pdegplot
Plot PDE geometry
Description
pdegplot(
plots with additional options specified by one or more name-value arguments. For
example, you can specify whether to display vertex, edge, face, and cell
labels.g,Name,Value)
h = pdegplot(___)
Examples
Plot the geometry of a region defined by a few simple shapes.
g = [2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4;
-1 -0.6 -0.5 -0.4 -0.5 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.5 -1 0.17;
1 -0.5 -0.4 -0.5 -0.6 0.5 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.17 1;
0 -0.25 -0.35 -0.25 -0.15 -0.25 -0.35 -0.25 -0.15 0 -0.74;
0 -0.35 -0.25 -0.15 -0.25 -0.35 -0.25 -0.15 -0.25 -0.74 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1;
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0;
0 -0.5 -0.5 -0.5 -0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0 0;
0 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25 0 0;
0 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 1 1;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.75 0.75;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0];
pdegplot(g)
View the vertex labels, edge labels, and the face label. Add space at the top of the plot to see the top edge clearly.
pdegplot(g,VertexLabels="on", ... EdgeLabels="on", ... FaceLabels="on") ylim([-.8,.1])

Import a 3-D geometry file. Plot the geometry and turn on face labels. To see the labels on all faces of the geometry, set the transparency to 0.5.
gm = fegeometry("BracketWithHole.stl"); pdegplot(gm,FaceLabels="on",FaceAlpha=0.5)

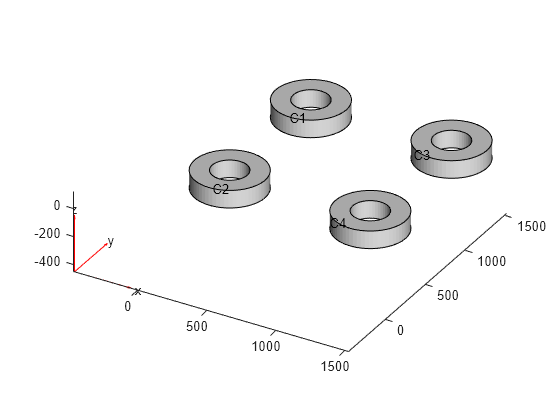
Import a 3-D geometry file. Plot the geometry and turn on cell labels.
gm = fegeometry("DampingMounts.stl"); pdegplot(gm,CellLabels="on")
Since R2023b
Create and plot a 3-D geometry consisting of three nested cuboids of the same height. By default, pdegplot uses lighting effects to display geometric features, like different cells, with more contrast.
gm = multicuboid([2 3 5],[4 6 10],3);
pdegplot(gm,CellLabels="on",FaceAlpha=0.3)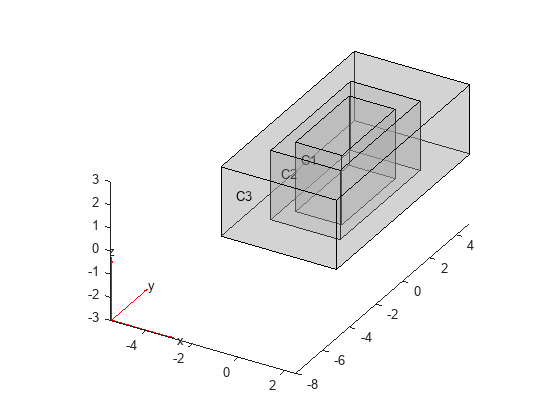
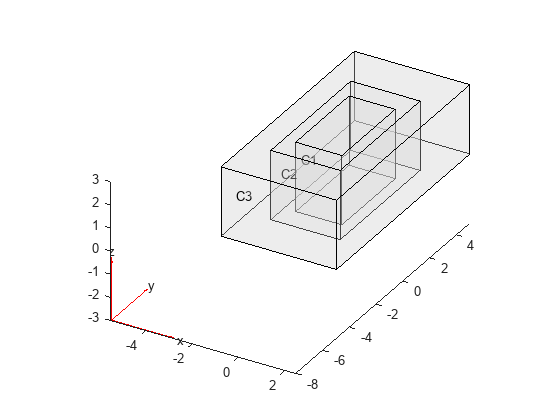
To obtain the same plot appearance as in R2023a or earlier, turn off the lighting effects.
figure pdegplot(gm,CellLabels="on",FaceAlpha=0.3,Lighting="off")
Since R2025a
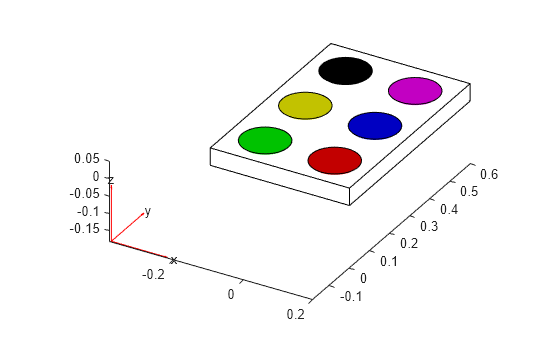
Create a plot showing a watercolor paint set with two rows, each containing three pans of paint. First, create the geometry representing the container for the paint set.
