SRS を使用した NR アップリンク チャネル状態情報の推定
この例では、同期、チャネル推定、およびアップリンク チャネル状態情報 (CSI) 推定にサウンディング基準信号 (SRS) を使用する方法を示します。
はじめに
サウンディング基準信号は、アップリンク チャネルのサウンディング (同期および CSI 推定を含む) のためにユーザー端末 (UE) によって使用されるアップリンク物理量信号です。CSI は、チャネル品質インジケーター (CQI)、ランク インジケーター (RI)、およびプリコーダー マトリックス インジケーター (PMI) で構成されます。この例では、SRS を使用して周波数選択性時変ノイズ チャネルで適切な PMI を選択する方法を示します。アップリンク コードブックベースの送信では、TS 38.211 の Section 6.3.1.5 [ 1 ] で定義されているように、PMI を使用します。
この例では、以下を含むシミュレーションを実行します。
SRS の構成と送信
完全な同期と完全なチャネル推定、および実用的な同期と実用的なチャネル推定
S/N 比 (SNR) の推定
PMI の選択
PMI 選択のパフォーマンス評価
シミュレーションの長さと SNR
シミュレーションの長さを 10 ms のフレームの数で設定します。シミュレーションを行うための SNR 点を設定します。SNR は RE ごとに定義され、それぞれの受信アンテナに適用されます。
numFrames = 1; % 10 ms frames snr = 20; % SNR in dB
UE と SRS の構成
シミュレーションの主なパラメーターを設定します。これには、次が含まれます。
リソース ブロックの帯域幅 (リソース ブロックごとに 12 個のサブキャリア)
サブキャリア間隔: 15、30、60、120、240 (kHz)
サイクリック プレフィックス長: normal または extended
送信アンテナと受信アンテナの数: 1、2、4 のいずれか。
レイヤーの数。これは、送信アンテナと受信アンテナの数以下でなければなりません。
指定する SRS パラメーターには、以下が含まれます。
SRS アンテナ ポートの数: 1、2、4
SRS に割り当てられたスロットごとの OFDM シンボルの数: 1、2、4
スロット内における SRS 送信の OFDM シンボル開始位置。通常の CP の場合は (8...13)、拡張 CP の場合は (6...11) でなければなりません。
RB で指定された周波数における SRS の開始位置
帯域幅および周波数ホッピングの構成
CSRS、BSRS、およびBHop。周波数ホッピングを無効にするには、BHop >= BSRSを設定します。サブキャリアで SRS 周波数密度を指定する送信櫛: 2、4
スロット内で繰り返される SRS シンボルの数。
Repetitionシンボルのブロックでの周波数ホッピングを無効にします。繰り返しなしの場合は、Repetition = 1に設定します。スロット内の SRS の周期性とオフセット。
有効なリソース タイプは 'periodic'、'semi-persistent'、および 'aperiodic'。非周期的な SRS リソース タイプでは、スロットごとに周波数ホッピング パターンがリセットされます。
% Create UE/carrier configuration ue = nrCarrierConfig; ue.NSizeGrid = 52; % Bandwidth in number of resource blocks (52RBs at 15kHz SCS for 10MHz BW) ue.SubcarrierSpacing = 15; % 15, 30, 60, 120, 240 (kHz) ue.CyclicPrefix = 'Normal'; % 'Normal' or 'Extended' nTxAnts = 2; % Number of transmit antennas (1,2,4) nRxAnts = 2; % Number of receive antennas nLayers = min(nTxAnts,nRxAnts); % Configure a periodic multi-port SRS and enable frequency hopping srs = nrSRSConfig; srs.NumSRSSymbols = 4; % Number of OFDM symbols allocated per slot (1,2,4) srs.SymbolStart = 8; % Starting OFDM symbol within a slot srs.NumSRSPorts = nTxAnts; % Number of SRS antenna ports (1,2,4). srs.FrequencyStart = 0; % Frequency position of the SRS in BWP in RBs srs.NRRC = 0; % Additional offset from FreqStart specified in blocks of 4 PRBs (0...67) srs.CSRS = 14; % Bandwidth configuration C_SRS (0...63). It controls the allocated bandwidth to the SRS srs.BSRS = 0; % Bandwidth configuration B_SRS (0...3). It controls the allocated bandwidth to the SRS srs.BHop = 0; % Frequency hopping configuration (0...3). Set BHop < BSRS to enable frequency hopping srs.KTC = 2; % Comb number (2,4). Frequency density in subcarriers srs.Repetition = 2; % Repetition (1,2,4). It disables frequency hopping in blocks of |Repetition| symbols srs.SRSPeriod = [2 0]; % Periodicity and offset in slots. SRSPeriod(2) must be < SRSPeriod(1) srs.ResourceType = 'periodic'; % Resource type ('periodic', 'semi-persistent','aperiodic'). Use 'aperiodic' to disable inter-slot frequency hopping
