earthSurfacePermittivity
地表材料の誘電率と伝導率
構文
説明
earthSurfacePermittivity 関数は、地表材料の実数の比誘電率と伝導率、ならびに複素比誘電率を計算します。計算は、国際電気通信連合勧告 (ITU-R) P.527-5 ~ ITU-R P.527-6 [1]に記載されているメソッドと方程式に基づいています。関数 earthSurfacePermittivity には、指定された表面材料に関連する特性を考慮してさまざまな構文が用意されています。
水
[ は、指定された周波数と温度における純水の実数の比誘電率と伝導率、ならびに複素比誘電率を計算します。epsilon,sigma,complexepsilon] = earthSurfacePermittivity("pure-water",fc,temp)
氷
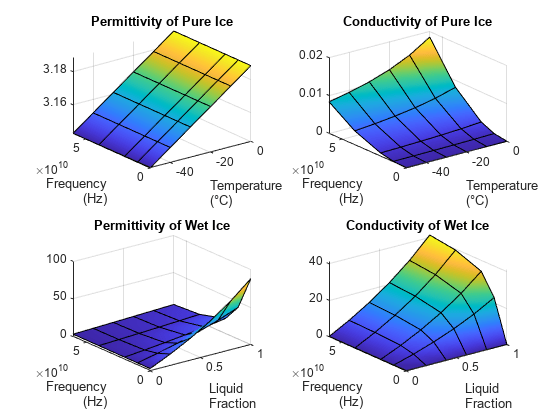
[ は、指定された周波数と温度における不純物がない氷の実数の比誘電率と伝導率、ならびに複素比誘電率を計算します。epsilon,sigma,complexepsilon] = earthSurfacePermittivity("pure-ice",fc,temp)
[ は、指定された周波数と液状水分体積分率における濡れた氷の実数の比誘電率と伝導率、ならびに複素比誘電率を計算します。epsilon,sigma,complexepsilon] = earthSurfacePermittivity("wet-ice",fc,liqfrac)
雪
土壌
[ は、指定された周波数、温度、砂体積率、粘土体積率、比重、および体積含水率における土壌の実数の比誘電率と伝導率、ならびに複素比誘電率を計算します。この構文は、近似式を使用して土壌のかさ密度を計算します。 epsilon,sigma,complexepsilon] = earthSurfacePermittivity("soil",fc,temp,sandpercent,claypercent,sg,vwc)
[ は、前の構文の入力引数に加えて土壌のかさ密度を指定します。epsilon,sigma,complexepsilon] = earthSurfacePermittivity("soil",fc,temp,sandpercent,claypercent,sg,vwc,bulkdensity)
例
入力引数
出力引数
詳細
参照
[1] International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector. Electrical Characteristics of the Surface of the Earth. Recommendation P.527. ITU-R, approved September 27, 2021. https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-P.527/en.
[2] Mohr, Peter J., Eite Tiesinga, David B. Newell, and Barry N. Taylor. “Codata Internationally Recommended 2022 Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants.” NIST, May 8, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/publications/codata-internationally-recommended-2022-values-fundamental-physical-constants.