Transition Between Exclusive States
Label Format for a State-to-State Transition
The following example shows the general label format for a transition entering a state.
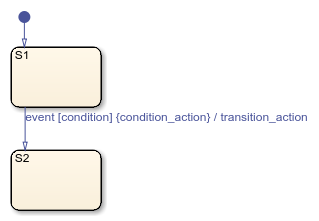
A chart executes this transition as follows:
When an event occurs, state
S1checks for an outgoing transition with a matching event specified.If a transition with a matching event is found, the condition for that transition (
[condition]) is evaluated.If the
conditionis true,condition_actionis executed.If there is a valid transition to the destination state, the transition is taken.
State
S1is exited.The
transition_actionis executed when the transition is taken.State
S2is entered.
Transition from State to State with Events
The following example shows the behavior of a simple transition focusing on the implications of whether states are active or inactive.
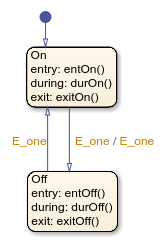
Process a First Event
Initially, the chart is asleep. State On and state
Off are OR states. State On is active.
Event E_one occurs and awakens the chart, which processes the
event from the root down through the hierarchy:
The chart root checks to see if there is a valid transition as a result of
E_one. A valid transition from stateOnto stateOffis detected.State
Onexit actions (exitOn()) execute and complete.State
Onis marked inactive.The event
E_oneis broadcast as the transition action.This second event
E_oneis processed, but because neither state is active, it has no effect. If the second broadcast ofE_oneresulted in a valid transition, it would preempt the processing of the first broadcast ofE_one. See Early Return Logic.State
Offis marked active.State
Offentry actions (entOff()) execute and complete.The chart goes back to sleep.
This sequence completes the execution of the Stateflow® chart associated with event E_one when state
On is initially active.
Process a Second Event
Using the same example, what happens when the next event,
E_one, occurs while state Off is
active?

Initially, the chart is asleep. State Off is active. Event
E_one occurs and awakens the chart, which processes the
event from the root down through the hierarchy:
The chart root checks to see if there is a valid transition as a result of
E_one.A valid transition from state
Offto stateOnis detected.State
Offexit actions (exitOff()) execute and complete.State
Offis marked inactive.State
Onis marked active.State
Onentry actions (entOn()) execute and complete.The chart goes back to sleep.
This sequence completes the execution of the Stateflow chart associated with the second event E_one
when state Off is initially active.
Process a Third Event
Using the same example, what happens when a third event,
E_two, occurs?

Notice that the event E_two is not used explicitly in this
example. However, its occurrence (or the occurrence of any event) does result in
behavior. Initially, the chart is asleep and state On is
active.
Event
E_twooccurs and awakens the chart.Event
E_twois processed from the root of the chart down through the hierarchy of the chart.The chart root checks to see if there is a valid transition as a result of
E_two. There is none.State
Onduring actions (durOn()) execute and complete.The chart goes back to sleep.
This sequence completes the execution of the Stateflow chart associated with event E_two when state
On is initially active.
Tip
Avoid using undirected local event broadcasts. Undirected local event broadcasts can cause unwanted recursive behavior in your chart. Instead, send local events by using directed broadcasts. For more information, see Broadcast Local Events to Synchronize Parallel States.
During simulation, Stateflow charts can detect undirected local event broadcasts. To control the level of
diagnostic action, open the Configuration Parameters dialog box and, in the Diagnostics > Stateflow pane, set the Undirected event broadcasts parameter to
none, warning, or
error. The default setting is
warning. For more information, see Undirected event broadcasts (Simulink).
Transition from a Substate to a Substate with Events
This example shows the behavior of a transition from an OR substate to an OR substate.
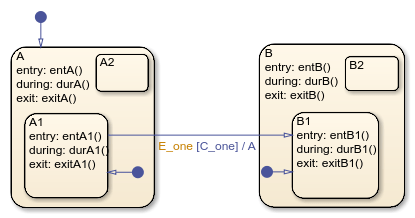
Initially, the chart is asleep. State A.A1 is active. Condition
C_one is true. Event E_one occurs and
awakens the chart, which processes the event from the root down through the
hierarchy:
The chart root checks to see if there is a valid transition as a result of
E_one. There is a valid transition from stateA.A1to stateB.B1. (ConditionC_oneis true.)State
Aduring actions (durA()) execute and complete.State
A.A1exit actions (exitA1()) execute and complete.State
A.A1is marked inactive.State
Aexit actions (exitA()) execute and complete.State
Ais marked inactive.The transition action,
A, is executed and completed.State
Bis marked active.State
Bentry actions (entB()) execute and complete.State
B.B1is marked active.State
B.B1entry actions (entB1()) execute and complete.The chart goes back to sleep.
This sequence completes the execution of this Stateflow chart associated with event E_one.