modelCalibration
Compute R-square, RMSE, correlation, and sample mean error of predicted and observed EADs
Since R2023a
Syntax
Description
CalMeasure = modelCalibration(eadModel,data)modelCalibration supports comparison against a reference
model and also supports different correlation types. By default,
modelCalibration computes the metrics in the EAD scale. You
can use the ModelLevel name-value argument to compute metrics
using the underlying model's transformed scale.
[
specifies options using one or more name-value arguments in addition to the input
arguments in the previous syntax.CalMeasure,CalData] = modelCalibration(___,Name=Value)
Examples
This example shows how to use fitEADModel to create a Tobit model and then use modelCalibration to compute the R-Square, RMSE, correlation, and sample mean error of predicted and observed EAD.
Load EAD Data
Load the EAD data.
load EADData.mat
head(EADData) UtilizationRate Age Marriage Limit Drawn EAD
_______________ ___ ___________ __________ __________ __________
0.24359 25 not married 44776 10907 44740
0.96946 44 not married 2.1405e+05 2.0751e+05 40678
0 40 married 1.6581e+05 0 1.6567e+05
0.53242 38 not married 1.7375e+05 92506 1593.5
0.2583 30 not married 26258 6782.5 54.175
0.17039 54 married 1.7357e+05 29575 576.69
0.18586 27 not married 19590 3641 998.49
0.85372 42 not married 2.0712e+05 1.7682e+05 1.6454e+05
rng('default'); NumObs = height(EADData); c = cvpartition(NumObs,'HoldOut',0.4); TrainingInd = training(c); TestInd = test(c);
Select Model Type
Select a model type for Tobit or Regression.
ModelType =  "Tobit";
"Tobit";Select Conversion Measure
Select a conversion measure for the EAD response values.
ConversionMeasure =  "LCF";
"LCF";Create Tobit EAD Model
Use fitEADModel to create a Tobit model using EADData.
eadModel = fitEADModel(EADData(TrainingInd,:),ModelType,PredictorVars={'UtilizationRate','Age','Marriage'}, ...
ConversionMeasure=ConversionMeasure,DrawnVar="Drawn",LimitVar="Limit",ResponseVar="EAD");
disp(eadModel); Tobit with properties:
CensoringSide: "both"
LeftLimit: 0
RightLimit: 1
ModelID: "Tobit"
Description: ""
UnderlyingModel: [1×1 risk.internal.credit.TobitModel]
PredictorVars: ["UtilizationRate" "Age" "Marriage"]
ResponseVar: "EAD"
LimitVar: "Limit"
DrawnVar: "Drawn"
ConversionMeasure: "lcf"
Display the underlying model. The underlying model's response variable is the transformation of the EAD response data. Use the 'LimitVar' and 'DrwanVar' name-value arguments to modify the transformation.
disp(eadModel.UnderlyingModel);
Tobit regression model:
EAD_lcf = max(0,min(Y*,1))
Y* ~ 1 + UtilizationRate + Age + Marriage
Estimated coefficients:
Estimate SE tStat pValue
__________ __________ _______ __________
(Intercept) 0.22467 0.031504 7.1315 1.2783e-12
UtilizationRate 0.4714 0.02066 22.817 0
Age -0.0014209 0.00077019 -1.8449 0.065163
Marriage_not married -0.010543 0.015835 -0.6658 0.5056
(Sigma) 0.3618 0.0049955 72.426 0
Number of observations: 2627
Number of left-censored observations: 0
Number of uncensored observations: 2626
Number of right-censored observations: 1
Log-likelihood: -1057.9
Predict EAD
EAD prediction operates on the underlying compact statistical model and then transforms the predicted values back to the EAD scale. You can specify the predict function with different options for the 'ModelLevel' name-value argument.
predictedEAD = predict(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel="ead"); predictedConversion = predict(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel="ConversionMeasure");
Validate EAD Model
For model validation, use modelDiscrimination, modelDiscriminationPlot, modelCalibration, and modelCalibrationPlot.
