5G NR Downlink Carrier Aggregation, Demodulation, and Analysis
This example shows how to generate, aggregate, and demodulate multiple downlink carriers using 5G Toolbox™ features.
Introduction
This example generates an NR waveform with carrier aggregation (CA). To perform carrier aggregation, the example calculates the frequency offsets for the intraband contiguous CA case, as described in TS 38.104 Section 5.3A. The example also supports customized intraband noncontiguous and interband CA scenarios.
To generate an aggregated downlink waveform, the example configures a standard-compliant downlink fixed reference channel (FRC) for each component carrier. TS 38.101-1 Annex A.3 defines the physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH) FRCs for FR1 and TS 38.101-2 Annex A.3 defines the PDSCH FRCs for FR2. For the FRC waveform generation, you can specify the channel bandwidth, the subcarrier spacing, the modulation, the duplexing mode, and the cell ID. For more information on how to generate DL FRCs, see 5G NR-TM and FRC Waveform Generation.
After generating the component carriers (CCs), the example resamples the waveforms to a common sample rate and combines the CCs to generate the aggregated waveform.
Finally, the example filters and downsamples a selected CC to perform EVM measurements and PDSCH decoding.

Selection of Component Carrier Parameters
The vector ChannelBandwidths specifies the bandwidth for each CC. The length of this vector corresponds to the number of CCs. The elements of ChannelBandwidths must be in the set {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 100} MHz for FR1 and in the set {50, 100, 200, 400} MHz for FR2. TS 38.101-1 Section 5.5A.1 Table 5.5A.1-1 and TS 38.101-2 Section 5.5A.1 Table 5.5A.1-1 list the valid combinations of bandwidths for FR1 and FR2 carrier aggregation, respectively.
If the ccSpacings vector is empty, the example calculates the spacings between consecutive carriers, ccSpacings, as described in TS 38.104. To select the spacings of your choice, add the spacings to the ccSpacings vector.
% Configure three carriers for the aggregation. You can select a different % number of carriers by modifying the number of elements in the % |channelBandwidths|, |SCSs|, |modulations|, and |nCellIDs| vectors. frequencyRange = 'FR1'; % (FR1 or FR2) channelRaster = 100; % Channel raster in kHz (15, 60 or 100) channelBandwidths = [60 40 40]; % Channel bandwidths in MHz % (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, % 90 or 100 for FR1) % (50, 100, 200 or 400 for FR2) SCSs = [30 30 30]; % Subcarrier spacings in kHz % (15, 30 or 60 for FR1) % (60 or 120 for FR2) modulations = {'QPSK' '64QAM' '256QAM'}; % ('QPSK', '64QAM' or '256QAM' for FR1) % ('QPSK', '16QAM' or '64QAM' for FR2) nCellIDs = [1 2 3]; % Cell IDs duplexMode = 'TDD'; % Duplex mode ('TDD' or 'FDD') numSubframes = 10; % Number of subframes to generate per carrier % Choose the spacings between consecutive carriers, |ccSpacings|, or leave % the vector empty for calculating the spacings, as described in TS 38.104 % Section 5.3A ccSpacings = []; % MHz % Select the CC to demodulate CCofInterest = 2; % Verify the number of CCs, channel bandwidths, subcarrier spacings, % modulations, and spacings. Additionally, check that the spacings are % greater than 0. hNRVerifyCarrierParameters(length(channelBandwidths),length(SCSs),... length(modulations),length(nCellIDs),ccSpacings);
Component Carrier Configuration
Generate a configuration structure for each CC using hNRReferenceWaveformGenerator. Store the configuration structures for all CCs in a cell array.
% Establish the number of component carriers numCC = length(channelBandwidths); % CC configuration referenceChannel = cell(1,numCC); wavegen = cell(1,numCC); for i = 1:numCC % Select a reference channel, FRC, based on the chosen modulation and % frequency range referenceChannel{i} = strcat('DL-FRC-',frequencyRange,'-',modulations{i}); % Create a generator object for the above PDSCH FRC reference channel wavegen{i} = hNRReferenceWaveformGenerator(referenceChannel{i},... channelBandwidths(i),SCSs(i),duplexMode,nCellIDs(i)); end
Carrier Aggregation Parameters Calculation
To perform the carrier aggregation, you must calculate the frequency parameters described in TS 38.104, Sections 5.3 and 5.4.

