LiDAR とカメラのキャリブレーション
この例では、3 次元 LiDAR センサーとカメラの間の剛体変換を推定し、その剛体変換行列を使用して LiDAR とカメラのデータを融合する方法を示します。
概要
自動運転の用途では、3 次元空間情報を LiDAR センサーで収集し、その空間の 2 次元イメージの外観とテクスチャをカメラで取得するため、LiDAR センサーとカメラがよく一緒に使用されます。それらのセンサーからのデータを融合することで、オブジェクトの検出や分類を向上させることができます。LiDAR カメラ キャリブレーションでは、2 つのセンサー間の相対的な回転と並進を与える変換行列を推定します。この行列を LiDAR とカメラのデータの融合を実行するときに使用します。
次の図は、LiDAR カメラ キャリブレーション (LCC) プロセスのワークフローを示しています。ここでは、チェッカーボードをキャリブレーション オブジェクトとして使用しています。LiDAR およびカメラのデータからチェッカーボードのコーナーと平面を抽出し、それらの座標系の間の幾何学的関係を確立してキャリブレーションを実行します。LiDAR カメラ キャリブレーション プロセスの詳細については、LiDAR カメラ キャリブレーションとはを参照してください。

この例では、 HDL-64 センサーと VLP-16 センサーの 2 種類の LiDAR センサーからのデータを使用します。HDL-64 センサーについては、Gazebo 環境から収集されたデータを使用します。
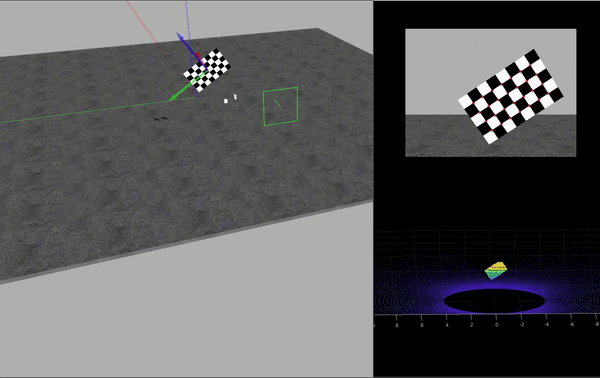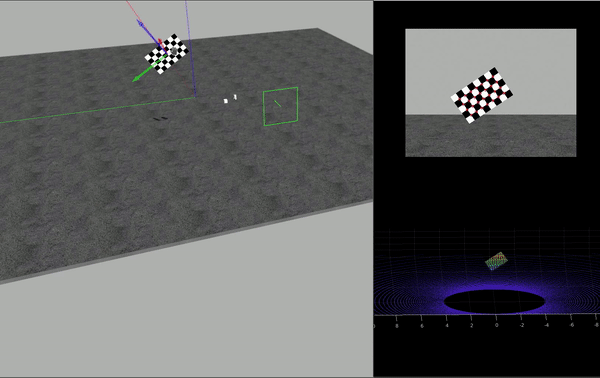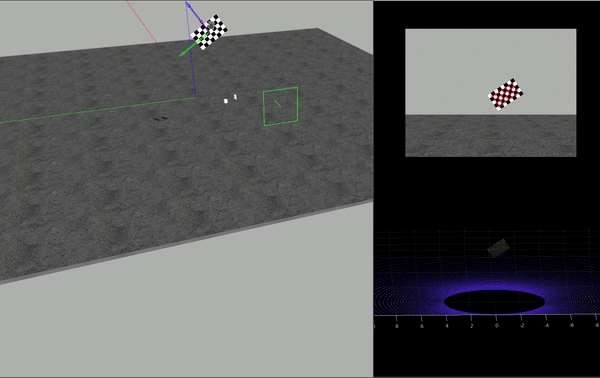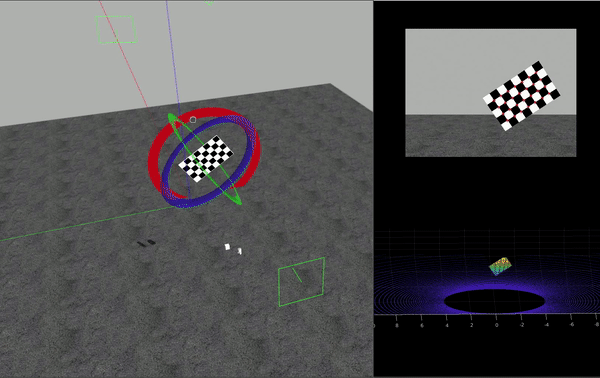
HDL-64 センサーは、データを PNG イメージと対応する PCD 点群のセットとして取得します。この例では、カメラの内部パラメーターが既知であることを前提としています。カメラの内部パラメーターの抽出に関する詳細については、単一カメラのキャリブレーションの精度の評価を参照してください。
データの読み込み
Velodyne HDL-64 センサーのデータを Gazebo から読み込みます。
imagePath = fullfile(toolboxdir('lidar'),'lidardata','lcc','HDL64','images'); ptCloudPath = fullfile(toolboxdir('lidar'),'lidardata','lcc','HDL64','pointCloud'); cameraParamsPath = fullfile(imagePath,'calibration.mat'); % Load camera intrinsics. intrinsic = load(cameraParamsPath); % Load images using imageDatastore. imds = imageDatastore(imagePath); imageFileNames = imds.Files; % Load point cloud files. pcds = fileDatastore(ptCloudPath,'ReadFcn',@pcread); ptCloudFileNames = pcds.Files; % Square size of the checkerboard. squareSize = 200; % Set random seed to generate reproducible results. rng('default')
