Quick Start Library Development
This example shows how to develop a code replacement
library that includes an entry for generating replacement code for
the math function sin. You use the Code Replacement Tool.
Prerequisites
To complete this example, install the following software:
MATLAB®
MATLAB Coder™
Embedded Coder®
C compiler
For instructions on installing MathWorks® products, see Installation and Licensing. If you have
installed MATLAB and want to see what other MathWorks products are installed, in the Command Window, enter
license('inuse').
For a list of supported compilers, see https://www.mathworks.com/support/compilers/current_release/.
Open the Code Replacement Tool
Start a new MATLAB session.
Create or navigate (
cd) to an empty folder.At the command prompt, enter the
crtoolcommand. The Code Replacement Tool window opens.
Create Code Replacement Table
In the Code Replacement Tool window, click New > Table.
In the right pane, name the table
crl_table_sinfcnand click Apply. Later, when you save the table, the tool saves it with the file namecrl_table_sinfcn.m.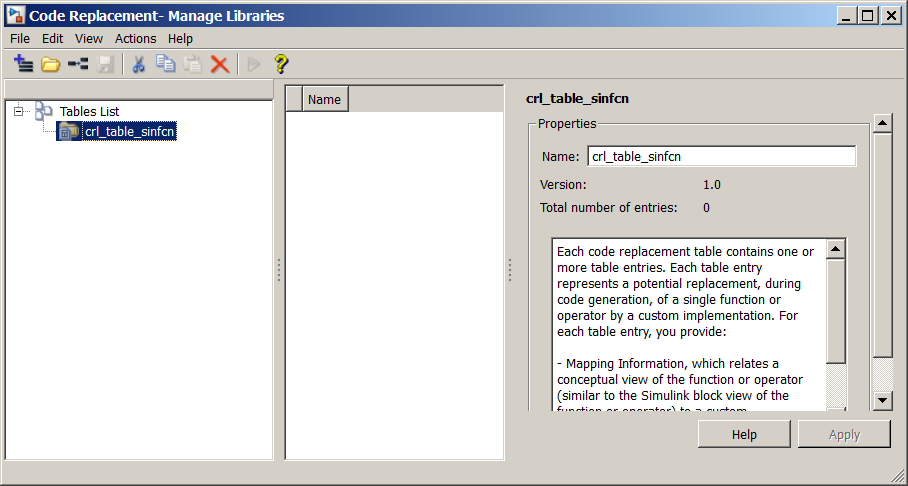
Create Table Entry
Create a table entry that maps a sin function
with double input and double output
to a custom implementation function.
In the left pane, select table
crl_table_sinfcn. Then, select New > Entry > Function Entry. The new entry appears in the middle pane, initially without a name.In the middle pane, select the new entry.
In the right pane, on the Mapping Information tab, from the Function menu, select
sin.Leave Algorithm set to
Unspecified, and leave parameters in the Conceptual function group set to default values.In the Replacement function group, name the replacement function
sin_dbl.Leave the remaining parameters in the Replacement function group set to default values.
Click Apply. The tool updates the Function signature preview to reflect the specified replacement function name.
Scroll to the bottom of the Mapping Information tab and click Validate entry. The tool validates your entry.
The following figure shows the completed mapping information.

Specify Build Information for Replacement Code
On the Build Information tab, for the Implementation header file parameter, enter
sin_dbl.h.Leave the remaining parameters set to default values.
Click Apply.

Optionally, you can revalidate the entry. Return to the Mapping Information tab and click Validate entry.
Create Another Table Entry
Create an entry that maps a sin function
with single input and double output
to a custom implementation function named sin_sgl.
Create the entry by copying and pasting the sin_dbl entry.
In the middle pane, select the
sin_dblentry.Click Copy then click Paste.
On the Mapping Information tab, in the Conceptual function section, set the data type of input argument
u1tosingle.In the Replacement function section, name the function
sin_sgl. Set the data type of input argumentu1tosingle.Click Apply. Note the changes that appear for the Function signature preview.
On the Build Information tab, for the Implementation header file parameter, enter
sin_sgl.h. Leave the remaining parameters set to default values and click Apply.
Validate the Code Replacement Table
Click Validate.
If the tool reports errors, fix them, and rerun the validation. Repeat fixing and validating errors until the tool does not report errors. The following figure shows a validation report.

Save the Code Replacement Table
Save the code replacement table to a MATLAB file in your working folder. Click Save. By default,
the tool uses the table name to name the file. For this example, the tool saves the table in
the file crl_table_sinfcn.m.
Review the Code Replacement Table Definition
Consider reviewing the MATLAB code for your code replacement table definition. After using the tool to create an initial version of a table definition file, you can update, enhance, or copy the file in a text editor.
To review it, in MATLAB or another text editor, open the
file crl_table_sinfcn.m.
Generate a Registration File
Before you can use your code replacement table, you must register it as part of a code replacement library. Use the Code Replacement Tool to generate a registration file.
In the Code Replacement Tool, click Generate Registration File.
In the Generate registration file dialog box, edit the dialog box fields to match the following settings, and then click OK.
Registry name —
Sin Function ExampleTable list —
crl_table_sinfcnBase CRL —
NoneDescription —
Example sin function replacement

In the Select location to save the registration file dialog box, specify a location for the registration file. The location must be on the MATLAB path or in the current working folder. Save the file. The tool saves the file as
rtwTargetInfo.m.
Register the Code Replacement Table
At the command prompt, enter:
RTW.TargetRegistry.getInstance('reset');Review and Test Code Replacements
Apply your code replacement library. Verify that the code generator makes code replacements that you expect.
Check for errors. At the command line, invoke the table definition file. For example:
If an error exists in the definition file, the invocation triggers a message to appear. Fix the error and try again.
tbl = crl_table_sinfcn tbl = TflTable with properties: Version: '1.0' ReservedSymbols: [] StringResolutionMap: [] AllEntries: [2x1 RTW.TflCFunctionEntry] EnableTrace: 1|Use the Code Replacement Viewer to check your code replacement entries. For example:
crviewer('Sin Function Example')In the viewer, select entries in your table and verify that the content is what you expect. The viewer can help you detect issues such as:
Incorrect argument order.
Conceptual argument names that do not match what is expected by the code generator.
Incorrect priority settings.
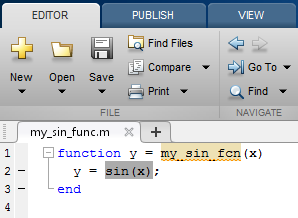
Identify existing or create new MATLAB code that calls the
sinfunction. For example:function y = my_sin_fnc(x) y = sin(x); end
Note
If you are replacing a custom function, use the
coder.replacefunction.Open the MATLAB Coder app.
Add the function that includes a call to the
sinfunction as an entry-point file. For example, addmy_sin_func.m. Define the types for the entry-point function inputs.Set Output type to generate a library or executable.
In the toolstrip, click Settings > View all settings.
Configure the code generator to use your code replacement library. On the Custom Code tab, set the Code replacement library parameter to the name of your library. For example,
Sin Function Example.Configure the code generation report. On the Debug tab, set the Always create a report, Code replacements, and Automatically launch a report if one is generated parameters.
Click Generate Code to generate C source code only and a report. You want to review your code replacements in the generated code before building an executable.
Review code replacement results in the Code Replacements Report section of the code generation report.
The report indicates that the code generator found a match and applied the replacement code for the function
sin_dbl.Review the code replacements. In the report, click the MATLAB function that triggered the replacement,
my_sin_func.m. The MATLAB Editor opens and highlights the function call that triggers the code replacement.