2 分法アルゴリズムの高位合成コード生成
2 分法アルゴリズムを実装して固定小数点表記の数値の平方根を計算する MATLAB® 設計から高位合成 (HLS) コードを生成できます。
MATLAB 設計
まず、sqrt モデルを設定します。
mlhdlc_demo_setup('sqrt'); % Design Sqrt design_name = 'mlhdlc_sqrt'; % Test Bench for Sqrt testbench_name = 'mlhdlc_sqrt_tb';
Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sqrt Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sqrt_runme Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sqrt_tb Successfully copied: mlhdlc_tutorial_sqrt Successfully copied: mlhdlc_msysobj_nonrestsqrt Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sysobj_nonrestsqrt Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sysobj_nonrestsqrt_runme Successfully copied: mlhdlc_sysobj_nonrestsqrt_tb Successfully copied: mlhdlc_tutorial_sysobj_nonrestsqrt
sqrt 設計を確認します。
dbtype(design_name)
1 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
2 % MATLAB design: Pipelined Bisection Square root algorithm
3 %
4 % Introduction:
5 %
6 % Implement SQRT by the bisection algorithm in a pipeline, for unsigned fixed
7 % point numbers (also why you don't need to run fixed-point conversion for this design).
8 % The demo illustrates the usage of a pipelined implementation for numerical algorithms.
9 %
10 % Key Design pattern covered in this example:
11 % (1) State of the bisection algorithm is maintained with persistent variables
12 % (2) Stages of the bisection algorithm are implemented in a pipeline
13 % (3) Code is written in a parameterized fashion, i.e. word-length independent, to work for any size fi-type
14 %
15 % Ref. 1. R. W. Hamming, "Numerical Methods for Scientists and Engineers," 2nd, Ed, pp 67-69. ISBN-13: 978-0486652412.
16 % 2. Bisection method, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bisection_method, (accessed 02/18/13).
17 %
18
19 % Copyright 2013-2015 The MathWorks, Inc.
20
21 %#codegen
22 function [y,z] = mlhdlc_sqrt( x )
23 persistent sqrt_pipe
24 persistent in_pipe
25 if isempty(sqrt_pipe)
26 sqrt_pipe = fi(zeros(1,x.WordLength),numerictype(x));
27 in_pipe = fi(zeros(1,x.WordLength),numerictype(x));
28 end
29
30 % Extract the outputs from pipeline
31 y = sqrt_pipe(x.WordLength);
32 z = in_pipe(x.WordLength);
33
34 % for analysis purposes you can calculate the error between the fixed-point bisection routine and the floating point result.
35 %Q = [double(y).^2, double(z)];
36 %[Q, diff(Q)]
37
38 % work the pipeline
39 for itr = x.WordLength-1:-1:1
40 % move pipeline forward
41 in_pipe(itr+1) = in_pipe(itr);
42 % guess the bits of the square-root solution from MSB to the LSB of word length
43 sqrt_pipe(itr+1) = guess_and_update( sqrt_pipe(itr), in_pipe(itr+1), itr );
44 end
45
46 %% Prime the pipeline
47 % with new input and the guess
48 in_pipe(1) = x;
49 sqrt_pipe(1) = guess_and_update( fi(0,numerictype(x)), x, 1 );
50
51 %% optionally print state of the pipeline
52 %disp('************** State of Pipeline **********************')
53 %double([in_pipe; sqrt_pipe])
54
55 return
56 end
57
58 % Guess the bits of the square-root solution from MSB to the LSB in
59 % a binary search-fashion.
60 function update = guess_and_update( prev_guess, x, stage )
61 % Key step of the bisection algorithm is to set the bits
62 guess = bitset( prev_guess, x.WordLength - stage + 1);
63 % compare if the set bit is a candidate solution to retain or clear it
64 if ( guess*guess <= x )
65 update = guess;
66 else
67 update = prev_guess;
68 end
69 return
70 end
設計のシミュレーション
コードの生成前にテスト ベンチを使用して設計をシミュレートし、実行時エラーがないか確認することをお勧めします。