Fc_offsetis a vector containing the center frequency of each CC at basebandF_offset_lowis the frequency offset from the lowerFc_offsetto the lower aggregated bandwidth edgeF_offset_highis the frequency offset from the upperFc_offsetto the upper aggregated channel bandwidth edgeF_edge_lowis the lower edge of the aggregated channel bandwidthF_edge_highis the upper edge of the aggregated channel bandwidthBW_channel_CAis the aggregated channel bandwidth of all CCs
Center the lower carrier component at baseband (Fc_offset(1) = 0 Hz) and compute the center frequency for the rest of the CCs. To determine the center frequencies by following the method described in TS 38.104 Section 5.3A, you must calculate the minimum guardbands and the minimum CC spacings. Alternatively, to select your own center frequencies, choose a nonempty ccSpacings vector.
% Get the largest SCS configuration, |SCSConfig|, among the SCS % configurations supported for each two consecutive channel bandwidths to % obtain the minimum guardband, as described in TS 38.104 Section 5.4.1.2. table = hGetGBTable(frequencyRange); % Minimum guardband table if isequal(frequencyRange,'FR1') if any(channelBandwidths(:) == 5) SCSConfig = 1; else SCSConfig = 2; end else SCSConfig = 3; end % Calculate the minimum guardband, as described in TS 38.104 Section 5.3.3 % Table 5.3.3-1 for FR1 and Table 5.3.3-1 for FR2, to obtain the minimum CC % spacings. minimumGuardBand = zeros(1,numCC); NDLRB = zeros(1,numCC); scs = strcat(num2str(2^SCSConfig*15),'kHz'); % Common SCS in kHz to extract % minimum guardband for i = 1:numCC NDLRB(i) = wavegen{i}.Config.SCSCarriers{1}.NSizeGrid; minimumGuardBand(i) = table{{scs},{strcat(num2str(channelBandwidths(i)),... 'MHz');}}; % kHz minimumGuardBand(i) = minimumGuardBand(i)*1e-3; % MHz end % Compute the minimum CC spacings, as defined in TS 38.104 Section % 5.4.1.2. Use these spacings to calculate the center frequencies and for % filtering each CC. minCCSpacings = zeros(1,numCC-1); % Minimum CC spacing for k = 2:numCC minCCSpacings(k-1) = hNRCarrierAggregationChannelSpacing( ... channelBandwidths(k-1), channelBandwidths(k), minimumGuardBand(k-1), ... minimumGuardBand(k),channelRaster,SCSConfig); % MHz end % Determine the center frequency for each CC with respect to 0 Hz. % Initially, the lower carrier frequency is at baseband (Fc_offset(1) = 0 Hz). Fc_offset = zeros(1,numCC); if isempty(ccSpacings) ccSpacings = minCCSpacings; end for k = 2:numCC Fc_offset(k) = Fc_offset(k-1) + ccSpacings(k-1); % MHz end
Calculate the frequency offsets from the lower and upper center frequencies to the lower and upper aggregated bandwidth edges, respectively, as described in TS 38.104 Section 5.3A.
F_offset_low = (NDLRB(1)*12+1)*(SCSs(1)*1e-3)/2 + minimumGuardBand(1); % MHz F_offset_high = (NDLRB(end)*12-1)*(SCSs(end)*1e-3)/2 + minimumGuardBand(end); %MHz
Compute the lower and upper edges of the aggregated channel bandwidth, TS 38.104 Section 5.3A.
F_edge_low = Fc_offset(1) - F_offset_low; % MHz F_edge_high = Fc_offset(end) + F_offset_high; % MHz
Calculate the aggregated channel bandwidth, TS 38.104 Section 5.3A
BW_channel_CA = F_edge_high - F_edge_low; % MHz fprintf('BW_channel_CA: %0.4f MHz\n',BW_channel_CA);
BW_channel_CA: 141.0800 MHz
Determine the frequency shift to center the aggregated channel bandwidth at baseband (0 Hz).
