identityLayer
説明
恒等層は、出力が入力と同一である層です。恒等層を使用して "スキップ接続" を作成できます。これにより、ニューラル ネットワークのメイン ブランチ内にある 1 つ以上の層で入力をスキップさせることができます。スキップ接続の詳細については、More Aboutを参照してください。
作成
説明
プロパティ
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
層への入力の数。1 として格納されます。この層は単一の入力のみを受け入れます。
データ型: double
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
入力名。{'in'} として格納されます。この層は単一の入力のみを受け入れます。
データ型: cell
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
層からの出力の数。1 として格納されます。この層には単一の出力のみがあります。
データ型: double
この プロパティ は読み取り専用です。
出力名。{'out'} として格納されます。この層には単一の出力のみがあります。
データ型: cell
例
層配列に恒等層を含めます。
layers = [ ...
imageInputLayer([28 28 1])
convolution2dLayer(5,20)
identityLayer
maxPooling2dLayer(2,Stride=2)
fullyConnectedLayer(10)
softmaxLayer]layers =
6×1 Layer array with layers:
1 '' Image Input 28×28×1 images with 'zerocenter' normalization
2 '' 2-D Convolution 20 5×5 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [0 0 0 0]
3 '' Identity Identity
4 '' 2-D Max Pooling 2×2 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0]
5 '' Fully Connected 10 fully connected layer
6 '' Softmax softmax
layers の 3 番目の層は、恒等層のプロパティを含む IdentityLayer オブジェクトです。
恒等層のプロパティを表示します。
layers(3)
ans =
IdentityLayer with properties:
Name: ''
残差ブロックと恒等層を含む深層学習ニューラル ネットワークを作成します。残差ニューラル ネットワークの詳細については、More Aboutを参照してください。
ブロック アーキテクチャの定義
残差ブロックを表すネットワーク層を返す関数を記述します。
function resblock = residualBlockLayer(name) reslayers = dlnetwork; layers = [ identityLayer(Name="split") convolution2dLayer(3,32,Padding="same") batchNormalizationLayer reluLayer convolution2dLayer(3,32,Padding="same") batchNormalizationLayer additionLayer(2,Name="add") reluLayer]; reslayers = addLayers(reslayers,layers); reslayers = connectLayers(reslayers,"split","add/in2"); resblock = networkLayer(reslayers,Name=name); end
residualBlockLayer 関数は、層の名前を受け入れ、残差ブロックを表すnetworkLayerオブジェクトを返します。この関数は、connectLayers関数と共に identityLayer を使用して、残差ブロックの入力と最終層の 2 番目の入力との間にスキップ接続を作成します。
残差ネットワークの作成と解析
residualBlockLayer を使用して残差ネットワークを作成し、残差ブロックを生成します。
layers = [
imageInputLayer([224 224 3])
convolution2dLayer(7,32,Stride=2,Padding="same")
batchNormalizationLayer
reluLayer
maxPooling2dLayer(3,Stride=2)
residualBlockLayer("resBlock1")
residualBlockLayer("resBlock2")
globalAveragePooling2dLayer
fullyConnectedLayer(5)
softmaxLayer];
resnet = dlnetwork(layers)resnet =
dlnetwork with properties:
Layers: [10×1 nnet.cnn.layer.Layer]
Connections: [9×2 table]
Learnables: [22×3 table]
State: [10×3 table]
InputNames: {'imageinput'}
OutputNames: {'softmax'}
Initialized: 1
View summary with summary.
resnet は、残差ネットワークを表す dlnetwork オブジェクトです。resnet には、2 つの残差ブロックに対応する 2 つの networkLayer オブジェクトが含まれています。
ネットワークの検証
expandLayers関数およびanalyzeNetwork関数を使用して、ディープ ネットワーク デザイナー アプリで残差ブロック層を検証します。ディープ ネットワーク デザイナーの左端のペインには、ネットワークの層とその接続が表示されます。
xresnet = expandLayers(resnet); analyzeNetwork(xresnet)
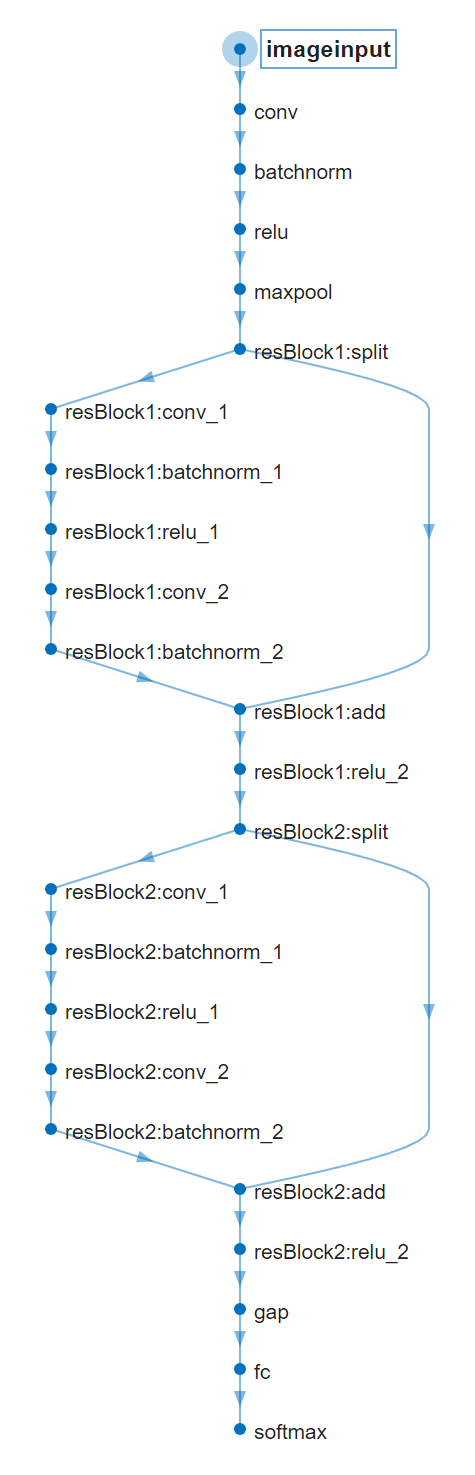
最初の残差ブロックと 2 番目の残差ブロックの層の名前は、それぞれ resBlock1: と resBlock2: で始まります。各ブロック内の最初の層は、残差ブロックの外部からの入力を受け入れる恒等層です。各恒等層には、加算層へのスキップ接続があります。恒等層の名前は resBlock1:split と resBlock2:split、加算層の名前は resBlock1:add と resBlock2:add です。
拡張機能
C/C++ コード生成
MATLAB® Coder™ を使用して C および C++ コードを生成します。
GPU コード生成
GPU Coder™ を使用して NVIDIA® GPU のための CUDA® コードを生成します。
バージョン履歴
R2024b で導入
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)