このページの内容は最新ではありません。最新版の英語を参照するには、ここをクリックします。
編集時チェックを定義し、モデル アドバイザーで指定した条件に準拠させる
この例では、特定のソフトウェア設計規格に準拠しているかどうかを確認する 3 つのカスタム編集時チェックを作成します。カスタム編集時チェックにより、モデルの設計レビュー プロセスで早期に問題を検出できますが、これらのチェックはモデル アドバイザーで問題も報告します。
最初のチェックは、Inport ブロックと Outport ブロックが出力データ型に応じた所定の色になっているかどうかを確認します。
2 番目のチェックは、Trigger ブロックがサブシステムの他のブロックよりも高い位置にあるかどうかを確認します。このチェックは、Trigger ブロックと同じサブシステム内の編集されたブロックとその他のブロックを確認する必要があります。
3 番目のチェックは、Outport ブロックに接続する信号にラベルがあるかどうかを確認します。
カスタム編集時チェックを登録して定義する
1.カスタム編集時チェックを登録するには、関数 sl_customization を作成します。この例では、コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力して、sl_customization_cec.m ファイルを sl_customization.m ファイルにコピーします。
copyfile sl_customization_cec.m sl_customization.m f
関数 sl_customization では、1 つの引数 (カスタマイズ マネージャー オブジェクト) を受け入れます。カスタム チェックを登録するには、addModelAdvisorCheckFcn メソッドを使用します。このメソッドへの入力は、チェック定義関数へのハンドルです。この例では、defineCheck がチェック定義関数です。sl_customization.m ファイルを開いて検証します。
function sl_customization(cm)
cm.addModelAdvisorCheckFcn(@defineCheck);
2.チェック定義関数を作成します。この例では、関数 defineCheck を開いて検証します。この関数には 3 つの ModelAdvisor.Check オブジェクトが、入力引数としてのチェック ID と共に含まれています。CallbackHandle プロパティは編集時チェックを定義するために作成するクラスの名前です。この例では、MyEditTimeChecks が名前空間で、PortColor、TriggerBlockPosition、SignalLabel がクラス名です。関数 mdladvRoot.publish はモデル アドバイザーの新しいフォルダーにチェックをパブリッシュします。この例では、フォルダー名は "Demo: Edit Time Checks" です。
function defineCheck %% Check the background color of Inport and Outport blocks. rec = ModelAdvisor.Check("advisor.edittimecheck.PortColor"); rec.Title = 'Check color of Inport and Outport blocks'; rec.CallbackHandle = 'MyEditTimeChecks.PortColor'; mdladvRoot = ModelAdvisor.Root; mdladvRoot.publish(rec,'DEMO: Edit Time Checks'); %% Check that determines whether Trigger block is the top-most block in a subsystem. rec= ModelAdvisor.Check("advisor.edittimecheck.TriggerBlock"); rec.Title = 'Check that Trigger block position is higher than other blocks'; rec.CallbackHandle = 'MyEditTimeChecks.TriggerBlockPosition'; mdladvRoot.publish(rec,'DEMO: Edit Time Checks'); %% Check that determines whether signals with SignalPropagation 'on' have labels. rec = ModelAdvisor.Check("advisor.edittimecheck.SignalLabel"); rec.Title = 'Check that signals have labels if they are to propagate those labels'; rec.CallbackHandle = 'MyEditTimeChecks.SignalLabels'; mdladvRoot.publish(rec,'DEMO: Edit Time Checks');
3.ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck 抽象基底クラスから派生するクラスを作成して、編集時チェックを作成します。PortColor.m ファイルを開いて、最初の編集時チェックを検証します。
classdef PortColor < ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck % Check that ports conform to software design standards for background color. % % Background Color Data Types % orange Boolean % green all floating-point % cyan all integers % Light Blue Enumerations and Bus Objects % white auto % methods function obj=PortColor(checkId) obj=obj@ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck(checkId); obj.traversalType = edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.BLKITER; end function violation = blockDiscovered(obj, blk) violation = []; if strcmp(get_param(blk,'BlockType'),'Inport') || strcmp(get_param(blk,'BlockType'),'Outport') dataType = get_param(blk,'OutDataTypeStr'); currentBgColor = get_param(blk,'BackgroundColor'); if strcmp(dataType,'boolean') if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'orange') % Create a violation object using the ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail class. violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with Boolean outputs should be orange.