DSP スライスを有する FPGA 向けのデータ型の最適化
この例では、fxpOptimizationOptions クラスの addSpecification メソッドを使用して、FPGA ターゲットの DSP スライス上の Product ブロックとのマッピングを向上する方法について説明します。addSpecification を使用して、システムでの既知のデータ型を指定します。これらの既知のパラメーターを指定した後に、システムのデータ型を最適化した場合、指定されたブロック パラメーターのデータ型は、最適化プロセスによって変更されません。
多くの FPGA ボードには、DSP スライスと呼ばれる、信号処理関数の実行を高速化する固有の積和演算ハードウェア アクセラレータを備えています。DSP スライスのサイズは、ベンダーによってさまざまです。DSP スライスによるハードウェア アクセラレーションのメリットを得るため、FPGA の設計では、アルゴリズム内の積和演算をこれらのスライスにマッピングすることが一般的です。
この例では、Xilinx® ボードの 3 つの DSP ファミリ、および汎用の 18x18 ビット入力に対してデータ型を最適化します。addSpecification メソッドを使用して、設計内の Product ブロックとターゲット DSP スライス間の良好なマッピングを実現します。
この例では、以下のことを前提とします。
DSP スライスへのマッピング ターゲットは、Product ブロックと Gain ブロックのみです。他のブロックも同じように扱えます。
Product ブロックの入力は 2 つのみです。
ドライバー ブロック (Product ブロックまたは Gain ブロックの前にあるブロック) は、パラメーターとして
OutDataTypeStrを持ちます。HDL プロパティ DSPStyle が
offに設定されていないブロックのみをターゲットとします。
モデルのインストルメント化と範囲の収集
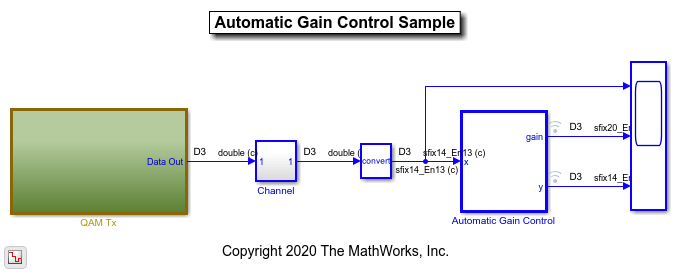
最初に、データ型を最適化するシステムを開きます。この例では、自動ゲイン制御アルゴリズムのデータ型を最適化します。
model = 'mQAMAGC'; sud = [model '/Automatic Gain Control']; open_system(model);
QAM Tx サブシステムを初期化します。
initQAM;
ターゲット DSP スライスのプロパティを記述する構造体配列を作成します。この例に含まれる関数 dspStyle は、DSP48A1 (18x18 ビット符号付き)、DSP48E1 (18x25 ビット符号付き)、および DSP48E2 (18x27 ビット符号付き) を含む一般的な Xilinx® DSP スライスに関する情報を提供します。また、汎用の 18x18 符号付き DSP スライスの例も提供します。
dspStyle = getDSPStyle('DSP48E2');
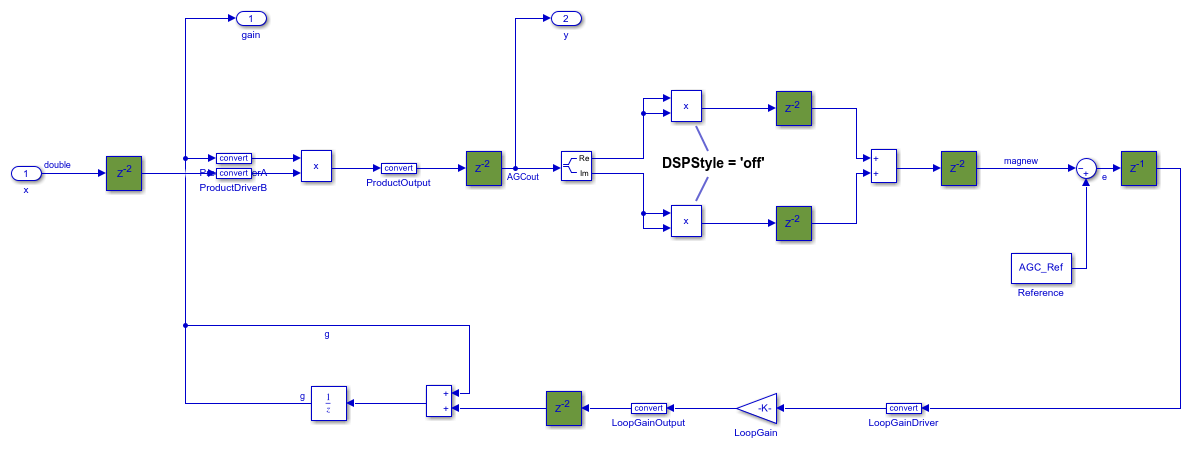
この例では、DSP スライスへのマッピング ターゲットは、Product ブロックと Gain ブロックのみです。設計内のシステムに含まれる、HDL ブロック プロパティ DSPStyle が off に設定されていない Product ブロックと Gain ブロックをすべて見つけます。詳細については、DSPStyle (HDL Coder)を参照してください。
productBlocks = find_system(sud,'LookUnderMasks','on','BlockType','Product'); hasDSPOff = cellfun(@(x)(isequal(hdlget_param(x,'DSPStyle'),'off')), productBlocks); productDSP = productBlocks(~hasDSPOff); gainBlocks = find_system(sud,'LookUnderMasks','on','BlockType','Gain'); hasDSPOff = cellfun(@(x)(isequal(hdlget_param(x,'DSPStyle'),'off')), productBlocks); gainDSP = gainBlocks(~hasDSPOff);
インストルメンテーションを有効にし、Product ブロックと Product ブロックの前にあるドライバー ブロックのシミュレーション中に、最小値、最大値、およびオーバーフロー データのログを作成します。モデルをシミュレーションし、範囲を収集します。
c = DataTypeWorkflow.Converter(sud,'TopModel',model); c.CurrentRunName = 'RangeCollection'; c.simulateSystem('MinMaxOverflowLogging','MinMaxAndOverflow');
Product ブロックの仕様の取得
Product ブロックを利用可能な DSP スライスに効率的にマッピングするため、Product ブロックの範囲要件を考慮します。範囲収集実行中に収集された Product ブロックのシミュレーションの最小値と最大値を格納するための構造体配列を作成します。
specs = struct('Block',productDSP{1},'Drivers',[],'Min',[],'Max',[]); %#ok<*SAGROW> r = c.results(c.CurrentRunName,@(x)(strcmp(x.ResultName,productDSP{1}))); specs.Min = r.SimMin; specs.Max = r.SimMax; predecessorBlocks = predecessors(productDSP{1}); for pIndex = 1:numel(predecessorBlocks) pBlkObj = get_param(predecessorBlocks{pIndex},'Object'); specs.Drivers(pIndex) = pBlkObj.Handle; r = c.results(c.CurrentRunName,@(x)(strcmp(x.ResultName,pBlkObj.getFullName()))); specs.Min(pIndex+1) = r.SimMin; specs.Max(pIndex+1) = r.SimMax; end
Product ブロックのこれらの既知のパラメーター指定を Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter オブジェクトに格納します。
bpProductBlock = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter.empty(0,3); fout = fi(max([abs(specs.Min(1)) abs(specs.Max(1))]),dspStyle.sout,dspStyle.wout); bpProductBlock(1) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(specs.Block, ... 'OutDataTypeStr', ... sprintf('fixdt(%i,%i,%i)',dspStyle.sout,dspStyle.wout,fout.FractionLength));
