dlupdate
カスタム関数を使用してパラメーターを更新する
構文
説明
netUpdated = dlupdate(fun,net)fun を評価することにより、dlnetwork オブジェクト net の学習可能なパラメーターを更新します。fun は、1 つのパラメーター配列を入力引数として受け取り、更新されたパラメーター配列を返す関数への関数ハンドルです。
例
パラメーター勾配の構造体に対して L1 正則化を実行します。
サンプル入力データを作成します。
dlX = dlarray(rand(100,100,3),'SSC');畳み込み演算の学習可能なパラメーターを初期化します。
params.Weights = dlarray(rand(10,10,3,50)); params.Bias = dlarray(rand(50,1));
この例の最後に定義されている補助関数 convGradients を使用して、畳み込み演算の勾配を計算します。
gradients = dlfeval(@convGradients,dlX,params);
正則化係数を定義します。
L1Factor = 0.001;
勾配を正則化する無名関数を作成します。無名関数を使用してスカラー定数を関数に渡すことで、定数値をパラメーター変数と同じサイズおよび構造に拡張する必要がなくなります。
L1Regularizer = @(grad,param) grad + L1Factor.*sign(param);
dlupdate を使用して、各勾配に正則化関数を適用します。
gradients = dlupdate(L1Regularizer,gradients,params);
grads 内の勾配が、関数 L1Regularizer に従って正則化されました。
convGradients 関数
convGradients 補助関数は、畳み込み演算の学習可能なパラメーターと入力データ dlX のミニバッチを受け取り、学習可能なパラメーターに関する勾配を返します。
function gradients = convGradients(dlX,params) dlY = dlconv(dlX,params.Weights,params.Bias); dlY = sum(dlY,'all'); gradients = dlgradient(dlY,params); end
dlupdate を使用して、確率的勾配降下アルゴリズム (モメンタムなし) を実装するカスタム更新関数でネットワークに学習させます。
学習データの読み込み
数字の学習データを読み込みます。
[XTrain,TTrain] = digitTrain4DArrayData; classes = categories(TTrain); numClasses = numel(classes);
ネットワークの定義
ネットワーク アーキテクチャを定義し、イメージ入力層で Mean オプションを使用してイメージの平均値を指定します。
layers = [
imageInputLayer([28 28 1],'Mean',mean(XTrain,4))
convolution2dLayer(5,20)
reluLayer
convolution2dLayer(3,20,'Padding',1)
reluLayer
convolution2dLayer(3,20,'Padding',1)
reluLayer
fullyConnectedLayer(numClasses)
softmaxLayer];層配列から dlnetwork オブジェクトを作成します。
net = dlnetwork(layers);
モデル損失関数の定義
この例の最後にリストされている補助関数 modelLoss を作成します。この関数は、dlnetwork オブジェクト、および入力データのミニバッチとそれに対応するラベルを受け取り、学習可能なパラメーターについての損失とその損失の勾配を返します。
確率的勾配降下関数の定義
この例の最後にリストされている補助関数 sgdFunction を作成します。この関数は、パラメーター、およびパラメーターに関する損失の勾配を受け取り、確率的勾配降下アルゴリズムを使用して更新されたパラメーターを返します。これは次のように表されます。
ここで、 は反復回数、 は学習率、 はパラメーター ベクトル、 は損失関数です。
学習オプションの指定
学習中に使用するオプションを指定します。
miniBatchSize = 128; numEpochs = 30; numObservations = numel(TTrain); numIterationsPerEpoch = floor(numObservations./miniBatchSize);
学習率を指定します。
learnRate = 0.01;
ネットワークの学習
学習の進行状況モニター用に合計反復回数を計算します。
numIterations = numEpochs * numIterationsPerEpoch;
TrainingProgressMonitor オブジェクトを初期化します。監視オブジェクトを作成するとタイマーが開始されるため、学習ループに近いところでオブジェクトを作成するようにしてください。
monitor = trainingProgressMonitor(Metrics="Loss",Info="Epoch",XLabel="Iteration");
カスタム学習ループを使用してモデルに学習させます。各エポックについて、データをシャッフルしてデータのミニバッチをループで回します。この例の最後に定義されている関数 sgdFunction を使って dlupdate を呼び出し、ネットワーク パラメーターを更新します。各エポックの最後に、学習の進行状況を表示します。
GPU が利用できる場合、GPU で学習を行います。GPU を使用するには、Parallel Computing Toolbox™ とサポートされている GPU デバイスが必要です。サポートされているデバイスの詳細については、GPU 計算の要件 (Parallel Computing Toolbox)を参照してください。
