カスタムの動作制約によるデータ型最適化の実行
この例では、周波数領域内でカスタムの動作制約を使用して、fxpopt で固定小数点データ型を最適化する方法について説明します。この例の Simulink® モデルは、Model Verification ライブラリのブロックを使用して、ローパス フィルターの SNR (S/N 比) でカスタムの動作制約を記述する 2 つの方法を示します。最初の例では、ノイズ フロアの近似を計算します。2 番目の例では、元のモデルと固定小数点データ型を使用する量子化モデルの間の SNR の差を計算します。
データ型最適化の動作の制約
データ型の最適化は、元のシステム動作を指定された許容誤差内で維持しながら、目的関数 (総ビット幅など) を最小化しようとします。最適化中に、ソフトウェアは元のモデルのシミュレーションを実行することで、ベースラインを確立します。次に、ソフトウェアはモデルの固定小数点バージョンを作成して、シミュレーションを実行し、新しいデータ型を使用して動作を決定します。最適化により、指定された動作の制約を満たし、かつ目的関数を最小化するモデルが選択されます。
新しい固定小数点実装の動作が許容可能かどうかを判定するために、最適化には正しく定義された動作の制約が必要です。少なくとも 1 つの動作の制約を指定しなければなりません。fxpopt で使用する動作の制約の指定方法には次の 2 つがあります。
1. 許容誤差ベースのシミュレーションとベースライン参照との比較 - fxpOptimizationOptions の addTolerance メソッドを使用して、信号ログを有効にしている信号に許容誤差を追加できます。許容誤差は、モデルのベースライン シミュレーションに関する引き渡し動作のエンべロープを指定します。
2. シミュレーションベースのアサーション チェック - Model Verification ブロック ライブラリのブロックを使用して、カスタムの検証式を作成できます。モデル内の有効なモデル検証ブロックは、最適化ソルバーによって動作制約として解釈されます。
信号の許容誤差と Model Verification ブロックの組み合わせを使用して、モデルの動作の制約を指定することもできます。詳細については、動作の制約の指定を参照してください。
例 1: ノイズ フロアの近似の計算
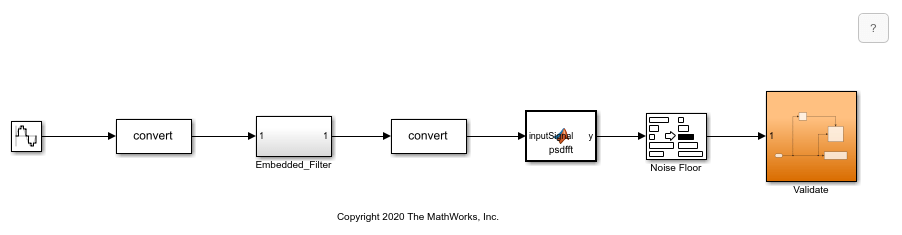
この例では、ローパス フィルターを変換して、fxpopt を使用して最適化された固定小数点データ型を使用します。組み込みバージョンが依然として SNR 要件を満たすようにするために、モデル mLowPass_NoiseFloor にはフィルターの出力時に信号のノイズ フロアを計算する追加のロジックが含まれています。次に、この信号は Validate サブシステムにルーティングされます。このサブシステムでは、Model Verification ブロック ライブラリの Check State Range ブロックが使用されます。シミュレーション中に計算されたノイズ フロアの値が指定された静的範囲外である場合、fxpopt はそのモデルを、動作の制約を渡さないものとして解釈します。
最初に、データ型を最適化するシステムを開きます。
model = 'mLowPass_NoiseFloor'; sud = [model '/Embedded_Filter']; open_system(model);
関数 fxpopt を使用して最適化を実行します。制約を指定するために Model Verification ブロックが使用されているため、fxpOptimizationOptions の addTolerance メソッドを使用して信号の許容誤差を指定する必要はありません。
result = fxpopt(model,sud)
+ Starting data type optimization...
+ Checking for unsupported constructs.
+ Preprocessing
+ Modeling the optimization problem
- Constructing decision variables
+ Running the optimization solver
- Evaluating new solution: cost 110, meets the behavioral constraints.
- Updated best found solution, cost: 110
+ Optimization has finished.
- Neighborhood search complete.
- Reached limit of number of iterations without updates to the current best solution.
+ Fixed-point implementation that satisfies the behavioral constraints found. The best found solution is applied on the model.
- Total cost: 110
- Use the explore method of the result to explore the implementation.
result =
OptimizationResult with properties:
Model: 'mLowPass_NoiseFloor'
SystemUnderDesign: 'mLowPass_NoiseFloor/Embedded_Filter'
FinalOutcome: 'Fixed-point implementation that satisfies the behavioral constraints found. The best found solution is applied on the model.'
