addTask
Class: padv.Process
Namespace: padv
Add task instance to process
Syntax
taskObj = addTask(process,task)
taskObj = addTask(___,Name=Value)
Description
taskObj = addTask(process,task)task to the process. A task represents a
single step in your process. You can access the task by using the task object
taskObj.
taskObj = addTask(___,Name=Value)Name=Value
arguments. For example, addTask(p1,t1,AlwaysRun=true) adds the task
t1 to the process p1 and specifies that the build
system should always force run the
t1 task, even if the task results are already up to date.
padv.Task objects have other properties, but you cannot set those
properties by using the name-value arguments.
Input Arguments
Process, specified as a padv.Process
object.
Example: padv.Process("p1")
Task, specified as either the:
Task name, specified as a string
Task instance, specified as a
padv.Taskobject
Example: "MyTaskName"
Example: padv.Task("MyCustomTask")
Example: padv.builtin.task.RunModelStandards()
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: addTask(p1,t1,AlwaysRun=true)
Parameterization
Type of artifact, specified as one or more of the values listed in this table. To specify multiple values, use an array.
| Category | Artifact Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MATLAB® | "m_class" | MATLAB class |
"m_file" | MATLAB file | |
"m_func" | MATLAB function | |
"m_method" | MATLAB class method | |
"m_property" | MATLAB class property | |
Model Advisor | "ma_config_file" | Model Advisor configuration file |
"ma_justification_file" | Model Advisor justifications file | |
Model Finder | "mf_database" | Model Finder database file |
Process Advisor | "padv_dep_artifacts" | Related artifacts that current artifact depends on |
"padv_output_file" | Process Advisor output file | |
Project | "project" | Current project file |
Requirements | "mwreq_file" | Requirement file (since R2024b) |
"mwreq_item" | Requirement (since R2024b) | |
| Requirement (for R2024a and earlier) | |
"sl_req_file" | Requirement file (for R2024a and earlier) | |
"sl_req_table" | Requirements Table | |
Stateflow® | "sf_chart" | Stateflow chart |
"sf_graphical_fcn" | Stateflow graphical function | |
"sf_group" | Stateflow group | |
"sf_state" | Stateflow state | |
"sf_state_transition_chart" | Stateflow state transition chart | |
"sf_truth_table_chart" | Stateflow truth table (since R2024a) | |
Simulink® | "sl_block_diagram" | Block diagram |
"sl_data_dictionary_file" | Data dictionary file | |
"sl_embedded_matlab_fcn" | MATLAB function | |
"sl_block_diagram" | Block diagram | |
"sl_library_file" | Library file | |
"sl_model_file" | Simulink model file | |
"sl_protected_model_file" | Protected Simulink model file | |
"sl_subsystem" | Subsystem | |
"sl_subsystem_file" | Subsystem file | |
System Composer™ | "zc_activity_diagram" | System Composer architecture (since R2026a) |
"zc_block_diagram" | System Composer architecture (for R2025b and earlier) | |
"zc_component" | System Composer architecture component | |
"zc_file" | System Composer architecture file | |
| Tests | "harness_info_file" | Harness info file |
"sl_harness_block_diagram" | Harness block diagram | |
"sl_harness_file" | Test harness file | |
"sl_test_case" | Simulink Test™ case | |
"sl_test_case_result" | Simulink Test case result | |
"sl_test_file" | Simulink Test file | |
"sl_test_iteration" | Simulink Test iteration | |
"sl_test_iteration_result" | Simulink Test iteration result | |
"sl_test_report_file" | Simulink Test result report (before R2024b) | |
"sl_test_result_file" | Simulink Test result file | |
"sl_test_resultset" | Simulink Test result set | |
"sl_test_seq" | Test Sequence | |
"sl_test_suite" | Simulink Test suite | |
"sl_test_suite_result" | Simulink Test suite result |
Artifacts that task iterates over, specified as a padv.Query
object or the name of a padv.Query object. By default, task objects
run one time and are associated with the project. When you specify
IterationQuery, the task runs one time for
each artifact returned by the padv.Query. In the
Process Advisor app, the artifacts returned by
IterationQuery appear under task title.