iteration = 0; epoch = 0; while epoch < numEpochs && ~monitor.Stop epoch = epoch + 1; % Shuffle data. idx = randperm(numel(TTrain)); XTrain = XTrain(:,:,:,idx); TTrain = TTrain(idx); i = 0; while i < numIterationsPerEpoch && ~monitor.Stop i = i + 1; iteration = iteration + 1; % Read mini-batch of data and convert the labels to dummy % variables. idx = (i-1)*miniBatchSize+1:i*miniBatchSize; X = XTrain(:,:,:,idx); T = zeros(numClasses, miniBatchSize,"single"); for c = 1:numClasses T(c,TTrain(idx)==classes(c)) = 1; end % Convert mini-batch of data to dlarray. X = dlarray(single(X),"SSCB"); % If training on a GPU, then convert data to a gpuArray. if canUseGPU X = gpuArray(X); end % Evaluate the model loss and gradients using dlfeval and the % modelLoss function. [loss,gradients] = dlfeval(@modelLoss,net,X,T); % Update the network parameters using the SGD algorithm defined in % the sgdFunction helper function. updateFcn = @(net,gradients) sgdFunction(net,gradients,learnRate); net = dlupdate(updateFcn,net,gradients); % Update the training progress monitor. recordMetrics(monitor,iteration,Loss=loss); updateInfo(monitor,Epoch=epoch + " of " + numEpochs); monitor.Progress = 100 * iteration/numIterations; end end
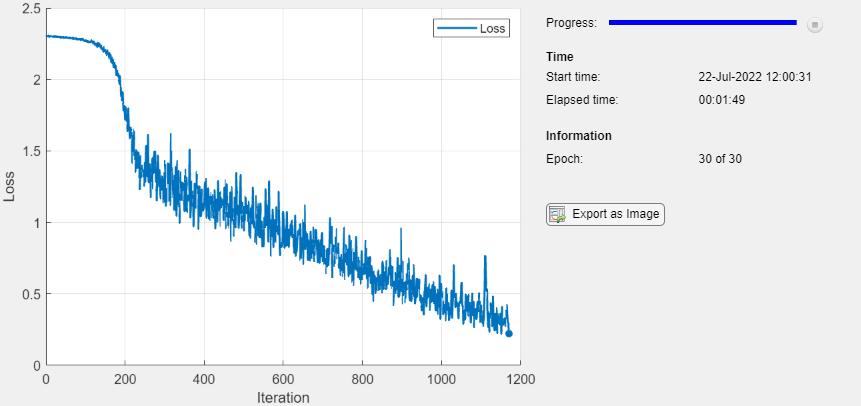
ネットワークのテスト
真のラベルをもつテスト セットで予測を比較して、モデルの分類精度をテストします。
[XTest,TTest] = digitTest4DArrayData;
次元形式 "SSCB" (空間、空間、チャネル、バッチ) を使用して、データを dlarray に変換します。GPU で予測する場合、データを gpuArray にも変換します。
XTest = dlarray(XTest,"SSCB"); if canUseGPU XTest = gpuArray(XTest); end
dlnetwork オブジェクトを使用してイメージを分類するには、関数 predict を使用してスコアが最も高いクラスを見つけます。
YTest = predict(net,XTest); [~,idx] = max(extractdata(YTest),[],1); YTest = classes(idx);
分類精度を評価します。
accuracy = mean(YTest==TTest)
accuracy = 0.9040
モデル損失関数
補助関数 modelLoss は、dlnetwork オブジェクト net、および入力データのミニバッチ X とそれに対応するラベル T を受け取り、net 内の学習可能なパラメーターについての損失とその損失の勾配を返します。勾配を自動的に計算するには、関数 dlgradient を使用します。
function [loss,gradients] = modelLoss(net,X,T) Y = forward(net,X); loss = crossentropy(Y,T); gradients = dlgradient(loss,net.Learnables); end
確率的勾配降下関数
補助関数 sgdFunction は、学習可能なパラメーター parameters、学習可能なパラメーターに対する損失の勾配、および学習率 learnRate を受け取り、確率的勾配降下アルゴリズムを使用して更新されたパラメーターを返します。これは次のように表されます。
ここで、 は反復回数、 は学習率、 はパラメーター ベクトル、 は損失関数です。
function parameters = sgdFunction(parameters,gradients,learnRate) parameters = parameters - learnRate .* gradients; end
入力引数
ネットワーク。dlnetwork オブジェクトとして指定します。
この関数は、dlnetwork オブジェクトの Learnables プロパティを更新します。net.Learnables は、3 つの変数をもつ table です。
Layer— 層の名前。string スカラーとして指定します。Parameter— パラメーター名。string スカラーとして指定します。Value— パラメーターの値。dlarrayを含む cell 配列として指定します。
ネットワークの学習可能なパラメーター。dlarray、数値配列、cell 配列、構造体、または table として指定します。
params を table として指定する場合、次の 3 つの変数を table に含めなければなりません。
