buffer
Description
buffered = buffer(shape,dist)dist. By default, the function outwardly buffers the shape.
Examples
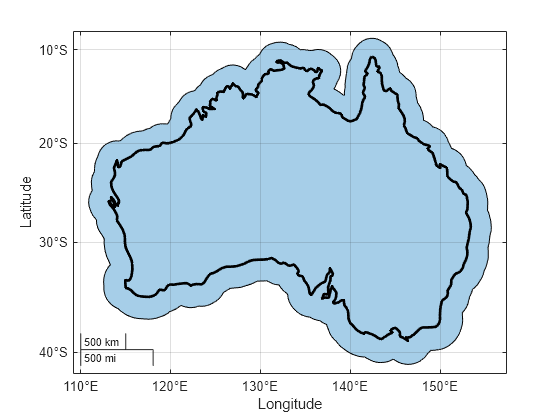
Read world land areas into the workspace as a geospatial table. The table represents the land areas using polygon shapes in geographic coordinates. Create a subtable that contains the table row for Australia. Then, extract the polygon shape for Australia.
land = readgeotable("landareas.shp"); australia = geocode("australia",land); shape = australia.Shape;
For shapes in geographic coordinates, the buffer distance units must match the angle unit of the geographic coordinate reference system (CRS) associated with the shape. Find the angle unit. The result indicates that the buffer distance must be in degrees.
shape.GeographicCRS.AngleUnit
ans = "degree"
Buffer the polygon shape by 2 degrees.
buffered = buffer(shape,2);
Create a map that displays the buffered shape and the outline of the original polygon.
figure geobasemap none geoplot(buffered) hold on geoplot(shape,LineWidth=2,FaceColor="none")
Read road data for an area in Concord, MA as a geospatial table. The table represents the roads using line shapes in planar coordinates. Create a subtable containing the line shapes for two named roads. Then, extract the line shapes.
roads = readgeotable("concord_roads.shp"); names = ["SOUTHFIELD CIRCLE","RIVERDALE ROAD"]; subroads = geocode(names,roads); shape = subroads.Shape
shape=4×1 maplineshape array with properties:
NumParts: [4×1 double]
Geometry: "line"
CoordinateSystemType: "planar"
ProjectedCRS: [1×1 projcrs]
For shapes in planar coordinates, the buffer distance units must match the length unit of the projected CRS associated with the shape. Find the length unit. The result indicates that the buffer distance must be in meters.
shape.ProjectedCRS.LengthUnit
ans = "meter"
Buffer the line shapes by 15 meters.
buffered = buffer(shape,15);
Create a map that displays the buffered shapes and the original lines. The overlapping buffered shapes indicate that the road consists of multiple line shapes.
figure
geoplot(buffered)
hold on
geoplot(shape,LineWidth=2)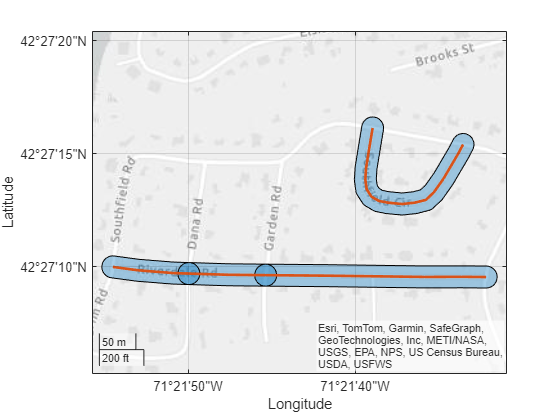
Read a shapefile containing the coordinates of locations in Boston as a geospatial table. The table represents the locations using point shapes in planar coordinates. Extract the point shapes.
places = readgeotable("boston_placenames.shp");
shape = places.Shapeshape =
13×1 mappointshape array with properties:
NumPoints: [13×1 double]
X: [13×1 double]
Y: [13×1 double]
Geometry: "point"
CoordinateSystemType: "planar"
ProjectedCRS: [1×1 projcrs]
Find the length unit to use for the buffer distances. The result indicates that the buffer distances must be in meters.
shape.ProjectedCRS.LengthUnit
ans = "meter"
For each shape, specify a random buffer distance between 100 meters and 400 meters. Then, buffer the point shapes.
sz = size(shape); dist = 100 + (400-100)*rand(sz); buffered = buffer(shape,dist);
Create a map that displays the buffered shapes and the original point shapes.
