センサー フュージョンを使用した電話の向きの推定
MATLAB® Mobile™ は、Apple または Android® のモバイル デバイスの加速度計、ジャイロスコープ、および磁力計からのセンサー データをレポートします。各センサーからの生データまたは融合した向きのデータを取得できます。この例では、電話からの融合した向きのデータをahrsfilter (Navigation Toolbox)オブジェクトからの向きの推定と比較する方法を示します。
加速度計、ジャイロスコープ、磁力計、およびオイラー角の読み取り
ログ記録された電話センサー データを読み取ります。MAT ファイル samplePhoneData.mat には、iPhone で 100 Hz のサンプル レートでログ記録されたセンサー データが含まれています。独自の電話データを使用してこの例を実行する場合は、MATLAB Mobile でのセンサー データの収集を参照してください。
matfile = 'samplePhoneData.mat'; SampleRate = 100; % This must match the data rate of the phone. [Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Magnetometer, EulerAngles] ... = exampleHelperProcessPhoneData(matfile);
北-東-下 (NED) 座標系への変換
MATLAB Mobile は以下のイメージに示されている規則を使用します。ahrsfilter オブジェクトを使用してセンサー データを処理するには、右手座標系である NED に変換します。NED 座標系では、正の回転角度は、原点から軸の正の方向を見たときの、軸を中心とした時計回りの回転に対応します。これは右手系と同等であり、正回転は、親指が回転軸の方向を向いているときに右手の指が曲がる方向によって示されます。各種センサー データで "x" 軸と "y" 軸を入れ替え、"z" 軸の符号を反転します。なお、加速度計の読み取り値の符号を反転させるのは、2 つの規則で読み取り値の符号が逆であるためです。
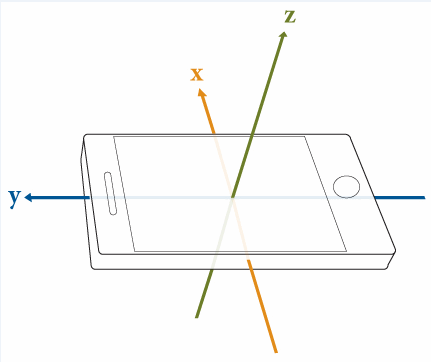
Accelerometer = -[Accelerometer(:,2), Accelerometer(:,1), -Accelerometer(:,3)]; Gyroscope = [Gyroscope(:,2), Gyroscope(:,1), -Gyroscope(:,3)]; Magnetometer = [Magnetometer(:,2), Magnetometer(:,1), -Magnetometer(:,3)]; qTrue = quaternion([EulerAngles(:,3), -EulerAngles(:,2), EulerAngles(:,1)], ... 'eulerd', 'ZYX', 'frame');
電話の初期回転の補正
電話の回転オフセットがランダムである場合があります。オフセットがわからなければ、ahrsfilter オブジェクトと電話の結果を比較できません。最初の 4 つのサンプルを使用して回転オフセットを判別してから、電話のデータを回転させて望ましい値に戻します。
% Get a starting guess at orientation using ecompass. No coefficients % required. Use the initial orientation estimates to figure out what the % phone's rotational offset is. q = ecompass(Accelerometer, Magnetometer); Navg = 4; qfix = meanrot(q(1:Navg))./meanrot(qTrue(1:Navg)); Orientation = qfix*qTrue; % Rotationally corrected phone data.
AHRS フィルターの調整
電話のノイズ パラメーターを最適化するために、ahrsfilter オブジェクトを調整します。MAT ファイルにデータをログ記録した電話上の特定の IMU に合わせてフィルターのパラメーターを調整する必要があります。ログ記録された向きのデータをグラウンド トゥルースとして使用して、関数tune (Navigation Toolbox)を使用します。
orientFilt = ahrsfilter('SampleRate', SampleRate); groundTruth = table(Orientation); sensorData = table(Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Magnetometer); tc = tunerconfig('ahrsfilter', "MaxIterations", 30, ... 'ObjectiveLimit', 0.001, 'Display', 'none'); tune(orientFilt, sensorData, groundTruth, tc);
センサー データとフィルターの融合
調整した ahrsfilter オブジェクトを使用してデバイスの向きを推定します。
reset(orientFilt); qEst = orientFilt(Accelerometer,Gyroscope,Magnetometer);
結果のプロット
それぞれの向きの推定のオイラー角および 2 つの向きの推定間の四元数距離をプロットします。四元数距離は、2 つの四元数間の角度として測定されます。この距離は、向きの推定の誤差メトリクスとして使用できます。
numSamples = numel(Orientation); t = (0:numSamples-1).'/SampleRate; d = rad2deg(dist(qEst, Orientation)); figure plot(t, eulerd(qEst, 'ZYX', 'frame')) legend yaw pitch roll title('ahrsfilter Euler Angles') ylabel('Degrees') xlabel('Time (s)')

figure plot(eulerd(Orientation, 'ZYX', 'frame')) legend yaw pitch roll title('Phone Euler Angles') ylabel('Degrees') xlabel('Time (s)')

figure plot(t, d) title('Orientation Error') ylabel('Degrees') xlabel('Time (s)') % Add RMS error rmsval = sqrt(mean(d.^2)); line(t, repmat(rmsval,size(t)),'LineStyle','-.','Color','red'); text(t(1),rmsval + 0.7,"RMS Error = " + rmsval,'Color','red')

poseplot を使用して、電話の向きの推定を 3 次元四角形として表示します。
figure pp = poseplot("MeshFileName", "phoneMesh.stl"); for i = 1:numel(qEst) set(pp, "Orientation", qEst(i)); drawnow end
