iirftransf
IIR frequency transformation of digital filter
Description
[
returns the numerator and the denominator coefficients of the transformed filter. num,den] = iirftransf(b,a,allpassNum,allpassDen)
The iirftransf function transforms a prototype filter, specified by
the numerator b and denominator a, by using an
allpass mapping filter, specified by the numerator allpassNum and the
denominator allpassDen. If you do not specify an allpass mapping
filter, then the function returns an original filter.
Examples
Using the iirftransf function, extend the passband of a lowpass IIR filter by using an allpass mapping filter.
Input Lowpass IIR Filter
Design a prototype real IIR lowpass elliptic filter with a gain of about –3 dB at 0.5π rad/sample.
[b,a] = ellip(3,0.1,30,0.409); freqz(b,a)
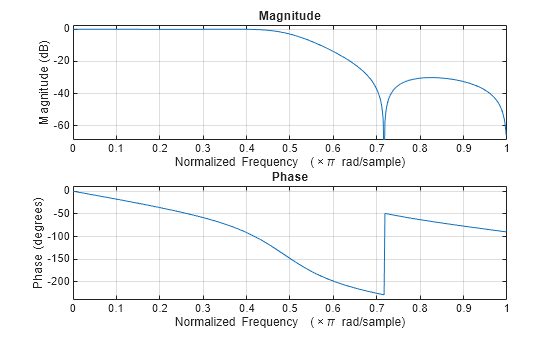
Transform Filter Using iirftransf
Extend the passband of the real prototype filter by specifying the allpass mapping filter as a vector of numerator and denominator coefficients, alpnum and alpden respectively. Use the allpasslp2lp function to generate the allpass mapping filter coefficients.
Specify the prototype filter as a vector of numerator and denominator coefficients, b and a respectively.
[b,a] = ellip(3,0.1,30,0.409); [alpnum,alpden] = allpasslp2lp(0.5,0.25); [num,den] = iirftransf(b,a,alpnum,alpden);
Compare the magnitude response of the filters.
filterAnalyzer(b,a,num,den,FilterNames=["PrototypeFilterTFForm","TransformedFilterFromTFForm"]);

You can also specify the input lowpass IIR filter as a matrix of coefficients. Pass the second-order section matrices as inputs. The numerator and the denominator coefficients of the transformed filter are given by num2 and den2, respectively.
[ss,g] = tf2sos(b,a);
[num2,den2] = iirftransf(ss(:,1:3),ss(:,4:6),...
alpnum,alpden);Compare the magnitude response of the filters.
filterAnalyzer(ss(:,1:3),ss(:,4:6),num2,den2,FilterNames=["PrototypeFilterSOSForm",... "TransformedFilterFromSOSForm"]);
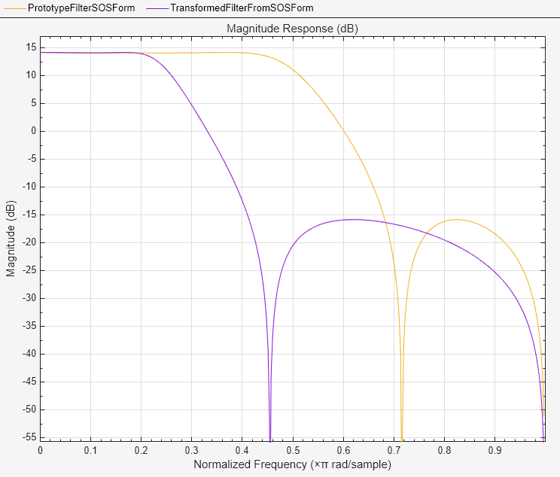
Input Arguments
Numerator coefficients of the prototype lowpass IIR filter, specified as either:
Row vector –– Specifies the values of [b0, b1, …, bn], given this transfer function form:
where n is the order of the filter.
Matrix –– Specifies the numerator coefficients in the form of an P-by-(Q+1) matrix, where P is the number of filter sections and Q is the order of each filter section. If Q = 2, the filter is a second-order section filter. For higher-order sections, make Q > 2.
In the transfer function form, the numerator coefficient matrix bik of the IIR filter can be represented using the following equation:
where,
a –– Denominator coefficients matrix. For more information on how to specify this matrix, see
a.k –– Row index.
i –– Column index.
When specified in the matrix form, b and a matrices must have the same number of rows (filter sections) Q.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Denominator coefficients for a prototype lowpass IIR filter, specified as one of these options:
Row vector –– Specifies the values of [a0, a1, …, an], given this transfer function form:
where n is the order of the filter.
Matrix –– Specifies the denominator coefficients in the form of an P-by-(Q+1) matrix, where P is the number of filter sections and Q is the order of each filter section. If Q = 2, the filter is a second-order section filter. For higher-order sections, make Q > 2.
In the transfer function form, the denominator coefficient matrix aik of the IIR filter can be represented using the following equation:
where,
b –– Numerator coefficients matrix. For more information on how to specify this matrix, see
b.k –– Row index.
i –– Column index.
When specified in the matrix form, a and b matrices must have the same number of rows (filter sections) P.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Numerator coefficients of the mapping filter, specified as a row vector.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Denominator coefficients of the mapping filter, specified as a row vector.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Output Arguments
Numerator coefficients of the transformed filter, returned as one of the following:
Row vector of length n+1, where n is the order of the input filter. The
numoutput is a row vector when the input coefficientsbandaare row vectors.P-by-(Q+1) matrix, where P is the number of filter sections and Q is the order of each section of the transformed filter. The
numoutput is a matrix when the input coefficientsbandaare matrices.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Denominator coefficients of the transformed filter, returned as one of the following:
Row vector of length n+1, where n is the order of the input filter. The
denoutput is a row vector when the input coefficientsbandaare row vectors.P-by-(Q+1) matrix, where P is the number of filter sections and Q is the order of each section of the transformed filter. The
denoutput is a matrix when the input coefficientsbandaare matrices.
Data Types: single | double
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2011a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)