MATLAB での 256 QAM 信号の平均パワーの計算
16 サンプルのスライディング ウィンドウを使用して、256 QAM 信号の平均パワーを計算します。
初期化
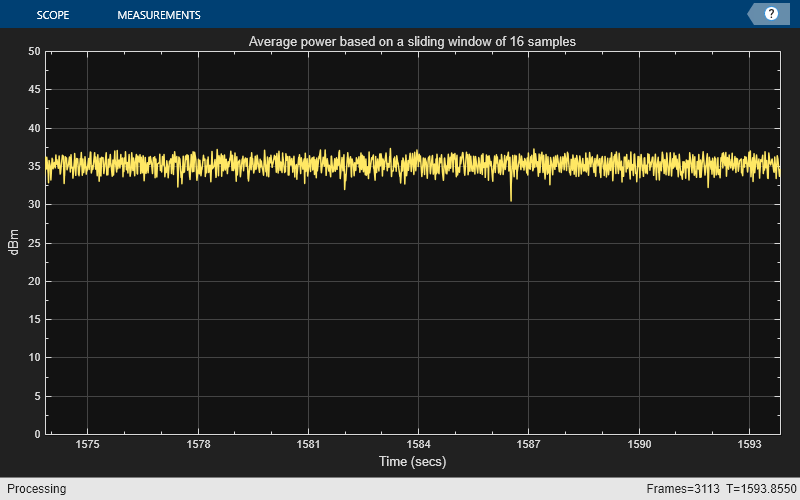
スライディング ウィンドウの長さが 16 サンプル、参照負荷が 50 オームのpowermeterオブジェクトを作成します。このオブジェクトを使用して、256 QAM 信号の平均パワーを dBm 単位で測定します。
timescopeオブジェクトを使用して、信号の平均パワーを可視化します。
FrameLength = 512; Fs = 1000; pm = powermeter(16, 'Measurement', 'Average power', ... 'ReferenceLoad', 50, ... 'PowerUnits', 'dBm'); scope = timescope('SampleRate',Fs,... 'TimeSpanSource','property',... 'TimeSpan',20,... 'YLabel','dBm',... 'YLimits',[0 50]); title = 'Average power based on a sliding window of 16 samples'; scope.Title = title;
平均パワーの計算
関数randiを使用して、[0 255] から等間隔で抽出された疑似乱数整数値のシーケンスを生成します。関数qammodを使用して、この信号に直交振幅変調 (QAM) を適用します。powermeter オブジェクトを使用して、この信号の平均パワーを計算します。timescope オブジェクトを使用して、計算した平均値を表示します。
tic; while (toc < 5) x = randi([0 255], FrameLength, 1); y = qammod(x, 256); averagePower = pm(y); scope(averagePower); end
参考
qammod | powermeter | dsp.TimeScope | randi