scaleruler
Add or modify graphic scale on axesm-based map
Description
scaleruler toggles the display of the graphic scale on the current
axesm-based map. A graphic scale shows distances on the ground at the
correct size for the projection. If the map does not have a graphic scale, then
scaleruler adds one. If the map has one or more graphic scales, then
scaleruler removes them.
scaleruler on adds a graphic scale to the current
axesm-based map. You can add multiple graphic scales to the same
axesm-based map.
scaleruler off removes all graphic scales from the current
axesm-based map.
scaleruler( adds a graphic scale to
the current Name,Value)axesm-based map and specifies properties using name-value
arguments. For example, "RulerStyle","patches"
displays a graphic scale with alternating black and white rectangles.
Examples
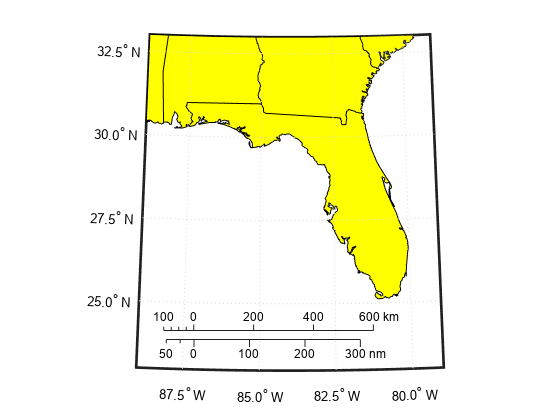
Create a map display of Florida.
usamap("Florida") geoshow("usastatelo.shp","FaceColor","yellow")
Add a graphic scale. Change the location of the scale by setting the XLoc and YLoc properties. Specify tick locations using the MajorTick property.
gs1 = scaleruler; setm(gs1,"XLoc",-3.21e5,"YLoc",2.81e6,"MajorTick",0:200:600)
Add a second graphic scale that shows distance in nautical miles. Change the direction of the tick marks and text by setting the TickDir property.
gs2 = scaleruler("Units","nm"); setm(gs2,"XLoc",-3.2e5,"YLoc",2.78e6,"TickDir","down", ... "MajorTick",0:100:300,"MinorTick",0:25:50, ... "MajorTickLength",km2nm(25),"MinorTickLength",km2nm(12.5))
Create a map of Texas and the surrounding states. Your map might look different because the polcmap function randomizes colors.
states = readgeotable("usastatehi.shp"); usamap("Texas") h = height(states); faceColors = makesymbolspec("Polygon",{'INDEX',[1 h],'FaceColor',polcmap(h)}); geoshow(states,"DisplayType","polygon","SymbolSpec",faceColors)
Add a graphic scale. By default, the graphic scale displays values in kilometers. Change the location, adjust the major tick marks, and set the font size to 8 points.
scaleruler on gs1 = handlem("scaleruler1"); setm(gs1,"XLoc",-6.2e5,"YLoc",3.03e6,"MajorTick",0:200:600,"FontSize",8)

Create a second graphic scale using units of nautical miles. Adjust the major and minor tick marks.
scaleruler("Units","nm") gs2 = handlem("scaleruler2"); setm(gs2,"XLoc",-6.2e5,"YLoc",3.0e6,"MajorTick",0:100:300,"MinorTick",0:25:50, ... "TickDir","down","MajorTickLength",km2nm(25),"MinorTickLength",km2nm(12.5),"FontSize",8)
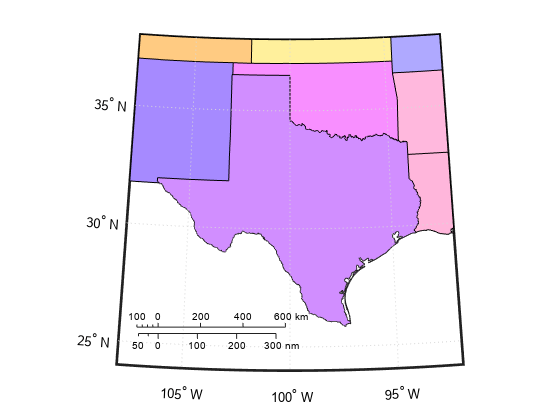
Change the ruler styles.
setm(gs1,"RulerStyle","lines") setm(gs2,"RulerStyle","patches")

Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: scaleruler("Units","nm") creates a graphic scale that
displays units in nautical miles
Ticks and Labels
Major tick mark locations, specified as a numeric vector in the units specified by
the Units property of the graphic scale.
Major tick mark labels, specified as a cell array of character vectors. The number of character vectors must match the number of major tick locations. By default, the graphic scale uses labels identical to the major tick mark locations.
Major tick mark length, specified as a numeric scalar in the units specified by
the Units property of the graphic scale.
Minor tick mark locations, specified as a numeric vector in the units specified by
the Units property of the graphic scale.
Minor tick mark labels, specified as a cell array of character vectors. The number of character vectors must match the number of minor tick locations. By default, the graphic scale uses labels identical to the last minor tick mark location.
Minor tick mark length, specified as a numeric scalar in the units specified by
the Units property of the graphic scale.
Direction of tick marks and tick labels, specified as one of these options:
"up"— Display tick marks and tick labels above the baseline."down"— Display tick marks and tick labels below the baseline.
