modelDiscrimination
Compute AUROC and ROC data
Syntax
Description
DiscMeasure = modelDiscrimination(pdModel,data)modelDiscrimination supports segmentation and comparison
against a reference model.
[
specifies options using one or more name-value pair arguments in addition to the
input arguments in the previous syntax.DiscMeasure,DiscData] = modelDiscrimination(___,Name,Value)
Examples
This example shows how to use fitLifetimePDModel to fit data with a Logistic model and then generate the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and ROC curve.
Load Data
Load the credit portfolio data.
load RetailCreditPanelData.mat
disp(head(data)) ID ScoreGroup YOB Default Year
__ __________ ___ _______ ____
1 Low Risk 1 0 1997
1 Low Risk 2 0 1998
1 Low Risk 3 0 1999
1 Low Risk 4 0 2000
1 Low Risk 5 0 2001
1 Low Risk 6 0 2002
1 Low Risk 7 0 2003
1 Low Risk 8 0 2004
disp(head(dataMacro))
Year GDP Market
____ _____ ______
1997 2.72 7.61
1998 3.57 26.24
1999 2.86 18.1
2000 2.43 3.19
2001 1.26 -10.51
2002 -0.59 -22.95
2003 0.63 2.78
2004 1.85 9.48
Join the two data components into a single data set.
data = join(data,dataMacro); disp(head(data))
ID ScoreGroup YOB Default Year GDP Market
__ __________ ___ _______ ____ _____ ______
1 Low Risk 1 0 1997 2.72 7.61
1 Low Risk 2 0 1998 3.57 26.24
1 Low Risk 3 0 1999 2.86 18.1
1 Low Risk 4 0 2000 2.43 3.19
1 Low Risk 5 0 2001 1.26 -10.51
1 Low Risk 6 0 2002 -0.59 -22.95
1 Low Risk 7 0 2003 0.63 2.78
1 Low Risk 8 0 2004 1.85 9.48
Partition Data
Separate the data into training and test partitions.
nIDs = max(data.ID); uniqueIDs = unique(data.ID); rng('default'); % for reproducibility c = cvpartition(nIDs,'HoldOut',0.4); TrainIDInd = training(c); TestIDInd = test(c); TrainDataInd = ismember(data.ID,uniqueIDs(TrainIDInd)); TestDataInd = ismember(data.ID,uniqueIDs(TestIDInd));
Create a Logistic Lifetime PD Model
Use fitLifetimePDModel to create a Logistic model.
pdModel = fitLifetimePDModel(data(TrainDataInd,:),"Logistic",... 'AgeVar','YOB',... 'IDVar','ID',... 'LoanVars','ScoreGroup',... 'MacroVars',{'GDP','Market'},... 'ResponseVar','Default'); disp(pdModel)
Logistic with properties:
ModelID: "Logistic"
Description: ""
UnderlyingModel: [1×1 classreg.regr.CompactGeneralizedLinearModel]
IDVar: "ID"
AgeVar: "YOB"
LoanVars: "ScoreGroup"
MacroVars: ["GDP" "Market"]
ResponseVar: "Default"
WeightsVar: ""
TimeInterval: 1
Display the underlying model.
pdModel.UnderlyingModel
ans =
Compact generalized linear regression model:
logit(Default) ~ 1 + ScoreGroup + YOB + GDP + Market
Distribution = Binomial
Estimated Coefficients:
Estimate SE tStat pValue
__________ _________ _______ ___________
(Intercept) -2.7422 0.10136 -27.054 3.408e-161
ScoreGroup_Medium Risk -0.68968 0.037286 -18.497 2.1894e-76
ScoreGroup_Low Risk -1.2587 0.045451 -27.693 8.4736e-169
YOB -0.30894 0.013587 -22.738 1.8738e-114
GDP -0.11111 0.039673 -2.8006 0.0051008
Market -0.0083659 0.0028358 -2.9502 0.0031761
388097 observations, 388091 error degrees of freedom
Dispersion: 1
Chi^2-statistic vs. constant model: 1.85e+03, p-value = 0
pdModel.UnderlyingModel.Coefficients
ans=6×4 table
Estimate SE tStat pValue
__________ _________ _______ ___________
(Intercept) -2.7422 0.10136 -27.054 3.408e-161
ScoreGroup_Medium Risk -0.68968 0.037286 -18.497 2.1894e-76
ScoreGroup_Low Risk -1.2587 0.045451 -27.693 8.4736e-169
YOB -0.30894 0.013587 -22.738 1.8738e-114
GDP -0.11111 0.039673 -2.8006 0.0051008
Market -0.0083659 0.0028358 -2.9502 0.0031761
Model Discrimination to Generate AUROC and ROC
Model "discrimination" measures how effectively a model ranks customers by risk. You can use the AUROC and ROC outputs to determine whether customers with higher predicted PDs actually have higher risk in the observed data.