ドライバー ブロックの最大の範囲に最大の型を割り当てます。これにより、最大の範囲要件を持つブロックに、ターゲット ハードウェアで利用可能な最大のデータ型が割り当てられます。
dMax1 = max([abs(specs.Min(2)) abs(specs.Max(2))]); dMax2 = max([abs(specs.Min(3)) abs(specs.Max(3))]); if dMax1 < dMax2 win_1 = dspStyle.win_1; sin_1 = dspStyle.sin_1; win_2 = dspStyle.win_2; sin_2 = dspStyle.sin_2; if dspStyle.win_1 >= dspStyle.win_2 win_1 = dspStyle.win_2; sin_1 = dspStyle.sin_2; win_2 = dspStyle.win_1; sin_2 = dspStyle.sin_1; end else win_1 = dspStyle.win_2; sin_1 = dspStyle.sin_2; win_2 = dspStyle.win_1; sin_2 = dspStyle.sin_1; if dspStyle.win_1 >= dspStyle.win_2 win_1 = dspStyle.win_1; sin_1 = dspStyle.sin_1; win_2 = dspStyle.win_2; sin_2 = dspStyle.sin_2; end end
Product ブロックの前にあるブロックの仕様を取得します。この例では、Product ブロックは 2 つの入力を持つと仮定していることに注意してください。
fin1 = fi(dMax1, sin_1, win_1); blkObj = get_param(specs.Drivers(1), 'Object'); bpProductBlock(2) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(blkObj.getFullName, ... 'OutDataTypeStr', ... sprintf('fixdt(%i, %i, %i)', sin_1, win_1, fin1.FractionLength)); fin2 = fi(dMax2, sin_2, win_2); blkObj = get_param(specs.Drivers(2), 'Object'); bpProductBlock(3) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(blkObj.getFullName, ... 'OutDataTypeStr', ... sprintf('fixdt(%i, %i, %i)', sin_2, win_2, fin2.FractionLength));
Gain ブロックの仕様の取得
Gain ブロックに関する既知のパラメーター指定を Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter オブジェクトに格納します。
bpGainBlock = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter.empty(0,3); specs = struct('Block',gainDSP{1},'Drivers',[],'Min',[],'Max',[]); %#ok<*SAGROW> r = c.results(c.CurrentRunName,@(x)(strcmp(x.ResultName,gainDSP{1}))); specs.Min = r.SimMin; specs.Max = r.SimMax; predecessorBlocks = predecessors(gainDSP{1}); pBlkObj = get_param(predecessorBlocks{1},'Object'); specs.Drivers(1) = pBlkObj.Handle; r = c.results(c.CurrentRunName,@(x)(strcmp(x.ResultName,pBlkObj.getFullName()))); specs.Min(2) = r.SimMin; specs.Max(2) = r.SimMax;
Gain ブロックの出力の仕様を取得します。
fout = fi(max(abs([specs.Min(1) specs.Max(1)])),dspStyle.sout,dspStyle.wout);
bpGainBlock(1) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(gainDSP{1}, ...
'OutDataTypeStr', ...
sprintf('fixdt(%i, %i, %i)',dspStyle.sout,dspStyle.wout,fout.FractionLength));
Gain ブロックの前にあるブロックの仕様を取得し、それを Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter オブジェクトの bpGainBlock の 1 つ目のコンフィギュレーションに割り当てます。
blkObj = get_param(specs.Drivers(1),'Object'); fin = fi(max(abs([specs.Min(2) specs.Max(2)])),dspStyle.sin_1,dspStyle.win_1); bpGainBlock(2) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(blkObj.getFullName, ... 'OutDataTypeStr', ... sprintf('fixdt(%i,%i,%i)',dspStyle.sin_1,dspStyle.win_1,fin.FractionLength));
設計対象のシステムの Gain パラメーターの指定を取得し、その値を bpGainBlock の 2 つ目のコンフィギュレーションに割り当てます。
paramValue = str2double(get_param(sud,'AGC_Gain')); fParam = fi(paramValue,dspStyle.sin_2,dspStyle.win_2); bpGainBlock(3) = Simulink.Simulation.BlockParameter(gainDSP{1}, ... 'ParamDataTypeStr', ... sprintf('fixdt(%i,%i,%i)',dspStyle.sin_2,dspStyle.win_2,fParam.FractionLength));
制約と許容誤差の定義
fxpOptimizationOptions オブジェクトを作成して、制約と許容誤差を定義します。許容される語長を 8 ビット~ 32 ビットの間で指定します。
options = fxpOptimizationOptions('AllowableWordLengths',8:2:32);
addTolerance メソッドを使用して、システムの元の動作と最適化された固定小数点データ型を使用した動作の差の許容誤差を定義します。
addTolerance(options,sud,1,'RelTol',1e-2); addTolerance(options,sud,2,'RelTol',1e-2); addTolerance(options,sud,1,'AbsTol',1e-3); addTolerance(options,sud,2,'AbsTol',1e-3);