OptimizationOptions: [1×1 fxpOptimizationOptions]
Solutions: [1×1 DataTypeOptimization.OptimizationSolution]
explore メソッドを使用して、最適化された固定小数点データ型が含まれる設計を調査します。
explore(result);
例 2: 元のモデルおよび量子化モデル間の SNR の差を計算
この例では、ローパス フィルター モデル mLowPass_SNR の固定小数点データ型を最適化します。異なる動作制約セットを使用し、組み込みフィルターの SNR を、倍精度データ型を使用する元のフィルターの SNR と比較します。ValidateSNR サブシステムは最初に SNR を計算し、次に Model Verification ライブラリの Check Static Lower Bound ブロックを使用して、SNR が 60 より大きいことをアサートします。SNR が指定されたこの値を下回ると、fxpopt はそのモデルを、動作制約を渡さないものとして解釈します。
最初に、データ型を最適化するシステムを開きます。
model = 'mLowPass_SNR'; sud = [model '/Embedded_Filter']; Source = 1; open_system(model);

この例では、Simulink.SimulationInput オブジェクトを作成することで、追加のシミュレーション シナリオを指定します。100 ラジアン/秒の周波数をもつ 1 つの正弦波入力と、500 ラジアン/秒の周波数をもつ 2 番目の正弦波入力を使用します。fxpopt は最適化中に両方のシミュレーション シナリオを考慮します。包括的な入力信号のセットは、最適化プロセス中に設計の動作範囲全体を確実にカバーするのに役立ちます。
si(1) = Simulink.SimulationInput(model); si(1) = si(1).setVariable('Source',1); si(2) = Simulink.SimulationInput(model); si(2) = si(2).setVariable('Source',2);
fxpOptimizationOptions オブジェクトを作成します。高度なオプションを使用して、最適化中に考慮するシミュレーション シナリオを定義します。
options = fxpOptimizationOptions(); options.AdvancedOptions.SimulationScenarios = si;
関数 fxpopt を使用して最適化を実行します。制約を指定するために Model Verification ブロックが使用されているため、fxpOptimizationOptions の addTolerance メソッドを使用して信号の許容誤差を指定する必要はありません。
result = fxpopt(model,sud,options);
+ Starting data type optimization... + Checking for unsupported constructs. + Preprocessing + Modeling the optimization problem - Constructing decision variables + Running the optimization solver - Evaluating new solution: cost 112, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 168, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 224, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 280, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 336, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 392, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 448, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 504, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 560, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 616, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 672, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 728, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 784, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 840, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 896, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 952, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 1008, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 1008 - Evaluating new solution: cost 995, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 995 - Evaluating new solution: cost 994, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 994 - Evaluating new solution: cost 993, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 993 - Evaluating new solution: cost 992, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 992 - Evaluating new solution: cost 991, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 991 - Evaluating new solution: cost 990, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 990 - Evaluating new solution: cost 989, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 989 - Evaluating new solution: cost 988, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 988 - Evaluating new solution: cost 987, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 987 - Evaluating new solution: cost 986, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 986 - Evaluating new solution: cost 985, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 985 - Evaluating new solution: cost 984, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 984 - Evaluating new solution: cost 982, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 982 - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 981, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 981 - Evaluating new solution: cost 980, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 980 - Evaluating new solution: cost 979, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 979, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 979 - Evaluating new solution: cost 978, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 978, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 978 - Evaluating new solution: cost 977, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 977, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 977 - Evaluating new solution: cost 976, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 976 - Evaluating new solution: cost 975, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 975 - Evaluating new solution: cost 974, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 974, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 974 - Evaluating new solution: cost 973, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 973, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 973 - Evaluating new solution: cost 972, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 972, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 972 - Evaluating new solution: cost 971, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 971 - Evaluating new solution: cost 970, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 970 - Evaluating new solution: cost 969, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 969 - Evaluating new solution: cost 968, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 968 - Evaluating new solution: cost 967, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 967 - Evaluating new solution: cost 966, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 966 - Evaluating new solution: cost 965, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 965 - Evaluating new solution: cost 964, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 964 - Evaluating new solution: cost 951, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 963, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 963, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 963, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 963, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 963, does not meet the behavioral constraints. + Optimization has finished. - Neighborhood search complete. - Maximum number of iterations completed. + Fixed-point implementation that satisfies the behavioral constraints found. The best found solution is applied on the model. - Total cost: 964 - Use the explore method of the result to explore the implementation.
explore メソッドを使用して、最適化された固定小数点データ型が含まれる設計を調査します。
explore(result);