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end elseif any(strcmp({'single','double'},dataType)) if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'green') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with floating-point outputs should be green.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end elseif any(strcmp({'uint8','uint16','uint32','int8','int16','int32'}, dataType)) if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'cyan') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with integer outputs should be cyan.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end elseif contains(dataType,'Bus:') if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'lightBlue') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with bus outputs should be light blue.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end elseif contains(dataType,'Enum:') if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'lightBlue') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with enumeration outputs should be light blue.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end elseif contains(dataType, 'auto') if ~strcmp(currentBgColor, 'white') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',Simulink.ID.getSID(blk)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Description = 'Inport/Outport blocks with auto outputs should be white.'; violation.title = 'Port Block Color'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end end end end function violation = finishedTraversal(obj) violation = []; end function success = fix(obj, violation) success = true; dataType = get_param(violation.Data,'OutDataTypeStr'); if strcmp(dataType,'boolean') set_param(violation.Data,'BackgroundColor','orange'); elseif any(strcmp({'single','double'},dataType)) set_param(violation.Data,'BackgroundColor','green'); elseif any(strcmp({'uint8','uint16','uint32','int8','int16','int32'}, dataType)) set_param(violation.Data,'BackgroundColor','cyan'); elseif contains(dataType,'Bus:') || contains(dataType,'Enum:') set_param(violation.Data,'BackgroundColor','lightBlue'); elseif contains(dataType,'auto') set_param(violation.Data,'BackgroundColor','white'); end end end end
PortColor クラスは、PortColor、blockDiscovered、fix という 3 つのメソッドを定義します。PortColor メソッドは CheckId プロパティおよび TraversalType プロパティを設定します。このチェックは新しく追加されたブロックと編集されたブロックを確認する必要がありますが、編集されたブロックまたは新しく追加されたブロックとして、同じサブシステムまたはモデル内の影響を受けたブロックを確認する必要はないため、チェックにはトラバーサル タイプの edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.BLKITER が含まれます。blockDiscovered メソッドには、Inport ブロックと Outport ブロックの色をチェックするアルゴリズムが含まれます。ブロックに違反があるため、次にアルゴリズムは Type プロパティを既定値の SID に設定して ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail 違反オブジェクトを作成し、違反しているブロックを強調表示します。fix メソッドは正しい色になっていないブロックを更新します。
4.TriggerBlockPosition.m ファイルを開いて、2 番目の編集時チェックを検証します。