Selection mode for ticks, specified as one of these options:
"auto"— MATLAB® chooses the ticks. SettingTickModeto"auto"clears any specified ticks and replaces them with default values."manual"— You manually control the ticks. When you specify any tick properties, MATLAB setsTickModeto"manual".
Label that displays along the graphic scale, specified as a character vector or
string scalar. You can use the label to indicate the scale of the map, for example
"1:50,000,000".
Font
Font name, specified as a supported font name. To display and print text properly, you must choose a font that your system supports. The default font depends on your operating system and locale.
To use a fixed-width font that looks good in any locale, use
"FixedWidth". The fixed-width font relies on the root FixedWidthFontName
property. Setting the root FixedWidthFontName property causes an
immediate update of the display to use the new font.
Character slant, specified as "normal" or
"italic".
Font size, specified as a positive scalar in point units. One point equals 1/72 of
an inch. To change the font units, use the FontUnits
argument.
Font size units, specified as one of the values in this table.
Units | Description |
|---|---|
"points" | Points. One point equals 1/72 of an inch. |
"inches" | Inches. |
"centimeters" | Centimeters. |
"normalized"
| Interpret font size as a fraction of the axes plot box height. If you
resize the axes, the font size changes accordingly. For example, if the
FontSize is 0.1 in normalized units,
then the text is 1/10 of the plot box height. |
"pixels" | Pixels. On Windows® and Macintosh systems, the size of a pixel is 1/96th of an inch. This size is independent of your system resolution. On Linux® systems, the size of a pixel is determined by your system resolution. |
If you set both the font size and the font units in one function call, you must
specify FontUnits first so that the axes correctly interprets the
specified font size.
Character thickness, specified as "normal" or
"bold".
MATLAB uses FontWeight to select a font from those
available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a
bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.
Position
Horizontal location of the graphic scale within the axes, specified as a numeric
scalar in Cartesian projected coordinates. To view the Cartesian grid labels, use the
showaxes function.
You can also interactively move the graphic scale by using your mouse.
Vertical location of the graphic scale within the axes, specified as a numeric
scalar in Cartesian projected coordinates. To view the Cartesian grid labels, use the
showaxes function.
You can also interactively move the graphic scale by using your mouse.
Color and Styling
Color of the graphic scale, tick marks, and text, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Style of the graphic scale, specified as one of these options:
"ruler"— Resembles the x-axis of anAxesobject."lines"— Displays three horizontal lines across the tick marks."patches"— Alternates black and white rectangles in place of lines and tick marks.
Line width of graphic scale, specified as a numeric scalar in point units.
Scaling
Azimuth of the scale computation, specified as a numeric scalar in the angle units
of the current axesm-based map. Within a projection, the scale of
a map varies with geographic location and azimuth. This value controls the azimuth
along which MATLAB computes the scaling between geographic and projected coordinates.
Latitude of the scale computation, specified as a numeric scalar in the angle
units of the current axesm-based map. Within a projection, the
scale of a map varies with geographic location and azimuth. This value controls the
latitude along which MATLAB computes the scaling between geographic and projected coordinates.
Longitude of the scale computation, specified as a numeric scalar in the angle
units of the current axesm-based map. Within a projection, the
scale of a map varies with geographic location and azimuth. This value controls the
longitude along which MATLAB computes the scaling between geographic and projected coordinates.
Name or radius of reference sphere, specified as "sun",
"moon", "mercury", "venus",
"earth", "mars", "jupiter",
"saturn", "uranus",
"neptune", "pluto", or a numeric scalar in
units specified by the Units property of the graphic scale. This
value controls the scaling between angular and surface distances.
Surface distance units, specified as one of these options:
These angular units.
Value Unit Name "degree","degrees","deg"Degrees "radian","radians","rad"Radians Any length unit supported by the
validateLengthUnitfunction.Value Unit Name "m","meter","meters","metre","metres"Meters "cm","centimeter","centimeters","centimetre","centimetres"Centimeters "mm","millimeter","millimeters","millimetre","millimetres"Millimeters "micron","microns"Microns "km","kilometer","kilometers","kilometre","kilometers"Kilometers "nm","naut mi","nautical mile","nautical miles"Nautical miles "ft","international ft","foot","international foot","feet","international feet"Feet "in","inch","inches"Inches "yd","yds","yard","yards"Yards "mi","mile","miles","international mile","international miles"Miles "sf","survey ft","US survey ft","U.S. survey ft","survey foot","US survey foot","U.S. survey foot","survey feet","US survey feet","U.S. survey feet"U.S. survey feet "sm","survey mile","survey miles","statute mile","statute miles","US survey mile","US survey miles","U.S. survey mile(s)","U.S. survey miles"U.S. survey miles (statute miles) "Clarke's foot","Clarkes foot"Clarke's feet "German legal metre","German legal meter"German legal metres "Indian foot"Indian feet
This argument is case insensitive.
Output Arguments
Tips
In addition to the syntax scaleruler off, you can remove graphic scales
from an axesm-based map by using one of these methods:
clmo scaleruler— Remove all graphic scales.clmo scalerulerN— Remove the Nth graphic scale, such asclmo scaleruler2.delete(— Remove the graphic scale specified bygs)gs.delete(handlem("scalerulerN"))— Remove the Nth graphic scale, such asdelete(handlem("scaleruler2")).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)