HE MU Transmission
Transmission Mode Options
The options for high-efficiency multi-user (HE MU) transmissions are:
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA)
Full-band multi-user multiple-input/multiple-output (MU-MIMO)
Mixed OFDMA and MU-MIMO
To choose a transmission mode, you must enable or disable SIGB compression by specifying the state of the SIGB compression bit in the HE-SIG-A field.
For a 20 MHz transmission, specify the SIGB compression bit directly by setting the
SIGBCompressionproperty of thewlanHEMUConfigobject.To enable SIGB compression, set the
SIGBCompressionproperty to1(true).To disable SIGB compression, set the
SIGBCompressionproperty to0(false).
For a 40, 80, or 160 MHz transmission, enable or disable SIGB compression by setting the
AllocationIndexproperty of thewlanHEMUConfigobject.
When SIGB compression is enabled, the transmission is full-bandwidth MU-MIMO. The HE-SIG-B field contains no common field, and the resource unit (RU) allocation in the user fields adheres to a standard-specified pattern. Because there is no common field in this case, no allocation index is transmitted. The number of users is determined by decoding the HE-SIG-A field.
When SIGB compression is disabled:
The transmission is either OFDMA or mixed OFDMA and MU-MIMO, depending on the
AllocationIndexproperty of the HE MU configuration object.The HE-SIG-B common field includes RU allocation subfields to specify the RU assignment and the number of users per RU for each 20 MHz bandwidth segment.
The 802.11ax Waveform Generation example introduces the concepts associated with HE transmission modes, RU allocation, and parameterization.
The Recovery Procedure for an 802.11ax Packet example demonstrates the required steps to detect and decode an HE MU transmission.
Allocation Index
When creating a wlanHEMUConfig
object, you must specify the value of the AllocationIndex property.
Once the object is created, the AllocationIndex property is
read-only.
The AllocationIndex property defines the RU allocation index or a
set of RU allocation indices.
Specify a single allocation index using one integer in either of these forms.
An integer in the interval [0, 223]
An 8-bit binary sequence specified as a string or character vector
Specify multiple allocation indices using two, four, or eight integer values in any of these forms.
A vector of integers in the interval [0, 223]
An 8-bit binary sequence specified as a string array
An 8-bit binary sequence specified as a cell array of character vectors
You can signal punctured 20 MHz or 40 MHz subchannels in an 80 MHz or 160 MHz transmission. To signal a punctured 20 MHz subchannel, set the corresponding element to
113. To signal a punctured 40 MHz subchannel, set the two corresponding adjacent elements to114. To signal an empty HE-SIG-B user field in an HE-SIG-B content channel, set the corresponding element to114or115.
An RU is a group of 26, 52, 106, 242, 484, 996, or 2×996 subcarriers defining an allocation unit in time and frequency.

The values specified in the AllocationIndex property correspond
to the 8-bit indices for each 20 MHz subchannel in the first column of Table 27-26 in
[1]. The
allocation indices define the number of RUs, RU sizes, and number of users assigned to
each RU. When SIGB compression is enabled, the number of users is determined by decoding
the HE-SIG-A field. When SIGB compression is disabled, the number of users is determined
by decoding the HE-SIG-B common field.
When SIGB compression is enabled, the HE-SIG-B field contains only the user field.
When SIGB compression is disabled, the HE-SIG-B field includes both the common and user fields. The common field carries the RU Allocation subfields in one or two content channels. Depending on the PPDU bandwidth, the common field can contain multiple RU Allocation subfields. For a discussion of the frequency-domain mapping of channel contents into the common field, see section 27.3.11.8.5 of [1].
This figure1 shows the structure of the HE-SIG-B field when SIGB compression is disabled.
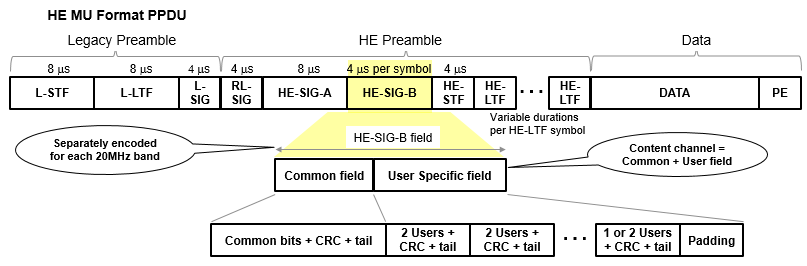
The format of the common field is defined in Table 27-24 of [1]. The RU Allocation subfield in the common field of HE-SIG-B consists of eight bits that indicate this information for each 20 MHz PPDU bandwidth.
RU assignment in the frequency domain, which determines the size of the RUs and their placement in the frequency domain.
Number of user fields in a 20 MHz band within the HE-SIG-B content channel, which determines the number of users multiplexed in the RUs. For RUs of size greater than or equal to 106 tones, which support MU-MIMO, the RU Allocation subfield indicates the number of users multiplexed using MU-MIMO. The HE-SIG-B field consists of N RU Allocation subfields, where:
N = 1 for 20 MHz and 40 MHz HE MU PPDUs
N = 2 for 80 MHz HE MU PPDUs
N = 4 for 160 MHz and 80+80 MHz HE MU PPDUs
This table2 lists the allocation indices and corresponding RU assignments for 20 MHz subchannels and RUs with at most 242 tones. The table shows the number of tones per RU and the number of users assigned for each allocation index.