チェッカーボードのコーナーの検出
この例では、チェッカーボード パターンをキャリブレーションに使用します。最初に、カメラ データからチェッカーボードのエッジを推定します。関数estimateCheckerboardCorners3dを使用して、チェッカーボードのコーナーの座標と実際のチェッカーボードのサイズ (ミリメートル) を計算します。この関数は、ワールド座標系の 3 次元座標としてコーナーを推定します。
[imageCorners3d,checkerboardDimension,dataUsed] = ... estimateCheckerboardCorners3d(imageFileNames,intrinsic.cameraParams,squareSize); % Remove image files that are not used. imageFileNames = imageFileNames(dataUsed);
補助関数 helperShowImageCorners を使用して、結果を可視化します。
% Display checkerboard corners.
helperShowImageCorners(imageCorners3d,imageFileNames,intrinsic.cameraParams)
チェッカーボード平面の検出
次に、関数detectRectangularPlanePointsを使用して、LiDAR データからチェッカーボード平面を検出します。この関数は、関数estimateCheckerboardCorners3dで計算されたボードの寸法を使用してチェッカーボードを検出します。
% Extract the checkerboard ROI from the detected checkerboard image corners. roi = helperComputeROI(imageCorners3d,5); % Filter the point cloud files that are not used for detection. ptCloudFileNames = ptCloudFileNames(dataUsed); [lidarCheckerboardPlanes,framesUsed,indices] = ... detectRectangularPlanePoints(ptCloudFileNames,checkerboardDimension,ROI=roi); % Remove ptCloud files that are not used. ptCloudFileNames = ptCloudFileNames(framesUsed); % Remove image files. imageFileNames = imageFileNames(framesUsed); % Remove 3-D corners from images. imageCorners3d = imageCorners3d(:,:,framesUsed);
関数 helperShowCheckerboardPlanes を使用して、検出されたチェッカーボードを可視化します。
helperShowCheckerboardPlanes(ptCloudFileNames,indices)

LiDAR とカメラのキャリブレーション
関数estimateLidarCameraTransformを使用して、LiDAR センサーとカメラの間の剛体変換行列を推定します。
[tform,errors] = estimateLidarCameraTransform(lidarCheckerboardPlanes, ...
