fismftype2
Interval type-2 fuzzy membership function
Description
Use a fismftype2 object to represent an interval type-2 fuzzy
membership function (MF), which introduces additional uncertainty into a fuzzy inference
system.
An interval type-2 membership function is represented by an upper and a lower membership function. The values of the upper membership function are always greater than or equal to the corresponding lower membership function values. The area enclosed by these membership functions is the footprint of uncertainty (FOU). For example, the following plot shows three type-2 membership functions for a given input variable.
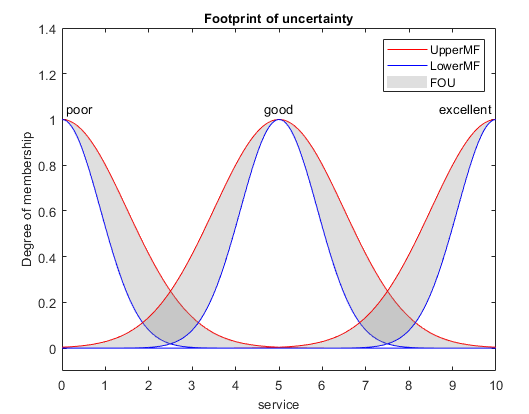
For more information on type-2 membership functions, see Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems.
Creation
Description
mf = fismftype2
mf = fismftype2(type,upperParameters)
mf = fismftype2(___,PropertyName=Value)
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Properties
Object Functions
evalmf | Evaluate fuzzy membership function |
Examples
Version History
Introduced in R2019b