同期、チャネル推定、および CSI 測定の構成
この例では、SRS 候補スロットで同期とチャネル推定を実行します。タイミングとチャネル推定は、SRS 送信を含むスロットでのみ更新されます。周波数ホッピング SRS の設定では、チャネル推定が SRS シンボルを含むリソース ブロックでのみ更新されます。SRS 送信がない場合、前のスロットのタイミングとチャネル推定値が保持され、CSI 取得に使用されます。同様に、ノイズ パワー推定値は、SRS 候補スロットでのみ更新されます。
logical 変数 practicalSynchronization は、チャネル同期の動作を制御します。true に設定した場合、この例は、受信した SRS の値に基づいて実用的な同期を実行します。false に設定した場合、この例は、完全な同期を実行します。同期は、SRS が送信されるスロットでのみ実行され、完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定の同期が維持されます。
practicalSynchronization = true;
この例では、キャリア帯域幅をいくつかのサブバンドに分割することで CSI を推定します。周波数サブバンドのサイズを RB 単位で指定します。
csiSubbandSize = 4; % Number of RBs per subband
伝播チャネル モデルの構成
TDL チャネル モデル オブジェクトを作成し、その伝播特性を指定します。チャネル遅延スプレッドと最大ドップラー シフトを選択し、シミュレーション期間とキャリア帯域幅内で時変周波数選択性チャネルを作成します。
channel = nrTDLChannel; channel.DelayProfile = 'TDL-C'; channel.DelaySpread = 40e-9; channel.MaximumDopplerShift = 30; channel.NumTransmitAntennas = nTxAnts; channel.NumReceiveAntennas = nRxAnts; channel.Seed = 5; % Set channel sample rate ofdmInfo = nrOFDMInfo(ue); channel.SampleRate = ofdmInfo.SampleRate; % Get the maximum delay of the channel chInfo = info(channel); maxChDelay = chInfo.MaximumChannelDelay; % Reset random generator for reproducibility rng('default');
処理ループ
スロットごとの CSI を測定します。CSI は、次の手順を使用して取得されます。
リソース グリッドの生成。SRS シンボルとインデックスを使用してリソース エレメント (RE) グリッドを作成します。
波形の生成。次に、生成されたグリッドを OFDM 変調します。
ノイズを含むチャネルのモデル化。TDL フェージング チャネルに波形を渡します。AWGN を付加します。各レイヤーの SNR は、受信アンテナ単位で RE ごとに定義されます。
同期と OFDM 復調の実行。完全な同期では、チャネル インパルス応答を再構築し、それを使用して受信波形を同期させます。実用的な同期では、受信波形と SRS の相関をとります。次に、同期した信号を OFDM 復調します。
チャネル推定の実行。完全なチャネル推定では、チャネル インパルス応答を再構築して OFDM 復調を実行し、チャネル推定を提供します。実用的なチャネル推定では、送信された SRS を使用します。
PMI の選択。各 CSI 推定サブバンドで最適な PMI を選択するため、SRS ベースのチャネル推定が使用されます。PMI の選択基準は、プリコーディング後の平均 signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio (SINR) を最大化するものです。
PMI の選択と SINR 損失。SINR 損失は、プリコーディング後の SINR を推定し、理想的な PMI と比較することによって計算されます。理想的な PMI は、完全なチャネル推定を使用して選択されます。
% Number of slots to simulate numSlots = numFrames*ue.SlotsPerFrame; % Total number of subcarriers and symbols per slot K = ue.NSizeGrid * 12; L = ue.SymbolsPerSlot; % Initialize arrays storing channel estimates allTxGrid = zeros([K L*numSlots nTxAnts]); slotGridSize = [K L nRxAnts nTxAnts]; hEst = zeros(slotGridSize); hestInterp = zeros(slotGridSize); hEstUpdate = zeros(slotGridSize); totalGridSize = [K L*numSlots nRxAnts nTxAnts]; allHest = zeros(totalGridSize); allHestPerfect = zeros(totalGridSize); allHestInterp = zeros(totalGridSize); % Initialize noise power estimate nvar = 0; % Calculate the number of CSI subbands for the carrier numCSISubbands = ceil(ue.NSizeGrid/csiSubbandSize); % Initialize SINR per subband, slot, and PMI maxPMI = hMaxPUSCHPrecodingMatrixIndicator(nLayers,nTxAnts); sinrSubband = zeros([numCSISubbands numSlots maxPMI+1]); % Initialize PMI matrix and SINR loss pmi = NaN(numCSISubbands,numSlots); pmiPerfect = pmi; loss = zeros(size(pmi)); % Initialize timing estimation offset offset = chInfo.ChannelFilterDelay; % Calculate SRS CDM lengths cdmLengths = hSRSCDMLengths(srs); % OFDM symbols used for CSI acquisition csiSelectSymbols = srs.SymbolStart + (1:srs.NumSRSSymbols); for nSlot = 0:numSlots-1 % Update slot counter ue.NSlot = nSlot; % Generate SRS and map to slot grid [srsIndices,srsIndInfo] = nrSRSIndices(ue,srs); srsSymbols = nrSRS(ue,srs); % Create a slot-wise resource grid empty grid and map SRS symbols txGrid = nrResourceGrid(ue,nTxAnts); txGrid(srsIndices) = srsSymbols; % Determine if the slot contains SRS isSRSSlot= ~isempty(srsSymbols); % OFDM Modulation [txWaveform,waveformInfo] = nrOFDMModulate(ue,txGrid); txWaveform = [txWaveform; zeros(maxChDelay, size(txWaveform,2))]; %#ok<AGROW> % required later to flush the channel filter to obtain the received signal % Transmission through channel [rxWaveform,pathGains] = channel(txWaveform); % Add AWGN to the received time domain waveform % Normalize noise power to take account of sampling rate, which is % a function of the IFFT size used in OFDM modulation. The SNR % is defined per RE for each receive antenna (TS 38.101-4). SNR = 10^(snr/10); N0 = 1/sqrt(2.0*nRxAnts*double(waveformInfo.Nfft)*SNR); noise = N0*complex(randn(size(rxWaveform)),randn(size(rxWaveform))); rxWaveform = rxWaveform + noise; % Perform timing offset estimation pathFilters = getPathFilters(channel); % Timing estimation is only performed in the slots where the SRS is % transmitted to keep the perfect and practical channel estimation % synchronized. if isSRSSlot if practicalSynchronization % Practical synchronization. Correlate the received waveform % with the SRS to give timing offset estimate offset = nrTimingEstimate(ue,rxWaveform,srsIndices,srsSymbols); else offset = nrPerfectTimingEstimate(pathGains,pathFilters); %#ok<UNRCH> end end % Perform OFDM demodulation rxGrid = nrOFDMDemodulate(ue,rxWaveform(1+offset:end,:)); % Perform practical channel estimation % Update channel estimates only in the symbols and RBs containing SRS % in this slot and hold the estimates from the previous slot in other % locations. nvar is not updated when there is no SRS transmission. Use % a time-averaging window that covers all the SRS symbols transmitted. if isSRSSlot % this slot contains an SRS transmission [hEst,nvar] = nrChannelEstimate(ue,rxGrid,srsIndices,srsSymbols,'AveragingWindow',[0 7],'CDMLengths',cdmLengths); % Use channel estimate from previous slot for OFDM symbols before the first SRS symbol hestInterp = repmat(hestInterp(:,end,:,:),1,ue.SymbolsPerSlot); % Update channel estimate in OFDM symbols and RB where the SRS is % present and hold all channel