shiftToCenter = -1*(BW_channel_CA/2 + F_edge_low); % Center aggregated bandwidth at baseband Fc_offset = Fc_offset + shiftToCenter; F_edge_low = Fc_offset(1) - F_offset_low; F_edge_high = Fc_offset(end) + F_offset_high; % Display frequency band edges fprintf('F_edge_low: %0.4f MHz\n',F_edge_low);
F_edge_low: -70.5400 MHz
fprintf('F_edge_high: %0.4f MHz\n',F_edge_high);F_edge_high: 70.5400 MHz
fprintf('F_offset_low: %0.4f MHz\n',F_offset_low);F_offset_low: 30.7050 MHz
fprintf('F_offset_high: %0.4f MHz\n',F_offset_high);F_offset_high: 20.6750 MHz
% Display carrier frequencies fprintf('\n'); for i = 1:numCC fprintf('Component Carrier %d:\n',i); fprintf(' Fc: %0.4f MHz\n', Fc_offset(i)); end
Component Carrier 1:
Fc: -39.8350 MHz
Component Carrier 2:
Fc: 9.9650 MHz
Component Carrier 3:
Fc: 49.8650 MHz
Oversampling Rate Calculation
Calculate the required oversampling factors for each component carrier, OSRs, to use a common sampling rate for the aggregated waveform.
% Obtain sample rates of the component carriers CCSR = zeros(1,numCC); carriers = cell(1,numCC); for i = 1:numCC carriers{i} = nrCarrierConfig; carriers{i}.NCellID = nCellIDs(i); carriers{i}.NSizeGrid = NDLRB(i); carriers{i}.SubcarrierSpacing = SCSs(i); carriers{i}.CyclicPrefix = wavegen{i}.Config.BandwidthParts{1}.CyclicPrefix; info = nrOFDMInfo(carriers{i}); CCSR(i) = info.SampleRate; % Hz end % Calculate the oversampling ratio for the largest BW CC to ensure the % waveform occupies a maximum of 85% of the total bandwidth, |bwfraction| bwfraction = 0.85; % Bandwidth utilization of 85% OSR = (BW_channel_CA/bwfraction)/(max(CCSR)/1e6); % To simplify the resampling operation, choose an oversampling ratio which % is a power of 2: calculate the next power of two above OSR OSR = 2^ceil(log2(OSR)); % Calculate the overall sample rate for the aggregated waveform SR = OSR*max(CCSR); % Hz fprintf('\nOutput sample rate: %0.4f Ms/s\n\n',SR/1e6);
Output sample rate: 245.7600 Ms/s
% Calculate the individual oversampling factors for the component carriers
OSRs = SR./CCSR;Waveform Generation and Carrier Aggregation
Call the generateWaveform function from the hNRReferenceWaveformGenerator helper file to generate the waveform for each CC. Resample each carrier to a common sample rate. Finally, use comm.MultibandCombiner to frequency modulate the carriers to the appropriate center frequency, and aggregate the CCs to form the combined waveform.
% Generate and aggregate the component carriers tmwaveinfo = cell(1,numCC); waveInfo = cell(1,numCC); resourcesInfo = cell(1,numCC); clear waveform for i = numCC:-1:1 % Generate each CC [wf,waveInfo{i},resourcesInfo{i}] = generateWaveform(wavegen{i},... numSubframes); % Resample the CCs so that they have the same sample rate waveform(:,i) = resample(wf,OSRs(i),1)/OSRs(i); end % Aggregate all CC. comm.MultibandCombiner applies the frequency offsets % and combines the resulting signals together. carrierAggregator = comm.MultibandCombiner(InputSampleRate = SR,... FrequencyOffsets = Fc_offset*1e6,... OutputSampleRateSource = 'Property',... OutputSampleRate = SR); waveform = carrierAggregator(waveform);
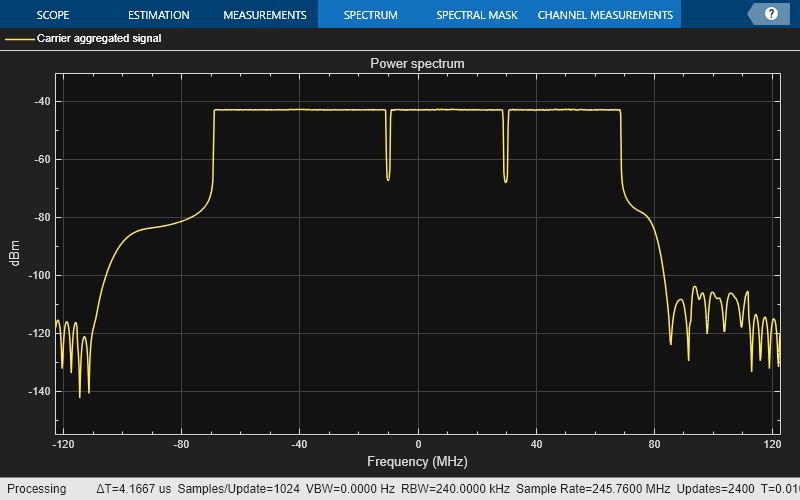
Plot Carrier Aggregated Spectrum
Display the spectrum of the carrier aggregated signal. This example does not upconvert the waveform to radio frequency (RF), the center of the aggregated bandwidth is at baseband (0 Hz).