imageCorners3d,intrinsic.cameraParams);キャリブレーションの後、この変換行列を使用して次のことが可能です。
関数
projectLidarPointsOnImageを使用して、LiDAR 点群をイメージに投影する。関数
fuseCameraToLidarを使用して、LiDAR 点群をイメージからのカラー情報を使用して拡張する。
関数 helperFuseLidarCamera を使用して、1 つに融合された LiDAR とイメージのデータを可視化します。
helperFuseLidarCamera(imageFileNames,ptCloudFileNames,indices, ...
intrinsic.cameraParams,tform);
キャリブレーション誤差の可視化
次のタイプの誤差を使用して、キャリブレーションの精度を推定できます。
平行移動誤差 — 点群と対応するイメージの間でのチェッカーボード平面の重心座標の差 (メートル)。
回転誤差 — 点群と対応するイメージの間でのチェッカーボード平面で定義される法線角度の差 (度単位)。
再投影誤差 — 点群と対応するイメージの間での投影 (変換) されたチェッカーボード平面の重心座標の差 (ピクセル)。
関数 helperShowError を使用して、推定誤差値をプロットします。
helperShowError(errors)

実データでのキャリブレーション
実際の VLP-16 LiDAR データで LCC ワークフローをテストして、そのパフォーマンスを評価します。
clear imagePath = fullfile(toolboxdir('lidar'),'lidardata','lcc','vlp16','images'); ptCloudPath = fullfile(toolboxdir('lidar'),'lidardata','lcc','vlp16','pointCloud'); cameraParamsPath = fullfile(imagePath,'calibration.mat'); % Load camera intrinsics. intrinsic = load(cameraParamsPath); % Load images using imageDatastore. imds = imageDatastore(imagePath); imageFileNames = imds.Files; % Load point cloud files. pcds = fileDatastore(ptCloudPath,'ReadFcn',@pcread); ptCloudFileNames = pcds.Files; % Square size of the checkerboard in mm. squareSize = 81; % Set random seed to generate reproducible results. rng('default') % Extract checkerboard corners from the images. [imageCorners3d,checkerboardDimension,dataUsed] = ... estimateCheckerboardCorners3d(imageFileNames,intrinsic.cameraParams,squareSize); % Remove the unused image files. imageFileNames = imageFileNames(dataUsed); % Filter the point cloud files that are not used for detection. ptCloudFileNames = ptCloudFileNames(dataUsed); % Extract ROI from the detected checkerboard image corners. roi = helperComputeROI(imageCorners3d,5); % Extract checkerboard plane from point cloud data. [lidarCheckerboardPlanes,framesUsed,indices] = detectRectangularPlanePoints( ... ptCloudFileNames,checkerboardDimension,RemoveGround=true,ROI=roi); imageCorners3d = imageCorners3d(:,:,framesUsed); % Remove ptCloud files that are not used. ptCloudFileNames = ptCloudFileNames(framesUsed); % Remove image files that are not used. imageFileNames = imageFileNames(framesUsed); [tform,errors] = estimateLidarCameraTransform(lidarCheckerboardPlanes, ... imageCorners3d,intrinsic.cameraParams); helperFuseLidarCamera(imageFileNames,ptCloudFileNames,indices, ... intrinsic.cameraParams,tform);

% Plot the estimated error values.
helperShowError(errors);
まとめ
この例では、LiDAR カメラ キャリブレーション ワークフローの概要を紹介し、剛体変換行列を使用して LiDAR とカメラのデータを融合する方法について説明しています。
参考文献
[1] Zhou, Lipu, Zimo Li, and Michael Kaess. "Automatic Extrinsic Calibration of a Camera and a 3D LiDAR Using Line and Plane Correspondences." In 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 5562–69. Madrid: IEEE, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8593660.
[2] Arun, K. S., T. S. Huang, and S. D. Blostein. "Least-Squares Fitting of Two 3-D Point Sets." IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence PAMI-9, no. 5 (September 1987): 698–700. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1987.4767965.