L = 0.6; W = 0.4; H = 0.05; g = multicuboid(W,L,H); g = fegeometry(translate(g,[0,L/2,0]));
Create the geometry representing an individual pan of paint.
gPan = fegeometry(multicylinder(W/6,H/2));
Create a vector containing the colors you want to use for the six pans of paint. For example, specify these colors.
color = ["red","green","blue","yellow","magenta","black"];
Specify the gap from the edge of the container to the first pan.
edgeGap = 0.1;
Plot the container and specify white as the face color. Use the vector color to specify the face colors for the pans of paint.
pdegplot(g,FaceColor="white") hold on i = 1; for k=linspace(edgeGap,L-edgeGap,3) % 3 pans in a row gColor = translate(gPan,[edgeGap,k,1.01*H/2]); pdegplot(gColor,FaceColor=color(i)) hold on i = i + 1; % Mirror the geometry to create a pan in the second row. gColor = scale(gColor,[-1 1 1]); pdegplot(gColor,FaceColor=color(i)) hold on i = i + 1; end
Input Arguments
Geometry description, specified by one of these values:
femodelobjectfegeometryobjectPDEModelobjectDiscreteGeometryobjectAnalyticGeometryobjectOutput of
decsgDecomposed geometry matrix (see Decomposed Geometry Data Structure)
Name of geometry file (see Parameterized Function for 2-D Geometry Creation)
Function handle to geometry file (see Parameterized Function for 2-D Geometry Creation)
Data Types: double | char | string | function_handle
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")
Example: pdegplot(g,FaceColor=[0 0 1])
Vertex labels for 2-D or 3-D geometry, specified as
"off" or "on".
Data Types: char | string
Boundary edge labels for 2-D or 3-D geometry, specified as
"off" or "on".
Data Types: char | string
Boundary face labels for 2-D or 3-D geometry, specified as
"off" or "on".
Data Types: char | string
Cell labels for 3-D geometry, specified as "off" or
"on".
Data Types: char | string
Surface transparency for 3-D geometry, specified as a real number from 0
through 1. The default value 1 indicates no
transparency. The value 0 indicates complete transparency.
Example: FaceAlpha=0.5
Data Types: double
Since R2025a
Face color, specified as a color name, an RGB triplet, or
"none". The specified color applies to all faces
of the geometry. You cannot specify colors for individual faces.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row
vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and
blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example, [0.4 0.6
0.7]. This table lists the long and short color name
options and the equivalent RGB triplet values. For details on acceptable
face colors, see FaceColor.
| Long Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet |
|---|---|---|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] |
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] |
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] |
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] |
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] |
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] |
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] |
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] |
Data Types: double | char | string
Since R2023b
Lighting effects for 3-D geometry, specified as
"on" or "off".
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
Handles to graphics objects, returned as a vector.
Alternative Functionality
App
If you create a 2-D geometry in the PDE Modeler app, you can view the geometry from Boundary Mode. To see the edge labels, select Boundary > Show Edge Labels. To see the face labels, select PDE > Show Subdomain Labels.
Version History
Introduced before R2006aSpecify the color for geometry faces by using the FaceColor
argument. The specified color applies to all faces of the geometry. You cannot
specify colors for individual faces.
pdegplot now uses lighting effects by default to display
geometric features with more contrast. To obtain the same plot appearance as in the
previous releases, you can turn off lighting effects by setting the
Lighting name-value argument to
"off".
pdegplot now plots geometries specified by fegeometry
and femodel
objects.
pdegplot shows faster rendering and better responsiveness for
plots that display many text labels. Code containing
findobj(fig,'Type','Text') no longer returns labels on
figures produced by pdegplot.
You can now set plot transparency by using FaceAlpha, and
display vertex and cell labels by using VertexLabels and
CellLabels, respectively.
The argument SubdomainLabels is no longer recommended. Use
FaceLabels for 2-D geometries instead.
Display edge and subdomain labels by setting EdgeLabels or
SubdomainLabels to 'on'.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)