% Create spectrum analyzer object specPlot = spectrumAnalyzer("SampleRate",SR,... "AveragingMethod","exponential",... "ForgettingFactor",1, ... "ChannelNames","Carrier aggregated signal",... "ShowLegend",true,... "Title","Power spectrum" ); % Plot spectrum specPlot(waveform);
CC Demodulation and Filtering
Choose a CC, then demodulate, filter and downsample the CC of your choice, following these steps.
Bring the CC to baseband (0 Hz)
Calculate the passband and stopband frequencies of the filter
Filter out the neighboring CCs by using the designed filter and downsample the CC.
% Verify carrier of interest ID if CCofInterest > numCC || CCofInterest <= 0 || mod(CCofInterest,1) ~= 0 error('nr5g:NRDownlinkCarrierAggregationExample:CCOutOfRange',... 'Cannot demodulate CC number %d, choose an integer number that falls between 1 and %d\n',... CCofInterest, numCC) ; end fprintf(1,'Extracting CC number %d: \n', CCofInterest);
Extracting CC number 2:
% Define downsampling filter order filterOrder = 201; % Precalculate the filter passband and stopband values for all CC firPassbandVec = (NDLRB*12-1).*(SCSs*1e-3)/2 / (SR/1e6/2); firStopbandVec = hNRCarrierAggregationStopband(minCCSpacings,NDLRB,SR,SCSs); % Choose the passband and stopband values for the carrier of interest firPassband = firPassbandVec(CCofInterest); firStopband = firStopbandVec(CCofInterest); % Pad signal with zeros to consider filter transient response length waveform = [waveform; zeros(filterOrder*2,size(waveform,2))]; % Center the carrier of interest at 0 Hz frequencyShifter = comm.PhaseFrequencyOffset(SampleRate = SR,... FrequencyOffset = -Fc_offset(CCofInterest)*1e6); demodulatedCC = frequencyShifter(waveform); % To ease the filter design requirements, apply the downsampling in two % stages if necessary. Use a downsampling factor of 4 in the initial stage. % If the quality of the resulting signal is not as required, consider a % different filter design in this initial stage. if (firStopband < 0.1) % Downsample by 4 in the initial stage SRC = 4; demodulatedCC = resample(demodulatedCC,1,SRC); % Update passband and stopband values firPassband = firPassband * SRC; firStopband = firStopband * SRC; else % Do not apply an extra downsampling SRC = 1; end % Design the lowpass filter to filter out the CC of your choice frEdges = [0 firPassband firStopband 1]; firFilter = dsp.FIRFilter; firFilter.Numerator = firpm(filterOrder,frEdges,[1 1 0 0]); % Display the response of the designed filter freqz(firFilter);

% Filter the signal to extract the component of interest rxWaveform = firFilter(demodulatedCC); filteredSpecPlot = spectrumAnalyzer("SampleRate",SR,... "AveragingMethod","exponential",... "ForgettingFactor",1,... "ChannelNames",{"Carrier aggregated signal", "Filtered signal"},... "ShowLegend",true,... "Title","Power spectrum"); filteredSpecPlot([demodulatedCC, rxWaveform]);
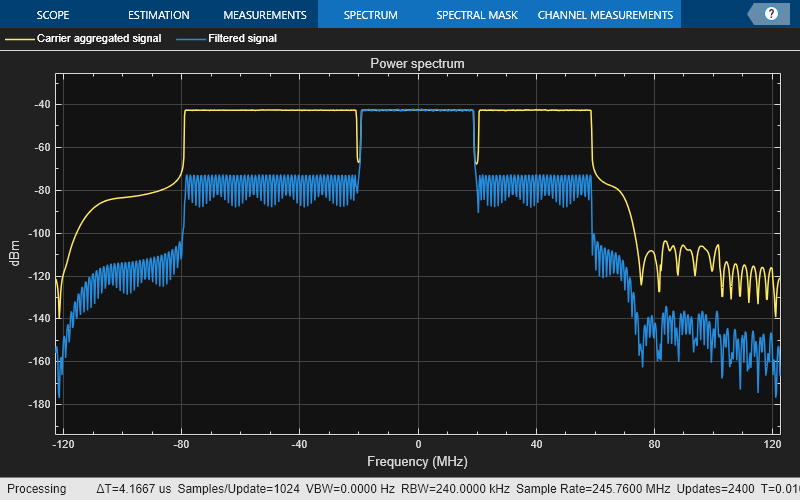
% Downsample the filtered carrier to its baseband rate
rxWaveform = downsample(rxWaveform,OSRs(CCofInterest)/SRC);EVM Measurements
The hNRDownlinkEVM helper function returns the PDSCH EVM by performing synchronization, OFDM demodulation, channel estimation, and equalization. The function displays the EVM for each slot and frame and the overall EVM averaged over the entire input waveform. The function also plots these graphs: EVM per OFDM symbol, slot, subcarrier, and overall EVM.