classdef TriggerBlockPosition < ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck properties TriggerBlock = []; position = []; end methods function obj=TriggerBlockPosition(checkId) obj=obj@ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck(checkId); obj.traversalType = edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.ACTIVEGRAPH; end function violation = blockDiscovered(obj, blk) violation = []; if strcmp(get_param(blk,'BlockType'),'TriggerPort') obj.TriggerBlock = blk; else h = get_param(blk,'Position'); obj.position = [obj.position, h(2)]; end end function violation = finishedTraversal(obj) violation = []; if isempty(obj.TriggerBlock) return; end triggerPosition = get_param(obj.TriggerBlock,'Position'); if min(obj.position) < triggerPosition(2) violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'SID',... Simulink.ID.getSID(obj.TriggerBlock)); violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.title = 'Trigger Block Position'; violation.Description = 'Trigger Block should be top block in subsystem'; violation.ViolationType = 'warn'; end obj.TriggerBlock = []; obj.position =[]; end end end
TriggerBlockPosition クラスは、TriggerBlockPosition、blockDiscovered、finishedTraversal という 3 つのメソッドを定義します。TriggerBlockPosition メソッドは CheckId プロパティおよび TraversalType プロパティを設定します。このチェックは Trigger ブロックと同じサブシステム内のその他のブロックを確認する必要があるため、トラバーサル タイプの edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.ACTIVEGRAPH が含まれます。blockDiscovered メソッドはサブシステム内の Trigger ブロックの位置を確認します。finishedTraversal メソッドは、これらの Trigger ブロックの位置がサブシステム内の他のブロックよりも高い位置にあるかどうかを確認します。ブロックに違反があるため、次にアルゴリズムは Type プロパティを既定値の SID に設定して ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail 違反オブジェクトを作成し、違反しているブロックを強調表示します。
5.SignalLabels.m ファイルを開いて、3 番目の編集時チェックを検証します。
classdef SignalLabels < ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck methods function obj=SignalLabels(checkId) obj=obj@ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck(checkId); obj.traversalType = edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.BLKITER; end function violation = blockDiscovered(obj, blk) violation = []; ports = get_param(blk,'Ports'); lh = get_param(blk, 'LineHandles'); if strcmp(get_param(blk,'BlockType'),'Outport') for j = 1 : ports(1) if lh.Inport(j) ~= -1 % failure case: no connection allsources = get_param(lh.Inport(j),'SrcPortHandle'); hiliteHandle = get_param(lh.Inport(j), 'DstPortHandle'); if (isempty(allsources) ~= 0) || (isempty(find(allsources==-1,1)) ~= 0) lh_obj = get_param(lh.Inport(j),'Object'); if isempty(lh_obj.Name) if strcmp(lh_obj.signalPropagation,'off') == 1 allsources_parent = get_param(allsources,'Parent'); if strcmp(get_param(allsources_parent,'BlockType'),'Inport') buscreator_outputs = get_param(allsources_parent,'IsBusElementPort'); else buscreator_outputs = 'off'; end if ~strcmp(buscreator_outputs,'on') violation = ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail; ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail.setData(violation,'Signal',hiliteHandle); violation.Description ='This signal should have a label.'; violation.CheckID = obj.checkId; violation.Title = 'Signal Label Missing'; end end end end end end end end end end