estimates until the end of the slot firstSymbol = srs.SymbolStart+1; lastSymbol = srs.SymbolStart + srs.NumSRSSymbols; hEstUpdate(:,firstSymbol:lastSymbol,:,:) = hEst(:,firstSymbol:lastSymbol,:,:); hEstUpdate(:,lastSymbol:L,:,:) = repmat(hEst(:,lastSymbol,:,:),1,ue.SymbolsPerSlot-lastSymbol+1); idxHEstUpdate = hEstUpdate ~= 0; % Indices of updated channel estimates hestInterp(idxHEstUpdate) = hEstUpdate(idxHEstUpdate); else % Hold previous channel estimates if this slot does not contain SRS hestInterp = repmat(hestInterp(:,end,:,:),1,ue.SymbolsPerSlot); end % PMI Selection % Select the precoder matrix indicators for a number of layers using % the interpolated channel estimates in the OFDM symbols specified by % csiSelectSymbols. The PMIs are estimated per CSI subband [pmi(:,nSlot+1),sinrSubband(:,nSlot+1,:),subbandIndices] = hPMISelect(nLayers, hestInterp(:,csiSelectSymbols,:,:), nvar, csiSubbandSize); % PMI selection SINR loss % Calculate the performance loss as a ratio of the SINR after precoding % with PMIs selected using a practical channel estimate and the SINR % after precoding with PMIs selected using a perfect channel estimate. % Calculate perfect channel estimate for perfect PMI selection hEstPerfect = nrPerfectChannelEstimate(ue,pathGains,pathFilters,offset); % Perfect noise estimate from noise realization noiseGrid = nrOFDMDemodulate(ue,noise(1+offset:end,:)); nvarPerfect = var(noiseGrid(:)); [loss(:,nSlot+1),pmiPerfect(:,nSlot+1)] = hPMISelectionSINRLoss(pmi(:,nSlot+1), nLayers, hEstPerfect(:,csiSelectSymbols,:,:), nvarPerfect); % Save a copy of all transmitted OFDM grids and channel estimates for % display purposes thisSlot = nSlot*L + (1:L); % Symbols of the current slot allTxGrid(:,thisSlot,:) = txGrid; allHest(:,thisSlot,:,:) = hEst; allHestInterp(:,thisSlot,:,:) = hestInterp; allHestPerfect(:,thisSlot,:,:) = hEstPerfect; end
結果
このセクションには、構成されたすべてのフレームについて、次の結果が表示されます。
SRS を含む送信された OFDM グリッド
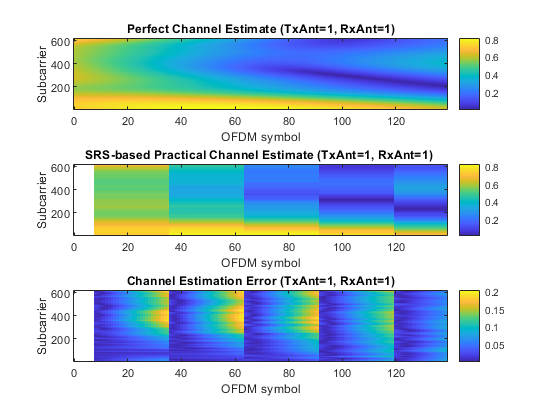
完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定、およびチャネル推定誤差。誤差は、完全なチャネル推定値と実用的なチャネル推定値の差の絶対値として計算されます。
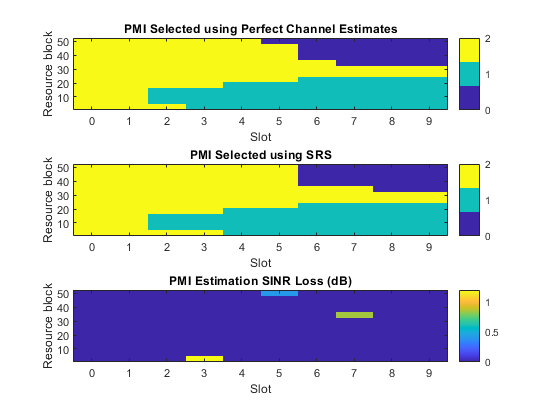
完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定を使用して選択された PMI、および PMI 絶対誤差。
最適な推定 PMI によるプリコーディング後のサブバンドごとの平均 SINR
SINR パフォーマンス損失
% Create x-axis and y-axis vectors
symbols = 0:(ue.NSlot+1)*ue.SymbolsPerSlot-1;
slots = 0:ue.NSlot;
subcarriers = 1:ue.NSizeGrid*12;
resourceBlocks = 1:ue.NSizeGrid;
SRS を含む送信された OFDM グリッドを表示します。
figure imagesc(symbols,subcarriers,abs(allTxGrid(:,:,1,1))); xlabel('OFDM symbol'); ylabel('Subcarrier'); axis xy; title('Transmitted SRS (port 1)');
完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定、および OFDM シンボルとサブキャリアごとのチャネル推定誤差を表示します。チャネル推定誤差は、完全なチャネル推定値と実用的なチャネル推定値の差の絶対値として定義されます。