% Parameterize the channel estimator configuration using the structure |cfg| cfg = struct(); cfg.Evm3GPP = true; % To measure EVM as defined in TS 38.104, Annex B(FR1) % / Annex C(FR2) set |Evm3GPP| to |true|. cfg.TargetRNTIs = []; cfg.PlotEVM = true; cfg.DisplayEVM = true; cfg.Label = wavegen{CCofInterest}.ConfiguredModel{1}; % Perform EVM measurements and plot results [evmInfo,eqSym,refSym] = hNRDownlinkEVM(wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config,... rxWaveform,cfg);
EVM stats for BWP idx : 1 Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 1: 2.797 7.912% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 1: 2.748 6.320% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 1: 2.797 7.912% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 1: 2.748 6.320% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 2: 2.797 7.472% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 2: 2.787 6.044% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 2: 2.797 7.472% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 2: 2.787 6.044% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 3: 2.820 7.541% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 3: 2.758 6.577% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 3: 2.820 7.541% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 3: 2.758 6.577% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 4: 2.802 7.551% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 4: 2.744 5.920% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 4: 2.802 7.551% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 4: 2.744 5.920% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 5: 2.800 7.593% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 5: 2.766 6.222% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 5: 2.800 7.593% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 5: 2.766 6.222% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 6: 2.817 7.948% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 6: 2.731 6.452% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 6: 2.817 7.948% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 6: 2.731 6.452% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 10: 2.790 8.589% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 10: 2.747 6.573% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 10: 2.790 8.589% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 10: 2.747 6.573% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 11: 2.788 7.994% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 11: 2.750 6.581% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 11: 2.788 7.994% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 11: 2.750 6.581% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 12: 2.806 8.468% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 12: 2.780 6.476% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 12: 2.806 8.468% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 12: 2.780 6.476% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 13: 2.819 7.483% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 13: 2.731 6.164% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 13: 2.819 7.483% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 13: 2.731 6.164% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 14: 2.810 7.989% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 14: 2.757 6.405% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 14: 