SignalLabels クラスは、SignalLabels および blockDiscovered という 2 つのメソッドを定義します。SignalLabels メソッドは CheckId プロパティおよび TraversalType プロパティを設定します。このチェックは新しく追加されたブロックと編集されたブロックを確認する必要がありますが、編集されたブロックまたは新しく追加されたブロックとして、同じサブシステムまたはモデル内の影響を受けたブロックを確認する必要はないため、チェックにはトラバーサル タイプの edittimecheck.TraversalTypes.BLKITER が含まれます。このチェックは信号用であるため、blockDiscovered メソッドはブロックのライン ハンドル LineHandles でパラメーターを使用し、違反のある信号を検出する必要があります。特に、Outport ブロックに接続する信号に対して、このアルゴリズムは Name 信号パラメーターに値があるかどうかを確認します。信号に違反があるため、次にアルゴリズムは、Type プロパティ値を Signal に設定して違反オブジェクトを作成し、その信号を強調表示します。
6.+MyEditTimeChecks という名前のフォルダーを作成し、そのフォルダーに 3 つのクラス定義ファイルを保存します。クラスは名前空間と同じ名前のフォルダー内に存在する必要があります。コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力します。
copyfile PortColor.m* +MyEditTimeChecks f copyfile TriggerBlockPosition.m +MyEditTimeChecks copyfile SignalLabels.m +MyEditTimeChecks
モデルで編集時チェックを実行する
1.カスタム チェックがモデル アドバイザーで表示されるようにするには、モデル アドバイザー チェックの情報キャッシュをリフレッシュしなければなりません。コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力します。
Advisor.Manager.refresh_customizations
2.コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力して、モデルを開きます。
open_system('AdvisorCustomizationExample.slx'); 
3.チェックのカスタム構成を作成するには、モデル アドバイザー構成エディターを開きます。[モデル化] タブで、[モデル アドバイザー]、[構成エディター] をクリックします。
4."DEMO: Edit Time Checks" フォルダーを除くすべてのフォルダーを削除し、この例にある 3 つの編集時チェックだけで構成されるカスタム構成を作成できます。この例に付属する my_config.json ファイルには、この構成が含まれています。モデル アドバイザー構成エディターを閉じます。
5. [モデル化] タブをクリックし、[モデル アドバイザー]、[編集時チェック] を選択して、カスタム構成を my_config.json ファイルに設定します。[コンフィギュレーション パラメーター] ダイアログ ボックスで、[モデル アドバイザー構成ファイル] パラメーターに構成ファイルのパスを指定します。あるいは、コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力します。
ModelAdvisor.setModelConfiguration('AdvisorCustomizationExample', 'my_config.json');
6.[モデル化] タブをクリックし、[モデル アドバイザー]、[編集時チェック] を選択して、編集時のチェックをオンにします。[コンフィギュレーション パラメーター] ダイアログ ボックスで、[編集時チェック] パラメーターを選択します。あるいは、コマンド プロンプトで次のコマンドを入力できます。
edittime.setAdvisorChecking('AdvisorCustomizationExample','on');
7.[モデル化] タブをクリックし、[モデル アドバイザー] を選択して、モデル アドバイザーを開きます。3 つの編集時チェックがモデル アドバイザーで唯一のチェックであることを確認します。モデル アドバイザーを閉じます。
8.編集時の警告を表示するには、黄色で強調表示されたブロックおよび信号をクリックします。
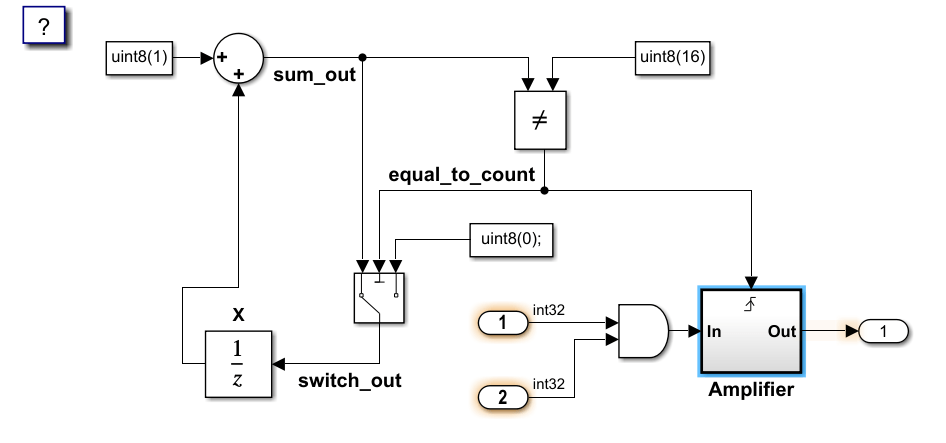
モデルの最上位レベルで、2 つの Inport ブロックの出力データ型が int32 になっています。これらはシアンでなければならないため、編集時の警告が生成されます。Outport ブロックについては、データ型が auto で白になっているため、違反は生成されません。"Amplifier" サブシステムで、Inport ブロックおよび Outport ブロックはデータ型が auto で白になっているため、編集時の警告は生成されません。Trigger ブロックはモデルの最上位ブロックであるため、編集時の警告は生成されません。Trigger ブロックを別のブロックの下に移動した場合、Trigger ブロックには編集時の警告があります。Outport ブロックに接続している信号にはラベルがないため、警告が生成されます。
9.2 つの Inport ブロックに対する編集時の警告を修正するには、編集時チェック警告のウィンドウで [修正] をクリックします。
10.モデルとモデル アドバイザーを閉じます。
bdclose;
10.作業ディレクトリからファイルを削除します。次のコマンドを入力して、モデル アドバイザー チェックの情報キャッシュをリフレッシュします。
Advisor.Manager.refresh_customizations
カスタム編集時チェックのパフォーマンスに関する考慮事項
モデルの編集中にカスタム編集時チェックがパフォーマンスに悪影響を及ぼさないように、現在の MATLAB® セッションにおいて、少なくとも 3 つの異なる Simulink® モデルでチェックの実行時間が 500 ミリ秒を超えると、モデル アドバイザーではカスタム編集時チェックが自動的に無効になります。
モデル アドバイザーでカスタム編集時チェックが無効になると、Simulink キャンバスに警告が表示されます。編集時チェックを再度有効にするには、次のいずれかを行います。
警告のハイパーリンク テキストをクリックします。
次のように関数
edittime.enableCheckにチェック識別子checkIDを渡します。
edittime.enableCheck(checkID)
カスタム編集時チェックが無効にならないようにするには、モデルでのチェックの実行時間が 500 ミリ秒未満になるようにチェックを作成してください。
参考
ModelAdvisor.EdittimeCheck | ModelAdvisor.Check | ModelAdvisor.ResultDetail