タイミング オフセットの推定
この例では、MATLAB® コードで実装された基本的なリードラグ タイミング オフセット推定アルゴリズムからの HDL コードの生成方法を示します。
はじめに
無線通信システムの RF フロント エンドで受信データがオーバーサンプリングされています。これは、受信フィルターのために十分なサンプリング レートを提供するなど、いくつかの目的を果たします。
その中でも最も重要な役割の 1 つは、受信波形の最大振幅点の近くでデータをサンプリングできるように、受信波形で複数のサンプリング点を提供することです。この例では、再帰的に動作する基本的なリードラグ時間オフセット推定コアを示します。
この設計で生成されるハードウェア コアは 1/os_rate で動作します。os_rate はオーバーサンプリング レートです。つまり、このコアはオーバーサンプリングされた 8 クロック サイクルごとに 1 回反復されます。出力はシンボル レートです。
design_name = 'mlhdlc_comms_toe'; testbench_name = 'mlhdlc_comms_toe_tb';
この MATLAB® 設計を見てみましょう。
type(design_name);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% MATLAB design: Time Offset Estimation
%
%% Introduction:
%
% The generated hardware core for this design operates at 1/os_rate
% where os_rate is the oversampled rate. That is, for 8 oversampled clock cycles
% this core iterates once. The output is at the symbol rate.
%
% Key design pattern covered in this example:
% (1) Data is sent in a vector format, stored in a register and accessed
% multiple times
% (2) The core also illustrates basic mathematical operations
%
% Copyright 2011-2015 The MathWorks, Inc.
%#codegen
function [tauh,q] = mlhdlc_comms_toe(r,mu)
persistent tau
persistent rBuf
os_rate = 8;
if isempty(tau)
tau = 0;
rBuf = zeros(1,3*os_rate);
end
rBuf = [rBuf(1+os_rate:end) r];
taur = round(tau);
% Determine lead/lag values and compute offset error
zl = rBuf(os_rate+taur-1);
zo = rBuf(os_rate+taur);
ze = rBuf(os_rate+taur+1);
offsetError = zo*(ze-zl);
% update tau
tau = tau + mu*offsetError;
tauh = tau;
q = zo;
type(testbench_name);
function mlhdlc_comms_toe_tb
%
% Copyright 2011-2015 The MathWorks, Inc.
os_rate = 8;
Ns = 128;
SNR = 100;
mu = .5; % smoothing factor for time offset estimates
% create simulated signal
rng('default'); % always default to known state
b = round(rand(1,Ns));
d = reshape(repmat(b*2-1,os_rate,1),1,Ns*os_rate);
x = [zeros(1,Ns*os_rate) d zeros(1,Ns*os_rate)];
y = awgn(x,SNR);
w = fir1(3*os_rate+1,1/os_rate)';
z = filter(w,1,y);
r = z(4:end); % give it an offset to make things interesting
%tau = 0;
Nsym = floor(length(r)/os_rate);
tauh = zeros(1,Nsym-1); q = zeros(1,Nsym-1);
for i1 = 1:Nsym-1
rVec = r(1+(i1-1)*os_rate:i1*os_rate);
% Call to the Timing Offset Estimation Algorithm
[tauh(i1),q(i1)] = mlhdlc_comms_toe(rVec,mu);
end
indexes = 1:os_rate:length(tauh)*os_rate;
indexes = indexes+tauh+os_rate-1-os_rate*2;
Fig1Loc=figposition([5 50 90 40]);
H_f1=figure(1); clf;
set(H_f1,'position',Fig1Loc);
subplot(2,1,1)
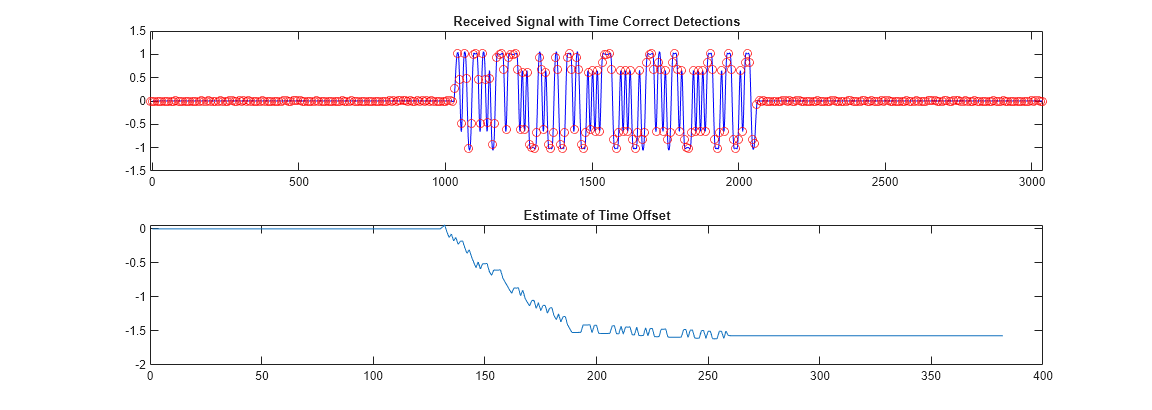
plot(r,'b');
hold on
plot(indexes,q,'ro');
axis([indexes(1) indexes(end) -1.5 1.5]);
title('Received Signal with Time Correct Detections');
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(tauh);
title('Estimate of Time Offset');
function y=figposition(x)
%FIGPOSITION Positions figure window irrespective of the screen resolution
% Y=FIGPOSITION(X) generates a vector the size of X.
% This specifies the location of the figure window in pixels
%
screenRes=get(0,'ScreenSize');
% Convert x to pixels
y(1,1)=(x(1,1)*screenRes(1,3))/100;
y(1,2)=(x(1,2)*screenRes(1,4))/100;
y(1,3)=(x(1,3)*screenRes(1,3))/100;
y(1,4)=(x(1,4)*screenRes(1,4))/100;
設計のシミュレーション
コードの生成前にテスト ベンチを使用して設計のシミュレーションを実行し、実行時エラーが発生しないことを常に確認することをお勧めします。
mlhdlc_comms_toe_tb
HDL Coder™ プロジェクトの新規作成
coder -hdlcoder -new mlhdlc_toe
次に、mlhdlc_comms_toe.m ファイルを MATLAB 関数としてプロジェクトに追加し、mlhdlc_comms_toe_tb.m を MATLAB テスト ベンチとして追加します。
MATLAB HDL Coder プロジェクトの作成と入力に関する詳細なチュートリアルについては、MATLAB から HDL へのワークフロー入門を参照してください。
固定小数点変換と HDL コード生成の実行
[ワークフロー アドバイザー] ボタンからワークフロー アドバイザーを起動し、[コード生成] のステップを右クリックして [選択したタスクまで実行] オプションを選択し、最初から HDL コード生成までのすべてのステップを実行します。
コード生成ログのウィンドウにあるハイパーリンクをクリックして、生成された HDL コードを確認します。