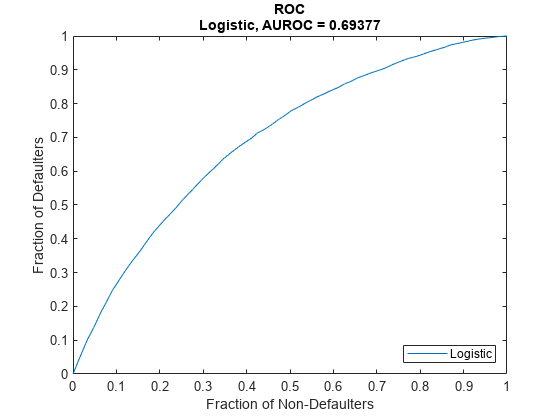
DataSetChoice ="Training"; if DataSetChoice=="Training" Ind = TrainDataInd; else Ind = TestDataInd; end DiscMeasure = modelDiscrimination(pdModel,data(TrainDataInd,:),'ShowDetails',true,'DataID',DataSetChoice); disp(DiscMeasure)
AUROC Segment SegmentCount WeightedCount
_______ __________ ____________ _____________
Logistic, Training 0.69377 "all_data" 3.881e+05 3.881e+05
Visualize the ROC for the Logistic model using modelDiscriminationPlot.
modelDiscriminationPlot(pdModel,data(TrainDataInd,:));
Data can be segmented to get the AUROC per segment and the corresponding ROC data.
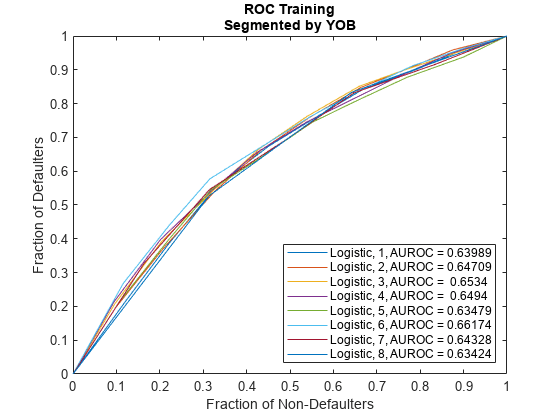
SegmentVar ="YOB"; DiscMeasure = modelDiscrimination(pdModel,data(Ind,:),'ShowDetails',true,'SegmentBy',SegmentVar,'DataID',DataSetChoice); disp(DiscMeasure)
AUROC Segment SegmentCount WeightedCount
_______ _______ ____________ _____________
Logistic, YOB=1, Training 0.63989 1 58092 58092
Logistic, YOB=2, Training 0.64709 2 56723 56723
Logistic, YOB=3, Training 0.6534 3 55524 55524
Logistic, YOB=4, Training 0.6494 4 54650 54650
Logistic, YOB=5, Training 0.63479 5 53770 53770
Logistic, YOB=6, Training 0.66174 6 53186 53186
Logistic, YOB=7, Training 0.64328 7 36959 36959
Logistic, YOB=8, Training 0.63424 8 19193 19193
Visualize the ROC segmented by YOB, ScoreGroup, or Year using modelDiscriminationPlot.
modelDiscriminationPlot(pdModel,data(Ind,:),'SegmentBy',SegmentVar,'DataID',DataSetChoice);
Input Arguments
Probability of default model, specified as a Logistic, Probit, or Cox object previously
created using fitLifetimePDModel. Alternatively, you can create a custom
probability of default model using customLifetimePDModel.
Note
The 'ModelID' property of the
pdModel object is used as the identifier or
tag for pdModel.