For example, if the IterationQuery for a task finds three
models, Model_A, Model_B, and
Model_C, the build system creates three task iterations under the
title of the task in the Tasks column.
For more information, see Overview of Process Model and Find Artifacts with Queries.
Data Types: string
Artifact dependencies for task inputs, specified as a padv.Query
object or the name of a padv.Query object.
The build system runs the query specified by
InputDependencyQuery to find the dependencies for the task
inputs, since those dependencies can impact if task results are up-to-date. Typically,
you specify InputDependencyQuery as
padv.builtin.query.GetDependentArtifacts to get the dependent
artifacts for each task input. For example, if you specify a model as an input to a
task and you specify InputDependencyQuery as
padv.builtin.query.GetDependentArtifacts, the build system can
find artifacts, such as data dictionaries, that the model uses.
For more information, see Overview of Process Model and Find Artifacts with Queries.
Inputs to the task, specified as:
a
padv.Queryobjectthe name of
padv.Queryobjectan array of
padv.Queryobjectsan array of names of
padv.Queryobjects
By default, padv.Task does not have inputs. When you
specify InputQueries, the task uses the artifacts returned by the
specified query or queries as inputs. Suppose a task runs once for each model in the
project and you want to provide the models as inputs to the task. If you specify
InputQueries as the built-in query
padv.builtin.query.GetIterationArtifact, the query returns each
artifact that the tasks iterates over, which in this example is each of the models in
the project.
To add an input query to an existing task object, you can use
addInputQueries.
For more information, see Overview of Process Model and Find Artifacts with Queries.
Location for standard outputs that the task produces, specified as a string.
Built-in tasks automatically specify OutputDirectory. If you
do not specify OutputDirectory for a custom task, the build
system stores task outputs in the DefaultOutputDirectory
specified by padv.ProcessModel.
Data Types: string
Type of task, specified as either:
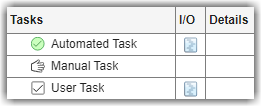
padv.TaskType.Automated— When you run an automated task, the task automatically performs the task action and returns a task status. In Process Advisor, you can see the task status in the Tasks column. For example, when a task passes, the Tasks column shows a green circle with a check mark .
.padv.TaskType.Manual— A manual task represents an action that a user manually performs as part of the process. The task is a reminder for the user. For example, you can have a manual task that reminds users to link their model requirements to tests. You can associate tools with the task to help users complete the task activity. The task does not have a status and you cannot run the task by using the build system. In Process Advisor, in the Tasks column, the manual task appears with a hand icon .
.
These values belong to the enumeration class padv.TaskType. To
create a group of tasks, create and add a subprocess to your process by using the
padv.Subprocess object and the addSubprocess
method.
Example: padv.TaskType.Manual
Behavior
Function that task can run, specified as the function handle.
If the task is defined in a function, the build system runs the function specified
by Action. If the task is defined in a class, the build system
ignores the Action and runs the run method for
the class instead. The built-in tasks are defined in classes, so the build system
calls the run method for those tasks.
Data Types: function_handle
Controls if the padv.Task is enabled in the process model,
specified as a numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false).
For an example, see Disable Task in Process Model.
Data Types: logical
Always force task to run, even if the task
results are already up to date, specified as a numeric or logical 0
(false) or 1 (true).
Data Types: logical
Description
Human readable name that appears in the Tasks column of the
Process Advisor app, specified as a string. By default, the Process
Advisor app uses the Name property of the task as the
Title.
Data Types: string
Task description, specified as a string.
Data Types: string
Path to task documentation, specified as a string.
Data Types: string
List of licenses that the task requires, specified as a string array.
Data Types: string
Tools
Function that launches a tool, specified as the function handle or a cell array of
function_handle objects. For each action that you specify in
LaunchToolAction, you must have corresponding text specified in
LaunchToolText.
When the property LaunchToolAction is specified, you can
point to the task in the Process Advisor app and click the ellipsis
(...) and then Open Tool
Name to open the tool associated with the task.
For tasks that are not built-in tasks, the task options show the ellipsis (...) and then Launch Tool.