2.810 7.989% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 14: 2.757 6.405% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 15: 2.797 8.219% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 15: 2.796 6.437% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 15: 2.797 8.219% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 15: 2.796 6.437% Low edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 16: 2.803 7.699% Low edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 16: 2.740 6.302% High edge PDSCH RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 16: 2.803 7.699% High edge DM-RS RMS EVM, Peak EVM, slot 16: 2.740 6.302% Averaged low edge RMS EVM, frame 0: 2.804% Averaged high edge RMS EVM, frame 0: 2.804% Averaged RMS EVM frame 0: 2.804%

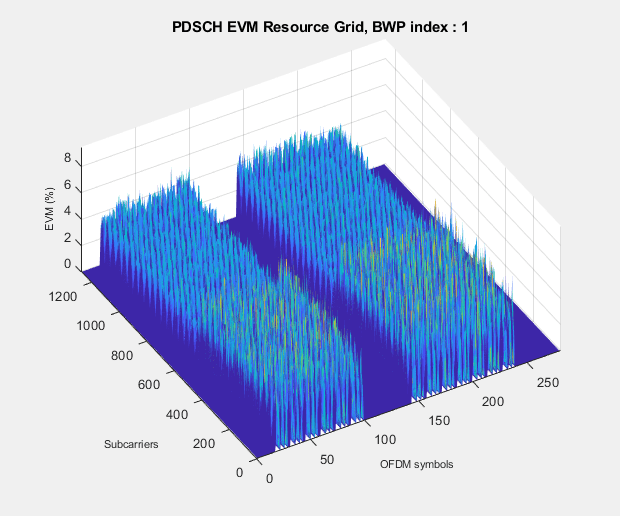
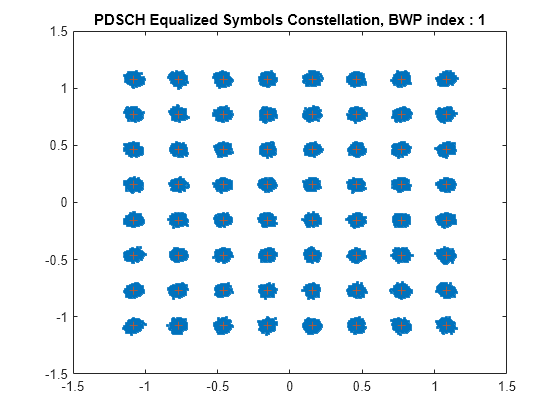
Averaged overall PDSCH RMS EVM: 2.804% Overall PDSCH Peak EVM = 8.5895%
PDSCH Decoding
Decode the PDSCH of the recovered signal and check the resulting CRC for errors.
% Perform time synchronization on the input waveform offset = nrTimingEstimate(carriers{CCofInterest},rxWaveform,... waveInfo{CCofInterest}.ResourceGridBWP); rxWaveform = rxWaveform(1+offset:end,:); % Perform OFDM demodulation rxGrid = nrOFDMDemodulate(carriers{CCofInterest},rxWaveform); % Get the allocated slots and OFDM symbols per slot allocatedSlots = zeros(1,size(resourcesInfo{CCofInterest}.WaveformResources.PDSCH.Resources,2)); for i=1:length(allocatedSlots) allocatedSlots(i) = resourcesInfo{CCofInterest}.WaveformResources.PDSCH.Resources(i).NSlot; end L = carriers{CCofInterest}.SymbolsPerSlot; % OFDM symbols per slot % Create a DLSCH decoder System object decodeDLSCH = nrDLSCHDecoder; decodeDLSCH.MultipleHARQProcesses = false; decodeDLSCH.TargetCodeRate = wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config.PDSCH{1}.TargetCodeRate; decodeDLSCH.LDPCDecodingAlgorithm = 'Normalized min-sum'; decodeDLSCH.MaximumLDPCIterationCount = 6; for NSlot=1:length(allocatedSlots) % Extract slot SlotID = allocatedSlots(NSlot); rxSlot = rxGrid(:,(1:L)+(SlotID*L),:); refSlot = waveInfo{CCofInterest}.ResourceGridBWP(:,(1:L)+(SlotID*L),:); % Perform channel estimation [estChannelGrid,noiseEst] = nrChannelEstimate(carriers{CCofInterest},... rxSlot,refSlot); % Get PDSCH resource elements from the received grid and channel estimate pdschIndices = resourcesInfo{CCofInterest}.WaveformResources.PDSCH.Resources(NSlot).ChannelIndices; [pdschRx,pdschHest] = nrExtractResources(pdschIndices,rxSlot,estChannelGrid); % Perform equalization [pdschEq,csi] = nrEqualizeMMSE(pdschRx,pdschHest,noiseEst); % Perform layer demapping, symbol demodulation, and descrambling modulation = wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config.PDSCH{1}.Modulation; RNTI = wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config.PDSCH{1}.RNTI; [dlschLLRs,rxSymbols] = nrPDSCHDecode(pdschEq,modulation,... carriers{CCofInterest}.NCellID,RNTI,noiseEst); % Scale LLRs by CSI csi = nrLayerDemap(csi); % CSI layer demapping NumCW = size(resourcesInfo{CCofInterest}.WaveformResources.PDSCH.Resources(NSlot).Codeword,2); for cwIdx = 1:NumCW Qm = length(dlschLLRs{cwIdx})/length(rxSymbols{cwIdx}); % Bits per symbol csi{cwIdx} = repmat(csi{cwIdx}.',Qm,1); % Expand by each bit per symbol dlschLLRs{cwIdx} = dlschLLRs{cwIdx} .