Use modelDiscrimination and then modelDiscriminationPlot to plot the ROC curve.
ModelLevel ="ead"; [DiscMeasure1,DiscData1] = modelDiscrimination(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel); modelDiscriminationPlot(eadModel,EADData(TestInd, :),ModelLevel=ModelLevel,SegmentBy="Marriage");
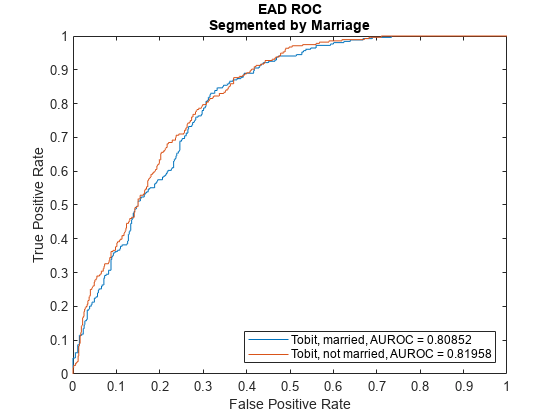
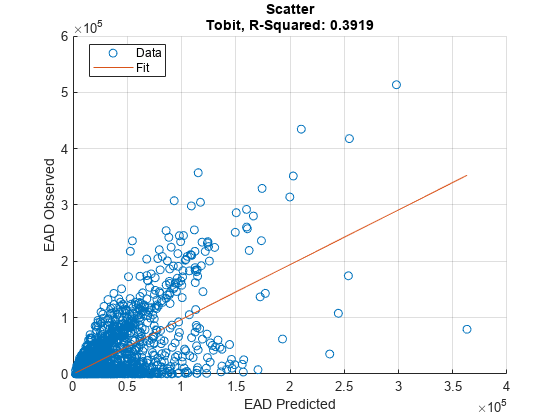
Use modelCalibration, and modelCalibrationPlot to show a scatter plot of the predictions.
YData =  "Observed";
[CalMeasure1,CalData1] = modelCalibration(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel)
"Observed";
[CalMeasure1,CalData1] = modelCalibration(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel)CalMeasure1=1×4 table
RSquared RMSE Correlation SampleMeanError
________ _____ ___________ _______________
Tobit 0.3919 42494 0.62602 -1240.7
CalData1=1751×3 table
Observed Predicted_Tobit Residuals_Tobit
__________ _______________ _______________
44740 14893 29847
54.175 8730.2 -8676
987.39 13244 -12257
9606.4 7367.5 2238.9
83.809 27501 -27417
73538 45726 27812
96.949 5522.5 -5425.5
873.21 4426.3 -3553.1
328.35 5952.4 -5624.1
55237 28040 27198
30359 19047 11312
39211 28368 10843
2.0885e+05 1.0539e+05 1.0346e+05
1921.7 19939 -18017
15230 5427.4 9802.4
20063 9359.6 10703
⋮
modelCalibrationPlot(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel,YData=YData);
This example shows how to use fitEADModel to create a Beta model and then use modelCalibration to compute the R-Square, RMSE, correlation, and sample mean error of predicted and observed EAD.
Load EAD Data
Load the EAD data.
load EADData.mat
head(EADData) UtilizationRate Age Marriage Limit Drawn EAD
_______________ ___ ___________ __________ __________ __________
0.24359 25 not married 44776 10907 44740
0.96946 44 not married 2.1405e+05 2.0751e+05 40678
0 40 married 1.6581e+05 0 1.6567e+05
0.53242 38 not married 1.7375e+05 92506 1593.5
0.2583 30 not married 26258 6782.5 54.175
0.17039 54 married 1.7357e+05 29575 576.69
0.18586 27 not married 19590 3641 998.49
0.85372 42 not married 2.0712e+05 1.7682e+05 1.6454e+05
rng('default'); NumObs = height(EADData); c = cvpartition(NumObs,'HoldOut',0.4); TrainingInd = training(c); TestInd = test(c);
Select Model Type
Select a model type for Beta.