Example: @openTool
Example: {@openToolA,@openToolB}
Data Types: cell | function_handle
Output Arguments
Task instance in process, returned as a padv.Task
object.
Examples
You can use addProcess to create a new process and
add that process to the process model. addProcess returns a
padv.Process object that can represent a group of tasks and
subprocesses in a process model. You can add a task to a specific process by using the
padv.Process object function addTask.
For example, this process model creates a new process, ProcessA,
adds tasks to the process, and adds a dependency between those tasks.
function processmodel(pm) % Defines the project's processmodel arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end % Create and add process to process model processA = pm.addProcess("ProcessA"); % Add tasks to Process A taskA = processA.addTask("taskA"); taskB = processA.addTask("taskB"); % Add dependency between tasks inside Process A processA.addDependsOnRelationship(... Source = taskB,... Dependency = taskA); end
In your process model, you can define multiple processes for
different workflows and environments. A process consists of the tasks and subprocesses
that you add to your padv.Process process by using the
addTask and addSubprocess methods. To specify the
relationships between tasks inside a specific process, use the
addDependsOnRelationship and addRunsAfterRelationship
methods.
Open the Process Advisor example project.
processAdvisorExampleStart
The model AHRS_Voter opens with the Process Advisor pane to the left of the Simulink canvas.
In the Process Advisor pane, click the Edit process model ![]() button to open the
button to open the processmodel.m file for the project.
Replace the contents of the processmodel.m file with the following example
code. The code:
Defines two processes,
processAandprocessBAdds example tasks and subprocess to the processes by using the
addTaskandaddSubprocessmethodsDefines task relationships inside a specific process by using the
addDependsOnRelationshipandaddRunsAfterRelationshipmethods
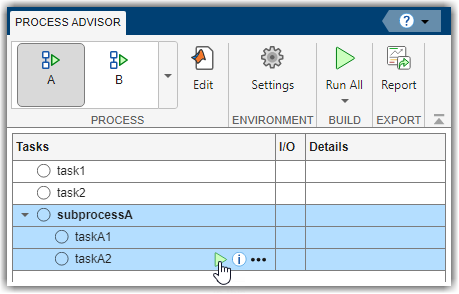
function processmodel(pm) % This function defines a process model for a project by setting up processes, % subprocesses, and tasks within those processes. arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end % --- Processes --- % Add processes to process model processA = pm.addProcess("A"); processB = pm.addProcess("B"); % --- Tasks --- % Create example tasks task1 = padv.Task("task1"); task2 = padv.Task("task2"); task3 = padv.Task("task3"); taskA1 = padv.Task("taskA1"); taskA2 = padv.Task("taskA2"); taskB1 = padv.Task("taskB1"); taskB2 = padv.Task("taskB2"); % --- Subprocesses --- % Add subprocesses to parent process subprocessA = processA.addSubprocess("subprocessA"); % Add to process A subprocessB = processB.addSubprocess("subprocessB"); % Add to process B % --- Add Tasks to Processes --- processA.addTask(task1); % Add task1 to process A processA.addTask(task2); % Add task2 to process A processB.addTask(task1); % Reuse task1 in process B processB.addTask(task3); % Add task3 to process B % --- Add Tasks to Subprocesses --- subprocessA.addTask(taskA1); % Add taskA1 to subprocessA under process A subprocessA.addTask(taskA2); % Add taskA2 to subprocessA under process A subprocessB.addTask(taskB1); % Add taskB1 to subprocessB under process B subprocessB.addTask(taskB2); % Add taskB2 to subprocessB under process B % --- Add Relationships Between Tasks --- % In processA, task2 should run after task1 processA.addRunsAfterRelationship(... Source = task2,... Predecessor = task1); % In processA, taskA2 depends on taskA1 processA.addDependsOnRelationship(... Source = taskA2,... Dependency = taskA1); end
In Process Advisor, refresh by clicking Refresh Tasks.
You can select which process you want to use from the Process gallery in the toolstrip. By default, processes appear in the order that you define them in the process model.
If you point to the run button for taskA2 in process A, Process Advisor highlights the dependency between taskA2 and taskA1.
See Also
Functions
Classes
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)