Layer— 層の名前。string スカラーとして指定します。Parameter— パラメーター名。string スカラーとして指定します。Value— パラメーターの値。dlarrayを含む cell 配列として指定します。
cell 配列、構造体、table、入れ子になった cell 配列、または入れ子になった構造体を使用し、ネットワークの学習可能なパラメーターのコンテナーとして params を指定できます。cell 配列、構造体、または table に含まれる学習可能なパラメーターは、データ型が double または single である dlarray または数値でなければなりません。
入力引数 A1,...,An のデータ型、順序、およびフィールド (構造体の場合) または変数 (table の場合) は、params とまったく同じでなければなりません。
データ型: single | double | struct | table | cell
fun への追加の入力引数。dlarray オブジェクト、数値配列、cell 配列、構造体、または変数 Value をもつ table として指定します。
A1,...,An の厳密な形式は、入力ネットワークまたは学習可能なパラメーターによって異なります。dlupdate に与えることができる入力について、A1,...,An で要求される形式を次の表に示します。
| 入力 | 学習可能なパラメーター | A1,...,An |
|---|---|---|
net | 変数 Layer、Parameter、および Value を含む table net.Learnables。変数 Value は、各学習可能なパラメーターが dlarray として格納された cell 配列から成ります。 | データ型、変数、および順序が net.Learnables と同じである table。A1,...,An は、各学習可能なパラメーターに適用する関数 fun の追加の入力引数が格納された cell 配列から成る変数 Value で構成されていなければなりません。 |
params | dlarray | データ型と順序が params と同じである dlarray。 |
| 数値配列 | データ型と順序が params と同じである数値配列。 | |
| cell 配列 | データ型、構造体、および順序が params と同じである cell 配列。 | |
| 構造体 | データ型、フィールド、および順序が params と同じである構造体。 | |
変数 Layer、Parameter、および Value をもつ table。変数 Value は、各学習可能なパラメーターが dlarray として格納された cell 配列で構成されていなければなりません。 | データ型、変数、および順序が params と同じである table。A1,...,An は、各学習可能なパラメーターに適用する関数 fun の追加の入力引数が格納された cell 配列から成る変数 Value で構成されていなければなりません。 |
出力引数
ネットワーク。dlnetwork オブジェクトとして返されます。
この関数は、dlnetwork オブジェクトの Learnables プロパティを更新します。
更新されたネットワークの学習可能なパラメーター。dlarray、数値配列、cell 配列、構造体、またはネットワークの更新された学習可能なパラメーターが格納された変数 Value をもつ table として返されます。
関数 fun からの追加の出力引数。ここで、fun は複数の出力を返す関数の関数ハンドルであり、dlarray オブジェクト、数値配列、cell 配列、構造体、または変数 Value をもつ table として返されます。
X1,...,Xm の厳密な形式は、入力ネットワークまたは学習可能なパラメーターによって異なります。dlupdate に与えることができる入力について、X1,...,Xm で返される形式を次の表に示します。
| 入力 | 学習可能なパラメーター | X1,...,Xm |
|---|---|---|
net | 変数 Layer、Parameter、および Value を含む table net.Learnables。変数 Value は、各学習可能なパラメーターが dlarray として格納された cell 配列から成ります。 | データ型、変数、および順序が net.Learnables と同じである table。X1,...,Xm は、各学習可能なパラメーターに適用される関数 fun の追加の出力引数が格納された cell 配列から成る変数 Value で構成されます。 |
params | dlarray | データ型と順序が params と同じである dlarray。 |
| 数値配列 | データ型と順序が params と同じである数値配列。 | |
| cell 配列 | データ型、構造体、および順序が params と同じである cell 配列。 | |
| 構造体 | データ型、フィールド、および順序が params と同じである構造体。 | |
変数 Layer、Parameter、および Value をもつ table。変数 Value は、各学習可能なパラメーターが dlarray として格納された cell 配列で構成されていなければなりません。 | データ型、変数、および順序が params と同じである table。X1,...,Xm は、各学習可能なパラメーターに適用される関数 fun の追加の出力引数が格納された cell 配列から成る変数 Value で構成されます。 |
拡張機能
dlupdate 関数は GPU 配列入力をサポートしますが、次の使用上の注意および制限があります。
以下の入力引数の少なくとも 1 つが、
gpuArrayまたは基となるデータがgpuArray型であるdlarrayである場合、この関数は GPU で実行されます。paramsA1,...,An
詳細については、GPU での MATLAB 関数の実行 (Parallel Computing Toolbox)を参照してください。
バージョン履歴
R2019b で導入
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)