ModelType =  "Beta";
"Beta";Select Conversion Measure
Select a conversion measure for the EAD response values.
ConversionMeasure =  "LCF";
"LCF";Create Beta EAD Model
Use fitEADModel to create a Beta model using the TrainingInd data.
eadModel = fitEADModel(EADData(TrainingInd,:),ModelType,PredictorVars={'UtilizationRate','Age','Marriage'}, ...
ConversionMeasure=ConversionMeasure,DrawnVar="Drawn",LimitVar="Limit",ResponseVar="EAD");
disp(eadModel); Beta with properties:
BoundaryTolerance: 1.0000e-07
ModelID: "Beta"
Description: ""
UnderlyingModel: [1×1 risk.internal.credit.BetaModel]
PredictorVars: ["UtilizationRate" "Age" "Marriage"]
ResponseVar: "EAD"
LimitVar: "Limit"
DrawnVar: "Drawn"
ConversionMeasure: "lcf"
Display the underlying model. The underlying model's response variable is the transformation of the EAD response data. Use the 'LimitVar' and 'DrwanVar' name-value arguments to modify the transformation.
disp(eadModel.UnderlyingModel);
Beta regression model:
logit(EAD_lcf) ~ 1_mu + UtilizationRate_mu + Age_mu + Marriage_mu
log(EAD_lcf) ~ 1_phi + UtilizationRate_phi + Age_phi + Marriage_phi
Estimated coefficients:
Estimate SE tStat pValue
_________ _________ ________ __________
(Intercept)_mu -0.65566 0.11484 -5.7093 1.2614e-08
UtilizationRate_mu 1.7014 0.078094 21.787 0
Age_mu -0.00559 0.0027603 -2.0252 0.042952
Marriage_not married_mu -0.012576 0.052098 -0.2414 0.80926
(Intercept)_phi -0.50132 0.094625 -5.2979 1.2685e-07
UtilizationRate_phi 0.39731 0.066707 5.956 2.9304e-09
Age_phi -0.001167 0.0023161 -0.50386 0.61441
Marriage_not married_phi -0.013275 0.042627 -0.31143 0.7555
Number of observations: 2627
Log-likelihood: -3140.21
Predict EAD
EAD prediction operates on the underlying compact statistical model and then transforms the predicted values back to the EAD scale. You can specify the predict function with different options for the 'ModelLevel' name-value argument.
predictedEAD = predict(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel="ead"); predictedConversion = predict(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel="ConversionMeasure");
Validate EAD Model
For model validation, use modelDiscrimination, modelDiscriminationPlot, modelCalibration, and modelCalibrationPlot.
Use modelDiscrimination and then modelDiscriminationPlot to plot the ROC curve.
ModelLevel ="ead"; [DiscMeasure1,DiscData1] = modelDiscrimination(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel); modelDiscriminationPlot(eadModel,EADData(TestInd, :),ModelLevel=ModelLevel,SegmentBy="Marriage");

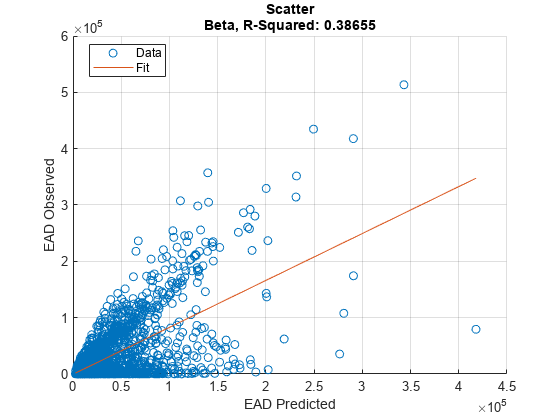
Use modelCalibration, and modelCalibrationPlot to show a scatter plot of the predictions.
