cordicsqrt
平方根の CORDIC ベースの近似
説明
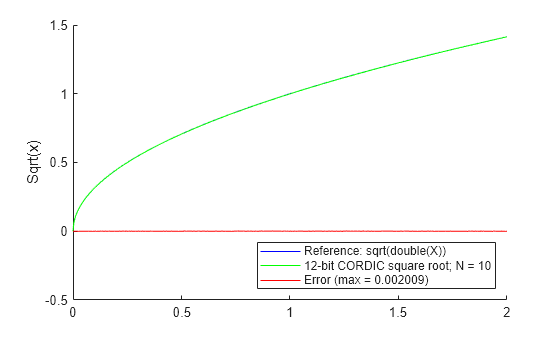
例
入力引数
出力引数
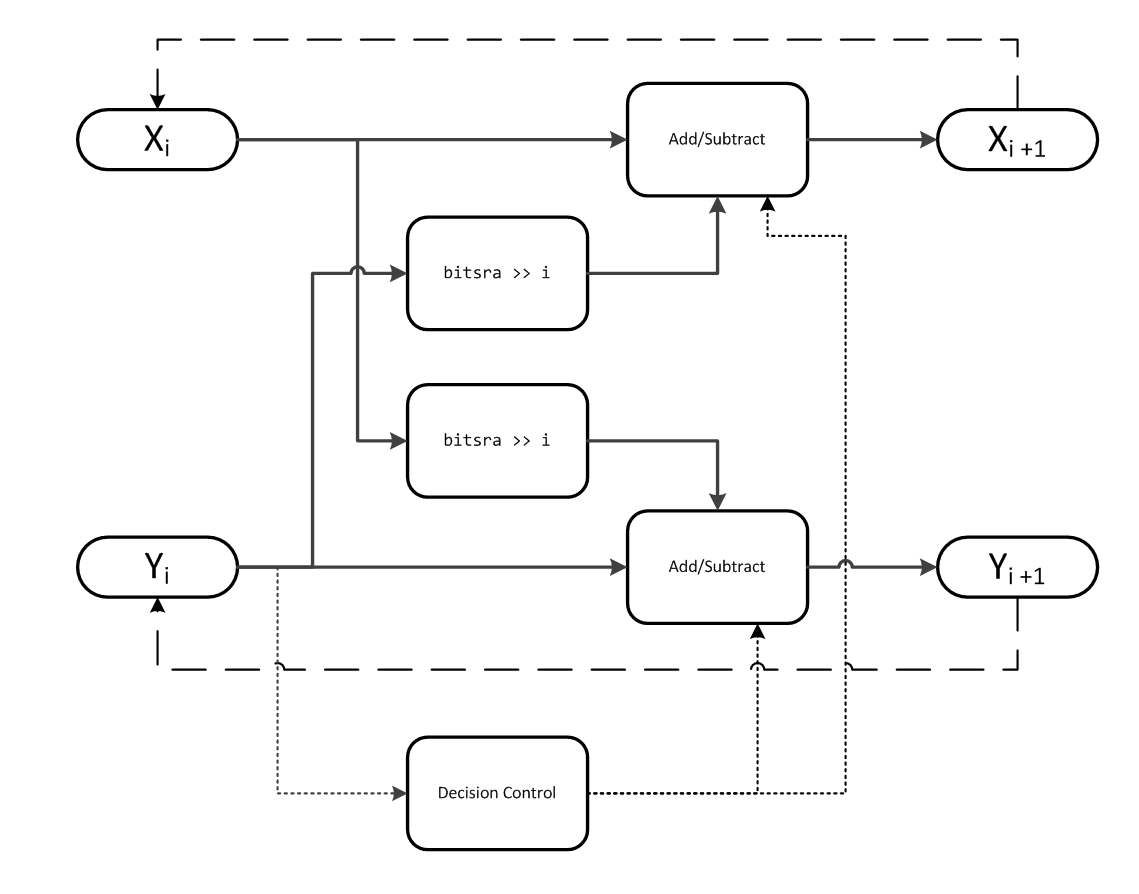
アルゴリズム
参照
[1] Volder, Jack E. “The CORDIC Trigonometric Computing Technique.” IRE Transactions on Electronic Computers. EC-8, no. 3 (Sept. 1959): 330–334.
[2] Andraka, Ray. “A Survey of CORDIC Algorithm for FPGA Based Computers.” In Proceedings of the 1998 ACM/SIGDA Sixth International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, 191–200. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/275107.275139.
[3] Walther, J.S. “A Unified Algorithm for Elementary Functions.” In Proceedings of the May 18-20, 1971 Spring Joint Computer Conference, 379–386. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1478786.1478840.
[4] Schelin, Charles W. “Calculator Function Approximation.” The American Mathematical Monthly, no. 5 (May 1983): 317–325. https://doi.org/10.2307/2975781.
拡張機能
バージョン履歴
R2014a で導入