インポート ツールを使用したスプレッドシート データの読み取り
この例では、インポート ツールを使用してスプレッドシートからワークスペースにデータをインポートする方法に加え、クリップボードからデータをインポートする方法も説明します。
対話モードでのデータの選択
[ホーム] タブの [変数] セクションで、[データのインポート]  をクリックします。または、[ファイル] パネルで、
をクリックします。または、[ファイル] パネルで、.xls、.xlsx、.xlsb または .xlsm の拡張子をもつファイルの名前をダブルクリックします。インポート ツールが開きます。
インポートするデータを選択します。たとえば、3 つの列ベクトルのデータに対応するデータをインポートします。変数名は編集できます。また、同じ変数に対して隣接していないセクションのデータも選択できます。
[インポート] タブの [出力タイプ] セクションで、データのインポート方法を選択します。選択するオプションにより、インポート データのデータ型が決まります。
| 選択したオプション | データのインポート方法 |
|---|---|
| 列ベクトル | 選択したデータの各列を個別の m 行 1 列のベクトルとしてインポートします。 |
| 数値行列 | 選択したデータを m 行 n 列の数値配列としてインポートします。 |
| string 配列 | 選択したデータを m 行 n 列の string 配列としてインポートします。 |
| cell 配列 | 選択したデータを、複数のデータ型 (数値データやテキストなど) を格納できる cell 配列としてインポートします。 |
| テーブル | 選択したデータをテーブルとしてインポートします。 |
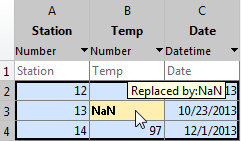
行列または数値列ベクトルとしてデータをインポートする場合は、ワークシート内の非数値データが強調表示されます。強調表示に使用される色はそれぞれ、データを数値配列に格納するために提示されたルールに対応します。たとえば、非数値を NaN に置換できます。また、個々のセルにカーソルを合わせると、データがどのようにインポートされるかを確認できます。

置き換える値を NaN から別の値に変更するなど、ルールの追加、削除、並べ替えまたは編集ができます。すべてのルールはインポートされたデータにのみ適用され、ファイルのデータは変更されません。範囲内に非数値データが含まれており、かつデータを行列または数値列ベクトルにインポートする場合は必ずルールを指定します。
#Error? が含まれるすべてのセルは、ゼロ除算などのスプレッドシート ファイルの式エラーと一致します。インポート ツールは、これらのセルを数値として認識しません。
[選択のインポート]  ボタンをクリックすると、インポート ツールによってワークスペースに変数が作成されます。
ボタンをクリックすると、インポート ツールによってワークスペースに変数が作成されます。
インポート ツール操作の詳細については、このビデオをご覧ください。
複数のスプレッドシートからのデータのインポート
複数のファイルに対して同じインポート操作を実行する場合は、インポート ツールからコードを生成することで、操作を簡単に繰り返すことができます。インポート ツールはすべてのプラットフォーム上でプログラム用のスクリプトを生成できるため、これを編集してファイルのインポートを実行できます。Excel® ソフトウェアがインストールされた Microsoft® Windows® では、インポート ツールを使用して関数を生成し、各ファイルを呼び出すことができます。
たとえば、現在のフォルダーに myfile01.xlsx から myfile25.xlsx までの名前をもつ一連のスプレッドシートが存在し、各ファイルの最初のワークシートから同じ範囲のデータ A2:G100 をインポートするとします。この場合は、次のようにコードを生成して、ファイルすべてをインポートします。
ファイルの 1 つをインポート ツールで開きます。
[選択のインポート] ボタンから [関数の生成] を選択します。インポート ツールによって次の抜粋と類似したコードが生成され、エディターで表示されます。
function data = importfile(workbookFile, sheetName, range) %IMPORTFILE Import numeric data from a spreadsheet ...
関数を保存します。
別のプログラム ファイルまたはコマンド ラインで
forループを作成して、各スプレッドシートのデータをmyDataという cell 配列にインポートします。numFiles = 25; range = 'A2:G100'; sheet = 1; myData = cell(1,numFiles); for fileNum = 1:numFiles fileName = sprintf('myfile%02d.xlsx',fileNum); myData{fileNum} = importfile(fileName,sheet,range); end
myData の各セルには、対応するワークシートのデータ配列が含まれます。たとえば、myData{1} には最初のファイル myfile01.xlsx のデータが含まれます。
クリップボードからのデータの貼り付け
データの対話的なインポートに加えて、クリップボードから MATLAB® にスプレッドシート データを貼り付けることもできます。
まず、Microsoft Excel でスプレッドシート データを選択してコピーし、次に以下のいずれかの方法を使用します。
ワークスペース パネルのタイトル バーでワークスペース アクション ボタン をクリックし、[貼り付け] を選択します。
変数エディターで既存の変数を開き、右クリックして [Excel データの貼り付け] を選択する。
uiimport -pastespecialを呼び出す。
参考
インポート ツール | readmatrix | readcell | readvars | readtable | detectImportOptions