figure
geoplot(buffered)
hold on
geoplot(shape)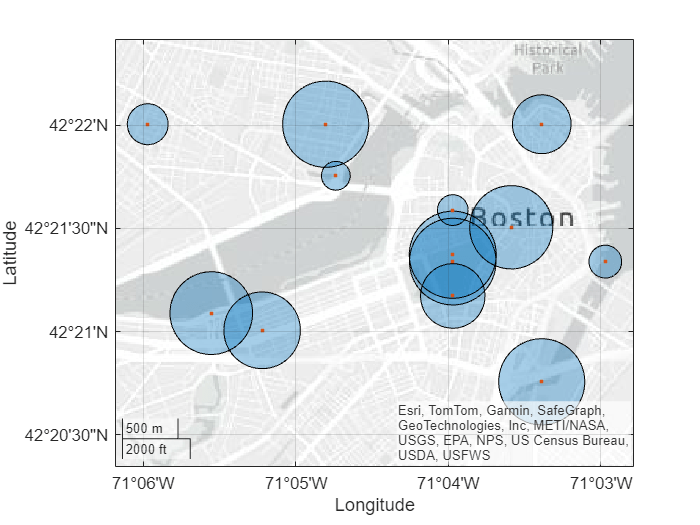
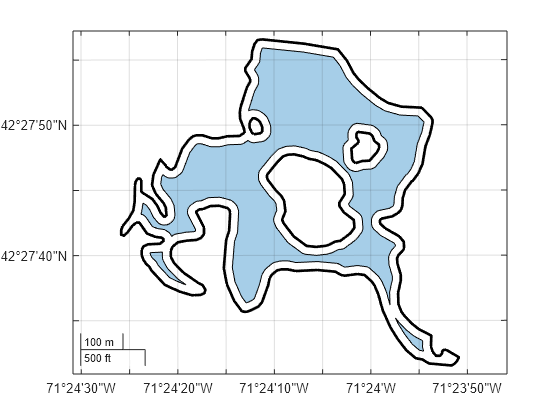
Read a shapefile containing hydrographic data for Concord, MA as a geospatial table. The table represents the data using polygon shapes in planar coordinates. Create a subtable containing the polygon shape for a pond. Then, extract the polygon shapes.
hydro = readgeotable("concord_hydro_area.shp");
pond = hydro(14,:);
shape = pond.Shapeshape =
mappolyshape with properties:
NumRegions: 1
NumHoles: 3
Geometry: "polygon"
CoordinateSystemType: "planar"
ProjectedCRS: [1×1 projcrs]
Find the length unit to use for the buffer distance. The result indicates that the buffer distance must be in meters.
shape.ProjectedCRS.LengthUnit
ans = "meter"
Inwardly buffer the polygon shape by 20 meters by specifying the Direction name-value argument.
buffered = buffer(shape,20,Direction="in");Create a map that uses the projected CRS associated with the shape. Then, display the buffered polygon and the outline of the original polygon.
figure newmap(shape.ProjectedCRS) geoplot(buffered) hold on geoplot(shape,LineWidth=2,FaceColor="none")
Since R2025a
To outwardly buffer a polygon shape, buffer the shape by using the buffer function and then remove the original shape by using the subtract function.
Read world land areas into the workspace as a geospatial table. The table represents the land areas using polygon shapes in geographic coordinates. Create a subtable that contains the table row for Australia. Then, extract the polygon shape for Australia.
land = readgeotable("landareas.shp"); australia = geocode("australia",land); shape = australia.Shape;
Buffer the polygon shape by 2 degrees.
buffered = buffer(shape,2);
Remove the original shape from the buffered shape by using the subtract function.
outbuffered = subtract(buffered,shape);
Create a map that displays the outwardly buffered shape.
figure
geobasemap none
geoplot(outbuffered)
Input Arguments
Shape, specified as one of these options:
An array of
geopointshape,geolineshape, orgeopolyshapeobjects — Point, line, or polygon shapes in geographic coordinates.An array of
mappointshape,maplineshape, ormappolyshapeobjects — Point, line, or polygon shapes in planar coordinates.
For each option, you can include a combination of point, line, and polygon shapes. You can also specify this argument as a scalar point, line, or polygon shape.
Buffer distance, specified as one of these options:
A nonnegative scalar — Use the same buffer distance for all the shape objects.
An array of nonnegative scalars — Use a different buffer distance for each shape object. The size of
distmust match the size ofshape.
The units you use to specify dist and the way the
buffer function interprets dist depends on
the type of shape.
| Type of Shape Object | Units | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
geopointshape, geolineshape, and
geopolyshape objects | Specify |
|
mappointshape, maplineshape, and
mappolyshape objects | Specify |
|
Buffer direction, specified as one of these options:
"out"— Outwardly buffer the shape."in"— Inwardly buffer the shape.
To use this argument, the shape argument must contain only
geopolyshape or mappolyshape objects.
If you inwardly buffer a polygon shape using a buffer distance that shrinks the
polygon to nothing, then the output polygon shape has no coordinate data and its
NumPoints property is 0.
Output Arguments
Buffered shape, returned as one of these options:
An array of
geopolyshapeobjects, whenshapecontains shapes in geographic coordinates.An array of
mappolyshapeobjects, whenshapecontains shapes in planar coordinates.
The size of buffered matches the size of
shape.
Version History
Introduced in R2024bThe buffer function shows improved performance when buffering
multiple shapes in planar coordinates. Represent shapes in planar coordinates using
mappointshape, maplineshape, or
mappolyshape objects.
For example, this code creates 500 line shapes in planar coordinates and then buffers
the shapes using the buffer function. The code is about 1.9 times
faster than in the previous release.
function timingTest % Get shapes x = linspace(1,100,1000); shp = maplineshape(x,x); shps = repmat(shp,500,1); % Buffer shapes b = buffer(shps,1); end
The approximate execution times are:
R2024b: 0.72 s
R2025a: 0.37 s
This code was timed on a Windows® 11, AMD EPYC™ 74F3 24-Core Processor @ 3.19 GHz test system, using the
timeit function:
timeit(@timingTest)
See Also
Functions
Objects
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)