wcsens
(Not recommended) Calculate worst-case sensitivity and complementary sensitivity functions of plant-controller feedback loop
wcsens is not recommended. Use wcgain instead. For more information, see Version History.
Syntax
wcst = wcsens(L) wcst = wcsens(L,type) wcst = wcsens(L,opt) wcst = wcsens(L,type,scaling) wcst = wcsens(L,type,scaling,opt) wcst = wcsens(P,C) wcst = wcsens(P,C,type) wcst = wcsens(P,C,opt) wcst = wcsens(P,C,type,scaling) wcst = wcsens(P,C,type,scaling,opt)
Description
The sensitivity function, S = (I + L)–1, and the complementary sensitivity function, T = L(I + L)–1, where L is the loop gain matrix associated with the input, CP, or output, PC, are two transfer functions related to the robustness and performance of the closed-loop system. The multivariable closed-loop interconnection structure, shown below, defines the input/output sensitivity, complementary sensitivity and loop transfer functions.
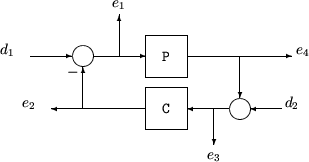
The following table gives the values of the input and output sensitivity functions for this control structure.
Description | Equation |
|---|---|
Input sensitivity Si (closed-loop transfer function from d1 to e1) | Si = (I + CP)–1 |
Input complementary sensitivity Ti (closed-loop transfer function from d1 to e2) | Ti = CP(I + CP)–1 |
Output sensitivity So (closed-loop transfer function from d2 to e3) | So = (I + PC)–1 |
Output complementary sensitivity To (closed-loop transfer function from d2 to e4) | To = PC(I + PC)–1 |
Input loop transfer function Li | Li = CP |
Output loop transfer function Lo | Lo = PC |
wcst = wcsens(L) calculates the worst-case
sensitivity and complementary sensitivity functions for the loop transfer matrix
L in feedback in negative feedback with an identity matrix. If
L is a uss object, the frequency range and number of
points are chosen automatically.
wcst = wcsens(P,C) calculates the worst-case
sensitivity and complementary sensitivity functions for the feedback loop C
in negative feedback with P. C should only be the compensator in the
feedback path, not any reference channels, if it is a 2-dof architecture (see
loopsens). If P and C are
ss/tf/zpk or uss objects, the frequency range and
number of points are chosen automatically. wcst is a structure with the
following substructures:
Fields of wcst
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Si | Worst-case input-to-plant sensitivity function |
Ti | Worst-case input-to-plant complementary sensitivity function |
So | Worst-case output-to-plant sensitivity function |
To | Worst-case output-to-plant complementary sensitivity function |
PSi | Worst-case plant times input-to-plant sensitivity function |
CSo | Worst-case compensator times output-to-plant sensitivity function |
Stable | 1 if nominal closed loop is stable, 0 otherwise. |
Each sensitivity substructure is a structures with five fields MaximumGain,
BadUncertainValues, System, BadSystem, Sensitivity derived from the outputs of
wcgain.
Fields of Si, So, Ti, To, PSi, CSo
Field | Description |
|---|---|
MaximumGain |
|
BadUncertainValues |
|
System | Uncertain sensitivity function ( |
BadSystem | Worst-case system based on the uncertain object values in
|
Sensitivity |
|
wcst = wcsens(L,type) and
wcst
= wcsens(P,C,type) allow selection of individual Sensitivity and
Complementary Sensitivity functions, type, as
'Si','Ti','So','To','PSi','CSo' corresponding to the sensitivity and
complementary sensitivity functions. Setting type to 'S'
or 'T' selects all sensitivity functions
('Si','So','PSi','CSo') or all complementary sensitivity functions
('Ti','To'). Similarly, setting type to
'Input' or 'Output' selects all input Sensitivity
functions ('Si','Ti','PSi') or all output sensitivity functions
('So,'To','CSo'). 'All' selects all six Sensitivity
functions for analysis (default). type may also be a cell array containing
multiple function types, such as {'Si','To'}.
wcst = wcsens(L,type,scaling) and
wcst
= wcsens(P,C,type,scaling) add a scaling to the
worst-case sensitivity analysis. scaling is one of the following:
'Absolute'(default) — Calculates bounds on the maximum gain of the uncertain sensitivity function.'Relative'— Finds bounds on the maximum relative gain of the uncertain sensitivity function. That is, the maximum relative gain is the largest ratio of the worst-case gain and the nominal gain evaluated at each frequency point in the analysis.LTI model (
ss,tf,zpk, orfrd) — Calculates bounds on the maximum scaled gain of the uncertain sensitivity function. The input/output dimensions of the LTI model must be either 1-by-1, or compatible withPandC.
You can also combine type and scaling in a cell
array, e.g.
wcst = wcsens(P,C,{'Ti','So'},'Abs','Si','Rel','PSi',wt)
wcst = wcsens(P,C,opt) or
wcst
= wcsens(P,C,type,scaling,opt) specifies options for the worst-case
gain calculation as defined by opt. (See wcgainOptions
for more details on the options for wcsens.)
The sensitivity of the worst-case sensitivity calculations to the individual uncertain
components can be determined using the options object opt. To compute the
sensitivities to the individual uncertain components, create a
wcgainOptions options object, and set the Sensitivity
property to 'on'.
opt = wcgainOptions('Sensitivity','on');
wcst = wcsens(P,C,opt)
Examples
The following constructs a feedback loop with a first order plant and a proportional-integral controller. The time constant is uncertain and the model also includes an multiplicative uncertainty. The nominal (input) sensitivity function has a peak of 1.09 at omega = 1.55 rad/sec. Since the plant and controller are single-input / single-output, the input/output sensitivity functions are the same.
delta = ultidyn('delta',[1 1]);
tau = ureal('tau',5,'range',[4 6]);
P = tf(1,[tau 1])*(1+0.25*delta);
C=tf([4 4],[1 0]);
looptransfer = loopsens(P,C);
Snom = looptransfer.Si.NominalValue;
norm(Snom,inf)
ans =
1.0864
wcsens is then used to compute the worst-case sensitivity function as
the uncertainty ranges over its possible values. More information about the fields in
wcst.Si can be found in the wcgain help. The
badsystem field of wcst.Si contains the worst case
sensitivity function. This worst case sensitivity has a peak of 1.52 at omega = 1.02 rad/sec.
The maxgainunc field of wcst.Si contains the
perturbation that corresponds to this worst case sensitivity function.
wcst = wcsens(P,C)
wcst =
Si: [1x1 struct]
Ti: [1x1 struct]
So: [1x1 struct]
To: [1x1 struct]
PSi: [1x1 struct]
CSo: [1x1 struct]
Stable: 1
Swc = wcst.Si.BadSystem;
omega = logspace(-1,1,50);
bodemag(Snom,'-',Swc,'-.',omega);
legend('Nominal Sensitivity','Worst-Case Sensitivity',...
'Location','SouthEast')
norm(Swc,inf)
ans =
1.5075
For multi-input/multi-output systems the various input/output sensitivity functions will, in general, be different.
References
J. Shin, G.J. Balas, and A.K. Packard, “Worst case analysis of the X-38 crew return vehicle flight control system,” AIAA Journal of Guidance, Dynamics and Control, vol. 24, no. 2, March-April 2001, pp. 261-269.
Version History
Introduced before R2006aSee Also
loopsens | robstab | usubs | wcgain | wcdiskmargin