% Remove first OFDM symbols not containing SRS to improve visualization of % channel estimation error hEstInterp = allHestInterp; idx = 1:(srs.SRSPeriod(2)*ue.SymbolsPerSlot + srs.SymbolStart); hEstInterp(:,idx,:,:) = NaN; hEstInterp((srs.NRB*12+1):end,:,:,:) = NaN; hChannelEstimationPlot(symbols,subcarriers,allHestPerfect,hEstInterp);
完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定を使用して、選択された PMI を表示し、スロットと RB あたりの PMI 選択の SINR 損失を表示します。SINR 損失は、プリコーディング後の推定 SINR と完全な PMI の比率として定義されます。推定 PMI は実用的なチャネル推定を使用して取得され、完全な PMI は完全なチャネル推定を使用して選択されます。
% First expand loss from subbands into RBs for display purposes
pmiRB = hExpandSubbandToRB(pmi, csiSubbandSize, ue.NSizeGrid);
pmiPerfectRB = hExpandSubbandToRB(pmiPerfect, csiSubbandSize, ue.NSizeGrid);
lossRB = hExpandSubbandToRB(loss, csiSubbandSize, ue.NSizeGrid);
hPMIPlot(slots,resourceBlocks,pmiRB,pmiPerfectRB,lossRB);
次に、完全なチャネル推定と実用的なチャネル推定の両方を使用して取得した PMI を比較します。これは、合計 PMI に対する正しい比率と、エラーが発生したリソース グリッド内の場所を示します。
numLayers = min(size(allHestInterp,[3 4])); if numLayers ~= 1 pmiErr = sum( abs(pmi - pmiPerfect) > 0, [1 2])./ sum( ~isnan(pmi), [1 2]); TotPMIEst = sum(~isnan(pmi),[1 2]); fprintf('Number of estimated PMI: %d \n', TotPMIEst); fprintf(' Number of wrong PMI: %d \n', ceil(pmiErr*TotPMIEst)); fprintf(' Relative error: %.1f (%%) \n', pmiErr*100); else fprintf('For a single layer, PMI is always 0.\n'); end
Number of estimated PMI: 130
Number of wrong PMI: 3
Relative error: 2.3 (%)
サブバンドごとに SINR を最大化する PMI を使用して、プリコーディング後に取得したスロットと RB あたりの SINR を表示します。
hBestSINRPlot(slots,resourceBlocks,sinrSubband,pmi,csiSubbandSize);

まとめとその他の調査
この例では、コードブック ベースのアップリンク送信モードで一般的に使用される同期、チャネル推定、および PMI 選択に SRS を使用する方法を示します。この例では、プリコーディング後に SINR を使用して、チャネル推定と PMI 選択のパフォーマンス損失も評価します。
より複雑な設定でチャネル推定と PMI 選択のパフォーマンスを調べることができます。SRS の周期性を高め、チャネル推定の経年劣化によってプリコーディング後にどのように遅延が発生し、SINR が悪化するかを観察します。さらに、SRS パラメーター BHop < BSRS を設定することにより、周波数ホッピング条件下でのパフォーマンスを調べることができます。この設定では、チャネル推定の経年劣化が周波数で一様ではありません。
付録
この例では、次の補助関数を使用します。
参考文献
3GPP TS 38.211. "NR; Physical channels and modulation" 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
3GPP TS 38.101-4. "NR; User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception. Part 4: Performance requirements" 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
ローカル関数
% Displays perfect and practical channel estimates and the channel % estimation error for the first transmit and receive ports. The channel % estimation error is defined as the absolute value of the difference % between the perfect and practical channel estimates. function hChannelEstimationPlot(symbols,subcarriers,allHestPerfect,allHestInterp) figure subplot(311) imagesc(symbols, subcarriers, abs(allHestPerfect(:,:,1,1))); axis xy; xlabel('OFDM symbol'); ylabel('Subcarrier'); colorbar; title('Perfect Channel Estimate (TxAnt=1, RxAnt=1)'); subplot(312) imagesc(symbols, subcarriers, abs(allHestInterp(:,:,1,1)), ... 