samples lost between consecutive calls to
read. The overrun is zero when
ReadMode is set to
oldest.
Data Types: double
More About
The gpsdev
object expects GPRMC, GPGGA, and GPGSA sentences as outputs from the GPS receiver to
get the required values. The read function errors out if these
sentences are not available.
The read function outputs NaN and
NaT in the following situations:
If the GPS module does not receive valid data because there is no satellite lock or when GPS does not give a particular value.
If there is a checksum failure, corresponding data points will be
NaNfor numeric outputs (lla,speed,course,dops) andNaTforgpsRecieverTime.llais taken from GPGGA sentence,speed,course, andgpsRecieverTimeis taken GPRMC sentence anddopsare taken from GPGSA sentence.
Because read function is non blocking, the following is
expected:
If no new data is available, the output of
readis the previous data. For example, if the delay between subsequent reads is less than theUpdateRateof the GPS receiver.
Because GPS data is validated in the first read operation, it
might take more time compared to the subsequent read
operations.
Version History
Introduced in R2020b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)