Data Types: object
Data, specified as a
NumRows-by-NumCols table with
projected predictor values to make lifetime predictions. The predictor names
and data types must be consistent with the underlying model.
Data Types: table
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: [PerfMeasure,PerfData] =
modelDiscrimination(pdModel,data(Ind,:),'DataID',"DataSetChoice")
Data set identifier, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting
of 'DataID' and a character vector or string.
Data Types: char | string
Name of a column in the data input, not necessarily a model variable,
to be used to segment the data set, specified as the comma-separated
pair consisting of 'SegmentBy' and a character vector
or string.
One AUROC value is reported for each segment and the corresponding ROC
data for each segment is returned in the PerfData
optional output.
Data Types: char | string
Since R2022a
Indicates if the output includes columns showing segment value,
segment count, and weighted count, specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'ShowDetails' and a scalar
logical.
Data Types: logical
Identifier for the reference model, specified as the comma-separated
pair consisting of 'ReferenceID' and a character
vector or string. 'ReferenceID' is used in the
modelDiscrimination output for reporting
purposes.
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
AUROC information for each model and each segment, returned as a table.
DiscMeasure has a single column named
'AUROC' and the number of rows depends on the number
of segments and whether you use a ReferenceID for a
reference model and ReferencePD for reference data. The
row names of DiscMeasure report the model IDs, segment,
and data ID. If the optional ShowDetails name-value
argument is true, the DiscMeasure
output displays Segment, SegmentCount,
and WeightedCount columns.
Note
If you do not specify SegmentBy and use
ShowDetails to request the segment details,
the two columns are added and show the Segment
column as "all_data" and the sample size (minus
missing values) for the SegmentCount
column.
ROC data for each model and each segment, returned as a table. There are
three columns for the ROC data, with column names 'X',
'Y', and 'T', where the first two
are the X and Y coordinates of the ROC curve, and T contains the
corresponding thresholds.
If you use SegmentBy, the function stacks the ROC
data for all segments and DiscData has a column with the
segmentation values to indicate where each segment starts and ends.
If reference model data is given using ReferenceID
and ReferencePD, the DiscData
outputs for the main and reference models are stacked, with an extra column
'ModelID' indicating where each model starts and
ends.
More About
Model discrimination measures the risk ranking.
Higher-risk loans should get higher predicted probability of default (PD) than
lower-risk loans. The modelDiscrimination function computes the
Area Under the Receiver Operator Characteristic curve (AUROC), sometimes called
simply the Area Under the Curve (AUC). This metric is between 0 and 1 and higher
values indicate better discrimination.
For more information about the Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curve, see Model Discrimination and ROC Curve and Performance Metrics.
References
[1] Baesens, Bart, Daniel Roesch, and Harald Scheule. Credit Risk Analytics: Measurement Techniques, Applications, and Examples in SAS. Wiley, 2016.
[2] Bellini, Tiziano. IFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SAS. San Diego, CA: Elsevier, 2019.
[3] Breeden, Joseph. Living with CECL: The Modeling Dictionary. Santa Fe, NM: Prescient Models LLC, 2018.
[4] Roesch, Daniel and Harald Scheule. Deep Credit Risk: Machine Learning with Python. Independently published, 2020.
Version History
Introduced in R2020bThe DiscMeasure output supports an additional column for
WeightedCount.
The pdModel input supports an option for a
customLifetimePDModel model object that you can create using
customLifetimePDModel.
There is an additional name-value pair for ShowDetails to
indicate if the DiscMeasure output includes columns for
Segment value and the SegmentCount.
See Also
predictLifetime | predict | modelDiscriminationPlot | modelCalibration | modelCalibrationPlot | fitLifetimePDModel | Logistic | Probit | Cox | customLifetimePDModel
Topics
- Basic Lifetime PD Model Validation
- Compare Logistic Model for Lifetime PD to Champion Model
- Compare Lifetime PD Models Using Cross-Validation
- Expected Credit Loss Computation
- Compare Model Discrimination and Model Calibration to Validate of Probability of Default
- Compare Probability of Default Using Through-the-Cycle and Point-in-Time Models
- Create Weighted Lifetime PD Model
- Overview of Lifetime Probability of Default Models
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)