mlhdlc_sqrt_tb
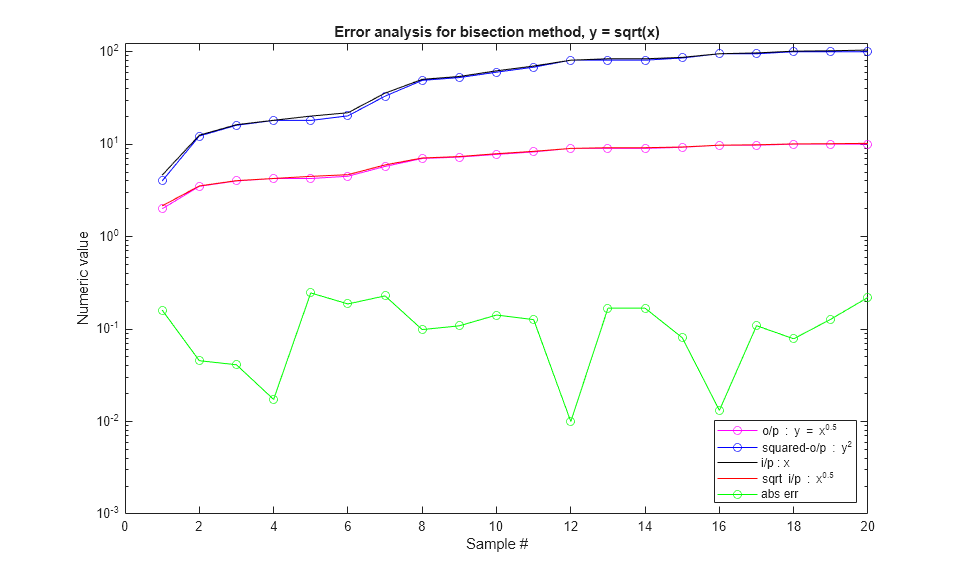
Iter = 01| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 02| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 03| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 04| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 05| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 06| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 07| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 08| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 09| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 10| Input = 0.000| Output = 0000000000 (0.00) | actual = 0.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 11| Input = 4.625| Output = 0000010000 (2.00) | actual = 2.150581 | abserror = 0.150581 Iter = 12| Input = 12.500| Output = 0000011100 (3.50) | actual = 3.535534 | abserror = 0.035534 Iter = 13| Input = 16.250| Output = 0000100000 (4.00) | actual = 4.031129 | abserror = 0.031129 Iter = 14| Input = 18.125| Output = 0000100010 (4.25) | actual = 4.257347 | abserror = 0.007347 Iter = 15| Input = 20.125| Output = 0000100010 (4.25) | actual = 4.486090 | abserror = 0.236090 Iter = 16| Input = 21.875| Output = 0000100100 (4.50) | actual = 4.677072 | abserror = 0.177072 Iter = 17| Input = 35.625| Output = 0000101110 (5.75) | actual = 5.968668 | abserror = 0.218668 Iter = 18| Input = 50.250| Output = 0000111000 (7.00) | actual = 7.088723 | abserror = 0.088723 Iter = 19| Input = 54.000| Output = 0000111010 (7.25) | actual = 7.348469 | abserror = 0.098469 Iter = 20| Input = 62.125| Output = 0000111110 (7.75) | actual = 7.881941 | abserror = 0.131941 Iter = 21| Input = 70.000| Output = 0001000010 (8.25) | actual = 8.366600 | abserror = 0.116600 Iter = 22| Input = 81.000| Output = 0001001000 (9.00) | actual = 9.000000 | abserror = 0.000000 Iter = 23| Input = 83.875| Output = 0001001000 (9.00) | actual = 9.158330 | abserror = 0.158330 Iter = 24| Input = 83.875| Output = 0001001000 (9.00) | actual = 9.158330 | abserror = 0.158330 Iter = 25| Input = 86.875| Output = 0001001010 (9.25) | actual = 9.320676 | abserror = 0.070676 Iter = 26| Input = 95.125| Output = 0001001110 (9.75) | actual = 9.753205 | abserror = 0.003205 Iter = 27| Input = 97.000| Output = 0001001110 (9.75) | actual = 9.848858 | abserror = 0.098858 Iter = 28| Input = 101.375| Output = 0001010000 (10.00) | actual = 10.068515 | abserror = 0.068515 Iter = 29| Input = 102.375| Output = 0001010000 (10.00) | actual = 10.118053 | abserror = 0.118053 Iter = 30| Input = 104.250| Output = 0001010000 (10.00) | actual = 10.210289 | abserror = 0.210289
HDL Coder™ プロジェクトの作成
HDL Coder プロジェクトを作成します。
coder -hdlcoder -new mlhdlc_sqrt_prj
mlhdlc_sqrt.m ファイルを MATLAB 関数としてプロジェクトに追加します。mlhdlc_sqrt_tb.m ファイルを MATLAB テスト ベンチとして追加します。
詳細については、Get Started with MATLAB to High-Level Synthesis Workflow Using the Command Line InterfaceまたはHDL Coder アプリを使用した MATLAB から高位合成へのワークフロー入門を参照してください。
HLS コード生成
この設計は既に固定小数点であり、HLS コード生成に適しています。この設計に対して浮動小数点から固定小数点への変換を実行する必要はありません。
MATLAB 設計から HLS コードを生成するには、次のようにします。
1. MATLAB コマンド ラインで、関数hdlsetuphlstoolpathを使用し、HLS コード生成のパスを設定します。
2. [ワークフロー アドバイザー] ボタンをクリックして、ワークフロー アドバイザーを開始します。
3. [HDL ワークフロー アドバイザー] で、[MATLAB から HLS] として [コード生成ワークフロー] を選択します。
4. [コード生成ターゲットを選択] ステップで、[合成ツール] リストから [Cadence Stratus HLS] を選択します。
5. [HLS コード生成] タスクを右クリックし [選択したタスクまで実行] を選択して、最初から HLS コード生成までのすべてのステップを実行します。
[HLS コード生成] ログ ウィンドウにあるハイパーリンクをクリックして、生成された HLS コードを確認します。