Current-Controlled Voltage Source
Linear current-controlled voltage source
Library
Electrical Sources
Description
The Current-Controlled Voltage Source block models a linear current-controlled voltage source, described with the following equation:
where
V | Voltage |
K | Transresistance |
I1 | Current flowing from the + to the – control port |
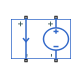
To use the block, connect the + and – ports on the left side of the block (the control ports) to the control current source. The arrow indicates the positive direction of the current flow. The two ports on the right side of the block (the output ports) generate the output voltage. Polarity is indicated by the + and – signs.
Variables
To set the priority and initial target values for the block variables prior to simulation, use the Initial Targets section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Set Priority and Initial Target for Block Variables.
Nominal values provide a way to specify the expected magnitude of a variable in a model. Using system scaling based on nominal values increases the simulation robustness. Nominal values can come from different sources, one of which is the Nominal Values section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Modify Nominal Values for a Block Variable.
Parameters
- Transresistance K
Ratio of the voltage between the two output terminals to the current passing between the two control terminals. The default value is
1Ω.
Ports
The block has four electrical conserving ports. Connections + and – on the left side of the block are the control ports. The arrow indicates the positive direction of the current flow. The other two ports are the electrical terminals that provide the output voltage. Polarity is indicated by the + and – signs.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2007a