| Allocation Index | 20 MHz Subchannel Resource Unit (RU) Assignment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26a |
| 1 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | |
| 2 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | |
| 3 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 52 | ||
| 4 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | |
| 5 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | ||
| 6 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | ||
| 7 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 52 | |||
| 8 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | |
| 9 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | ||
| 10 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | ||
| 11 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | 52 | |||
| 12 | 52 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | ||
| 13 | 52 | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | |||
| 14 | 52 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | |||
| 15 | 52 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 52 | ||||
| 16-23 (15 + NumUsers) | 52 | 52 | -b | 106 (1-8 users)c | |||||
| 24-31 (23 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | - | 52 | 52 | |||||
| 32-39 (31 + Num Users) | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | |||
| 40-47 (39 + NumUsers) | 26 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||
| 48-55 (47 + NumUsers) | 52 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||
| 56-63 (55 + NumUsers) | 52 | 52 | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | |||||
| 64-71 (63 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | |||
| 72-79 (71 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 | ||||
| 80-87 (79 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | 26 | 52 | 26 | 26 | ||||
| 88-95 (87 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | 26 | 52 | 52 | |||||
| 96-103 (95 + NumUsers) | 106 | - | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 104-112 (103 + NumUsers) | 106 (1-8 users) | - | 106 | ||||||
| 112 | 52 | 52 | - | 52 | 52 | ||||
| 113 | Empty 242-tone RU - No user assignedd | ||||||||
| 116-127 | Reserved | ||||||||
| 128-135 (127 + NumUsers) | 106 | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 136-143 (135 + NumUsers) | 106 (2 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users)e | ||||||
| 144-151 (143 + NumUsers) | 106 (3 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 152-159 (151 + NumUsers) | 106 (4 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 160-167 (159 + NumUsers) | 106 (5 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 168-175 (167 + NumUsers) | 106 (6 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 176-183 (175 + NumUsers) | 106 (7 users) | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 184-191 (183 + NumUsers) | 106 (8 users)f | 26 | 106 (1-8 users) | ||||||
| 192-199 (191 + NumUsers) | 242 (1-8 users) | ||||||||
a 26-tone RU assigned to one user as part of a 20-MHz subchannel assignment of nine 26-tone RUs b No users assigned to this RU; no data field transmitted on these subcarriers c The number of users assigned to this 106-tone RU depends on the allocation index d If selected, this 20-MHz subchannel is unused; the subchannel is punctured e The number of users assigned to the upper 106-tone RU depends on the allocation index, but two users are always assigned to the lower 106-tone RU f From 2 to 8 users assigned to the lower 106-tone RU depending on the allocation index | |||||||||
This table lists the allocation indices and corresponding RU assignments for subchannels greater than 20 MHz and RUs of more than 242 tones.
| Allocation Index | RU Allocation & Number of Users on the Corresponding HE-SIG-B Content Channel for RU Size > 242 |
|---|---|
| 114 | 484-tone RU with no users signaled on the corresponding HE-SIG-B content channela |
| 115 | 996-tone RU with no users signaled on the corresponding HE-SIG-B content channel |
| 200-207 (199 + NumUsers) | Full band 40 MHz (1-8 users), or 484-tone RU with 1-8 users signaled in the corresponding HE-SIG-B content channelb |
| 208-215 (207 + NumUsers) | Full band 80 MHz (1-8 users), or 996-tone RU with 1-8 users signaled in the corresponding HE-SIG-B content channel |
| 216-223 (215 + NumUsers) | Full band 160 MHz (1-8 users) |
| 224-225 | Reserved |
a Must be used with other allocation indices. Signifies a 484-tone RU with zero users signaled on the corresponding HE-SIG-B content channel b A single allocation index between 200-207 configures a full-band 40 MHz 484-tone RU with 1-8 users | |
The format of the user field for non-MU-MIMO and MU-MIMO allocations are defined in Tables 27-28 and 27-29, of [1], respectively.
This table shows allocation index options required to specify transmission type for all channel bandwidths.
| Transmission Type | 20 MHz Transmission | 40 MHz Transmission | 80 MHz Transmission | 160 MHz Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Full-bandwidth MU-MIMO |
Specify |
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify
|
The wlanHEMUConfig object sets
the SIGBCompression property to 1
(true), and splits users between the two content channels. | ||||
| Full-bandwidth MU-MIMO |
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify |
Specify |
The wlanHEMUConfig object sets
the SIGBCompression property to 0
(false). All users are in content channel 1. | ||||
| Full-bandwidth MU-MIMO |
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify |
Specify |
The wlanHEMUConfig object sets
the SIGBCompression property to 0
(false). All users are in content channel 2. | ||||
| Full bandwidth MU-MIMO |
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify |
The wlanHEMUConfig object sets
the SIGBCompression property to 0
(false). Users are in their respective content channels. For example, in the 80
MHz transmission case, the users represented by allocation indices
a and c are in content channel 1, and
the users represented by allocation indices b and
d are in content channel 2. | ||||
| Mixed OFDMA and MU-MIMO |
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify
|
Specify |
| 20 MHz transmissions have only one content channel. | The wlanHEMUConfig object sets
the SIGBCompression property to 0
(false). Users are in their respective content channels. For example, in the 80
MHz transmission case, the users represented by allocation indices
a and c are in content channel 1, and
the users represented by allocation indices b and
d are in content channel 2. | |||
References
[1] IEEE® Std 802.11ax™-2021 (Amendment to IEEE Std 802.11™-2020). “Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. Amendment 1: Enhancements for High Efficiency WLAN.” IEEE Standard for Information Technology — Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems. Local and Metropolitan Area Networks — Specific Requirements.
See Also
Topics
1 IEEE Std 802.11ax-2021 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2021. All rights reserved.
2 © IEEE 2021. All rights reserved.