YData =  "Observed";
[CalMeasure1,CalData1] = modelCalibration(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel)
"Observed";
[CalMeasure1,CalData1] = modelCalibration(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel)CalMeasure1=1×4 table
RSquared RMSE Correlation SampleMeanError
________ _____ ___________ _______________
Beta 0.38655 43817 0.62173 -7393.4
CalData1=1751×3 table
Observed Predicted_Beta Residuals_Beta
__________ ______________ ______________
44740 18039 26701
54.175 10560 -10506
987.39 15551 -14564
9606.4 8407.7 1198.8
83.809 33318 -33234
73538 52120 21418
96.949 6598.1 -6501.2
873.21 5471.1 -4597.9
328.35 7335 -7006.6
55237 32580 22658
30359 21563 8796.4
39211 33177 6033.6
2.0885e+05 1.2586e+05 82987
1921.7 23319 -21397
15230 6565.9 8664
20063 11075 8987.5
⋮
modelCalibrationPlot(eadModel,EADData(TestInd,:),ModelLevel=ModelLevel,YData=YData);
Input Arguments
Loss given default model, specified as a previously created Regression,
Tobit, or Beta object using
fitEADModel.
Data Types: object
Data, specified as a
NumRows-by-NumCols table with
predictor and response values. The variable names and data types must be
consistent with the underlying model.
Data Types: table
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: [CalMeasure,CalData] =
modelCalibration(eadModel,data(TestInd,:),DataID='Testing',CorrelationType='spearman')
Correlation type, specified as CorrelationType and
a character vector or string.
Data Types: char | string
Data set identifier, specified as DataID and a
character vector or string. The DataID is included in
the output for reporting purposes.
Data Types: char | string
Model level, specified as ModelLevel and a
character vector or string.
Note
Regression models support all three model levels,
but a Tobit
or Beta
model supports model levels only for "ead"
and "conversionMeasure".
Data Types: char | string
Identifier for the reference model, specified as
ReferenceID and a character vector or string.
ReferenceID is used in the
modelCalibration output for reporting
purposes.
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
Calibration measure, returned as a table with columns
'RSquared', 'RMSE',
'Correlation', and
'SampleMeanError'. CalMeasure has
one row if only the eadModel accuracy is measured and
it has two rows if reference model information is given. The row names of
CalMeasure report the model ID and data ID (if
provided).
Calibration data, returned as a table with observed EAD values, predicted
EAD values, and residuals (observed minus predicted). Additional columns for
predicted and residual values are included for the reference model, if
provided. The ModelID and
ReferenceID labels are appended in the column
names.
More About
Model calibration measures the accuracy of the predicted probability of EAD values using different metrics.
R-squared — To compute the R-squared metric,
modelCalibrationfits a linear regression of the observed EAD values against the predicted EAD values:The R-square of this regression is reported. For more information, see Coefficient of Determination (R-Squared).
RMSE — To compute the root mean square error (RMSE),
modelCalibrationuses the following formula where N is the number of observations:Correlation — This metric is the correlation between the observed and predicted EAD:
For more information and details about the different correlation types, see
corr.Sample mean error — This metric is the difference between the mean observed EAD and the mean predicted EAD or, equivalently, the mean of the residuals:
References
[1] Baesens, Bart, Daniel Roesch, and Harald Scheule. Credit Risk Analytics: Measurement Techniques, Applications, and Examples in SAS. Wiley, 2016.
[2] Bellini, Tiziano. IFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SAS. San Diego, CA: Elsevier, 2019.
[3] Brown, Iain. Developing Credit Risk Models Using SAS Enterprise Miner and SAS/STAT: Theory and Applications. SAS Institute, 2014.
[4] Roesch, Daniel and Harald Scheule. Deep Credit Risk. Independently published, 2020.
Version History
Introduced in R2023a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)