'AlphaData',~isnan(allHestInterp(:,:,1,1))) axis xy; xlabel('OFDM symbol'); ylabel('Subcarrier'); colorbar; title('SRS-based Practical Channel Estimate (TxAnt=1, RxAnt=1) '); % Display channel estimation error, defined as the difference between the % SRS-based and perfect channel estimates subplot(313) hestErr = abs(allHestInterp - allHestPerfect); imagesc(symbols, subcarriers, hestErr(:,:,1,1),... 'AlphaData',~isnan(hestErr(:,:,1,1))); axis xy; xlabel('OFDM symbol'); ylabel('Subcarrier'); colorbar; title('Channel Estimation Error (TxAnt=1, RxAnt=1)'); end % Displays the PMI evolution and PMI estimation SINR loss over time and % frequency. The SINR loss is defined as a ratio of the SINR after % precoding with estimated and perfect PMIs. Estimated PMIs are % obtained using a practical channel estimate and perfect PMIs are % selected using a perfect channel estimate. function hPMIPlot(slots,resourceBlocks,pmiRB,pmiPerfectRB,lossRB) figure subplot(311) imagesc(slots,resourceBlocks,pmiPerfectRB,'AlphaData',~isnan(pmiPerfectRB)); axis xy; c = clim; cm = colormap; colormap( cm(1:floor(size(cm,1)/(c(2)-c(1)) -1):end,:) ); % Adjust colormap to PMI discrete values colorbar xlabel('Slot'); ylabel('Resource block'), title('PMI Selected using Perfect Channel Estimates') subplot(312) imagesc(slots,resourceBlocks,pmiRB,'AlphaData',~isnan(pmiRB)); axis xy; colorbar, xlabel('Slot'); ylabel('Resource block'), title('PMI Selected using SRS') subplot(313) imagesc(slots,resourceBlocks,lossRB,'AlphaData',~isnan(lossRB)); colormap(gca,cm) xlabel('Slot'); ylabel('Resource block'); axis xy; colorbar; title('PMI Estimation SINR Loss (dB)') end % Displays the SINR per resource block obtained after precoding with the % PMI that maximizes the SINR per subband. function hBestSINRPlot(slots,resourceBlocks,sinrSubband,pmi,csiBandSize) % Display SINR after precoding with best PMI bestSINRPerSubband = nan(size(sinrSubband,[1 2])); % Get SINR per subband and slot using best PMI [sb,nslot] = find(~isnan(pmi)); for i = 1:length(sb) bestSINRPerSubband(sb(i),nslot(i)) = sinrSubband(sb(i),nslot(i),pmi(sb(i),nslot(i))+1); end % First expand SINR from subbands into RBs for display purposes bestSINRPerRB = hExpandSubbandToRB(bestSINRPerSubband, csiBandSize, length(resourceBlocks)); figure sinrdb = 10*log10(abs(bestSINRPerRB)); imagesc(slots,resourceBlocks,sinrdb,'AlphaData',~isnan(sinrdb)); axis xy; colorbar; xlabel('Slot'); ylabel('Resource block') title('Average SINR Per Subband and Slot After Precoding with Best PMI (dB)') end % Expands a 2D matrix of values per subband in the first dimension into a % matrix of values per resource block. function rbValues = hExpandSubbandToRB(subbandValues, bandSize, NRB) lastBandSize = mod(NRB,bandSize); lastBandSize = lastBandSize + bandSize*(lastBandSize==0); rbValues = [kron(subbandValues(1:end-1,:),ones(bandSize,1));... subbandValues(end,:).*ones(lastBandSize,1)]; end