* csi{cwIdx}(:); % Scaled symbols end % Calculate the transport block sizes for the codewords in the slot trBlkSize = resourcesInfo{CCofInterest}.WaveformResources.PDSCH.Resources(NSlot).TransportBlockSize; % Decode the DL-SCH transport channel decodeDLSCH.TransportBlockLength = trBlkSize; NLayers = wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config.PDSCH{1}.NumLayers; RVSequence = wavegen{CCofInterest}.Config.PDSCH{1}.RVSequence; [decbits,crc] = decodeDLSCH(dlschLLRs,modulation,NLayers,RVSequence); % Display the CRC status if crc disp(['Slot ' num2str(SlotID) ': CRC failed']); else disp(['Slot ' num2str(SlotID) ': CRC passed']); end end
Slot 1: CRC passed Slot 2: CRC passed Slot 3: CRC passed Slot 4: CRC passed Slot 5: CRC passed Slot 6: CRC passed Slot 10: CRC passed Slot 11: CRC passed Slot 12: CRC passed Slot 13: CRC passed Slot 14: CRC passed Slot 15: CRC passed Slot 16: CRC passed
Bibliography
3GPP TS 38.104 "NR; Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception" 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
3GPP TS 38.101-1 "NR; User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 1 Standalone." 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
3GPP TS 38.101-2 "NR; User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception: Part 2: Range 2 Standalone." 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
Local Functions
function table = hGetGBTable(frequencyRange) %hGetGBTable Minimum guardband table % GB = hGetGBTable(FREQUENCYRANGE) extracts the minimum guardband, GB, in % kHz for the frequency range, FREQUENCYRANGE. For FR1, the table is % described in TS 38.104 Table 5.3.3-1 and for FR2, the table is % described in TS 38.104 Table 5.3.3-2. if isequal(frequencyRange,'FR1') % GB MHz 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 60 70 80 90 100 gbTable = [242.5 312.5 382.5 452.5 522.5 592.5 572.5 552.5 712.5 692.5 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN; % 15 kHz 505 665 645 805 785 945 925 905 1065 1045 825 965 925 885 845; % 30 kHz NaN 1010 990 1330 1310 1290 1630 1610 1590 1570 1530 1490 1450 1410 1370]; % 60 kHz % Package GB array into a table table = array2table(gbTable,"RowNames",["15kHz","30kHz","60kHz"],"VariableNames",["5MHz", "10MHz", "15MHz", "20MHz", "25MHz", "30MHz", "35MHz", "40MHz", "45MHz", "50MHz", "60MHz", "70MHz", "80MHz", "90MHz", "100MHz"]); table.Properties.Description = 'TS 38.104 Table 5.3.3-1: Minimum guardband (kHz) FR1'; else % GB MHz 50 100 200 400 gbTable = [1210 2450 4930 NaN; % 60 kHz 1900 2420 4900 9860]; % 120 kHz % Package GB array into a table table = array2table(gbTable,"RowNames",["60kHz","120kHz"],"VariableNames",["50MHz", "100MHz", "200MHz", "400MHz"]); table.Properties.Description = 'TS 38.104 Table 5.3.3-2: Minimum guardband (kHz) FR2'; end end function spacing = hNRCarrierAggregationChannelSpacing(BW1,BW2,GB1,GB2,channelRaster,mu) %hNRCarrierAggregationChannelSpacing NR nominal channel spacing % SPACING = hNRCarrierAggregationChannelSpacing(BW1,BW2,GB1,GB2,CHANNELRASTER,MU) % is the NR nominal channel spacing in MHz between two adjacent carriers % with bandwidths BW1 and BW2, also expressed in MHz. GB1 and GB2 are the % minimum guardbands for bandwidth BW1 and bandwidth BW2, respectively. % The NR nominal channel calculation depends on the channel raster, % CHANNELRASTER, and the subcarrier spacing (SCS) configuration, MU, % which is the largest SCS value among the SCS configurations supported % for both of the channel bandwidths. switch channelRaster case 15 % Nominal channel spacing (MHz) as defined in TS 38.104 5.4.1.2 % for NR operating bands with a 15 kHz channel raster n = mu; spacing = floor((BW1+BW2-2*abs(GB1-GB2))/(0.015*2^(n+1)))*(0.015*2^(n)); case 60 % Nominal channel spacing (MHz) as defined in TS 38.104 5.4.1.2 % for NR operating bands with a 60 kHz channel raster n = mu-2; spacing = floor((BW1+BW2-2*abs(GB1-GB2))/(0.06*2^(n+1)))*(0.06*2^(n)); case 100 % Nominal channel spacing (MHz) as defined in TS 38.104 5.4.1.2 % for NR operating bands with a 100 kHz channel raster spacing = floor((BW1+BW2-2*abs(GB1-GB2))/0.6)*0.3; otherwise error('nr5g:hNRCarrierAggregationChannelSpacing:IncorrectRaster','The channel raster (%.2fkHz) must be 15, 60 or 100kHz.',channelRaster); end end function stopband = hNRCarrierAggregationStopband(ccSpacing,NDLRB,SR,SCS) %hNRCarrierAggregationStopband Stopband values for NR carrier selection % STOPBAND = hNRCarrierAggregationStopband(CCSPACING,NDLRB,SR,SCS) % calculates the stopband values, STOPBAND, in a 5G carrier aggregation % scenario given the component carrier spacing vector CCSPACING, the % vector of bandwidths for each CC, NDLRB, the sampling rate of the % aggregated waveform, SR, and the subcarrier spacing of each component % carrier, SCS. numCC = length(NDLRB); stopband = zeros(numCC,1); for i = 1:numCC % Compute two possible stopbands based on spacing with component % carrier before and after if (i > 1) % There is a carrier component before the one being considered frStopband1 = ccSpacing(i-1)-(NDLRB(i-1)*12-2)*(SCS(i-1)*1e-3)/2; else frStopband1 = NaN; end if (i < numCC) % There is a carrier component after the one being considered frStopband2 = ccSpacing(i)-(NDLRB(i+1)*12-2)*(SCS(i+1)*1e-3)/2; else frStopband2 = NaN; end % Take the minimum value stopband(i) = min(frStopband1,frStopband2) / (SR/1e6/2); end end function hNRVerifyCarrierParameters(numberBWs,numberSCSs,numberModulations,numberCellIDs,spacings) %hNRVerifyCarrierParameters Carrier aggregation parameters verification % hNRVerifyCarrierParameters(NUMBERBWS,NUMBERSCSS,NUMBERMODULATIONS,NUMBERCELLIDS,SPACINGS) % verifies if the number of channel bandwidths, NUMBERBWS, subcarrier % spacings, NUMBERSCSS, modulations, NUMBERMODULATIONS, and cell IDs, % NUMBERCELLIDS, are the same. This function also checks the spacing % between two consecutive carriers, SPACINGS. % Verify that there is a channel bandwidth, a subcarrier spacing and a % modulation per carrier if ~(numberBWs == numberSCSs && numberSCSs == numberModulations && numberModulations == numberCellIDs) error('nr5g:hNRVerifyCarrierParameters:NumberCCConfigParams','Please specify the same number of channel bandwidths (%d), SCSs (%d), modulations (%d) and cell IDs (%d).',numberBWs,numberSCSs,numberModulations,numberCellIDs); end % Check if there are at least two component carriers numCC = numberBWs; if numCC<2 error('nr5g:hNRVerifyCarrierParameters:OneCarrier','Please specify more than one channel bandwidth value.'); end % Check the number of spacings and their values if ~isempty(spacings) if length(spacings) ~= numCC-1 error('nr5g:hNRVerifyCarrierParameters:NumberSpacings','The number of CC spacings (%d) is not compatible with the number of carriers (%d). Please specify one CC spacing per two consecutive carriers.',length(spacings),numCC); end if any(spacings<=0) error('nr5g:hNRVerifyCarrierParameters:SpacingsLowerEqualZero','The CC spacings should be greater than 0.'); end end end