addSpecification メソッドを使用して、Product ブロックと Gain ブロックの仕様を定義します。
addSpecification(options,'BlockParameter',bpProductBlock); % set the specifications for the product block addSpecification(options,'BlockParameter',bpGainBlock); % set the specifications for the gain block showSpecifications(options);
Index Name BlockPath Value
_____ ________________ _____________________________________________ __________________
1 OutDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/LoopGain 'fixdt(1, 45, 53)'
2 ParamDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/LoopGain 'fixdt(1,27,35)'
3 OutDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/LoopGainDriver 'fixdt(1,18,16)'
4 OutDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/Product 'fixdt(1,45,43)'
5 OutDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/ProductDriverA 'fixdt(1, 27, 25)'
6 OutDataTypeStr mQAMAGC/Automatic Gain Control/ProductDriverB 'fixdt(1, 18, 17)'
varSpecs
________
固定小数点データ型の最適化
関数 fxpopt を使用して最適化を実行します。設計対象のシステム内のオブジェクトの範囲と fxpOptimizationOptions オブジェクトで指定された制約がソフトウェアで解析され、総ビット幅を最小限に抑えながら異種混合のデータ型がシステムに適用されます。addSpecification メソッドを使用してインクルードされた既知のパラメーター指定は、最適化プロセスの影響を受けません。
result = fxpopt(model,sud,options);
+ Starting data type optimization... + Checking for unsupported constructs. + Preprocessing + Modeling the optimization problem - Constructing decision variables + Running the optimization solver Backing up simulation data to base workspace. To skip this operation, set Export=false. - Evaluating new solution: cost 200, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 250, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 300, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 350, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 400, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 450, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 500, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 500 - Evaluating new solution: cost 496, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 496 - Evaluating new solution: cost 492, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 492 - Evaluating new solution: cost 488, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 488 - Evaluating new solution: cost 484, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 484 - Evaluating new solution: cost 480, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 480 - Evaluating new solution: cost 478, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 478 - Evaluating new solution: cost 476, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 472, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 476, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 476 - Evaluating new solution: cost 474, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 474 - Evaluating new solution: cost 468, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 468 - Evaluating new solution: cost 458, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 458 - Evaluating new solution: cost 454, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 454 - Evaluating new solution: cost 450, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 450 - Evaluating new solution: cost 446, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 446 - Evaluating new solution: cost 442, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 442 - Evaluating new solution: cost 438, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 438 - Evaluating new solution: cost 436, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 436 - Evaluating new solution: cost 434, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 430, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 434, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 434 - Evaluating new solution: cost 432, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 432 - Evaluating new solution: cost 426, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 426 - Evaluating new solution: cost 416, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 416 - Evaluating new solution: cost 412, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 412 - Evaluating new solution: cost 408, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 408 - Evaluating new solution: cost 404, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 404 - Evaluating new solution: cost 400, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 400 - Evaluating new solution: cost 396, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 396 - Evaluating new solution: cost 394, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 394 - Evaluating new solution: cost 392, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 388, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 392, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 392 - Evaluating new solution: cost 390, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 390 - Evaluating new solution: cost 384, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 384 - Evaluating new solution: cost 374, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 374 - Evaluating new solution: cost 370, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 370 - Evaluating new solution: cost 366, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 366 - Evaluating new solution: cost 362, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 362 - Evaluating new solution: cost 358, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 358 - Evaluating new solution: cost 354, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 354 - Evaluating new solution: cost 352, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 352 - Evaluating new solution: cost 350, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 346, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 350, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 350 - Evaluating new solution: cost 348, meets the behavioral constraints. - Updated best found solution, cost: 348 - Evaluating new solution: cost 342, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 338, does not meet the behavioral constraints. - Evaluating new solution: cost 344, does not meet the behavioral constraints. + Optimization has finished. - Neighborhood search complete. - Maximum number of iterations completed. + Fixed-point implementation that satisfies the behavioral constraints found. The best found solution is applied on the model. - Total cost: 348 - Maximum absolute difference: 0.006126 - Use the explore method of the result to explore the implementation.
OptimizationResult オブジェクトの explore メソッド、result を使用して、シミュレーション データ インスペクターを開き、設計を調査します。
explore(result)
ans =
OptimizationSolution with properties:
Cost: 348
Pass: 1
MaxDifference: 0.0061
RunID: 24040
RunName: {'solution_56ed4ad01b357d644b124a742c8b97a4bc862de7_1'}