誤差曲面を示すパターンの関連付け
ターゲット出力を使用して特定の入力に応答するように線形ニューロンの設計を行います。
X は、2 つの 1 要素入力パターン (列ベクトル) を定義します。T は、関連する 1 要素ターゲット (列ベクトル) を定義します。
X = [1.0 -1.2]; T = [0.5 1.0];
ERRSURF は、可能な重みとバイアスの値の y 範囲を使用して y ニューロンの誤差を計算します。PLOTES は、この誤差曲面と、その下の y 等高線図を併せてプロットします。最適な重みとバイアスの値は、誤差曲面の最低点が得られる値です。
w_range = -1:0.1:1;
b_range = -1:0.1:1;
ES = errsurf(X,T,w_range,b_range,'purelin');
plotes(w_range,b_range,ES);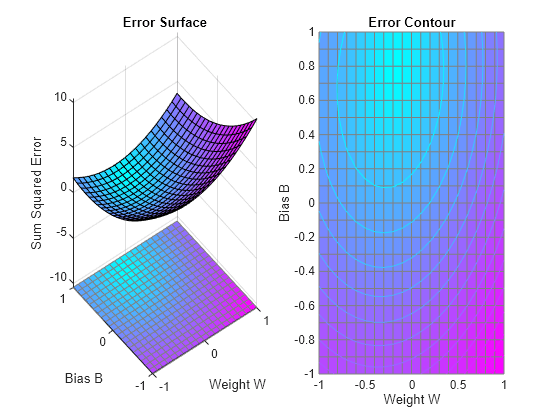
関数 NEWLIND は、最小誤差で実行される y ネットワークを設計します。
net = newlind(X,T);
SIM を使用して入力 X でネットワークをシミュレートします。その後、ニューロンの誤差を計算できます。SUMSQR は二乗誤差を合計します。
A = net(X)
A = 1×2
0.5000 1.0000
E = T - A
E = 1×2
0 0
SSE = sumsqr(E)
SSE = 0
PLOTES は誤差曲面を再プロットします。PLOTEP は、SOLVELIN から返された重みとバイアスの値を使用してネットワークの "位置" をプロットします。プロットからわかるように、SOLVELIN は誤差が最小の解を見つけました。
plotes(w_range,b_range,ES);
plotep(net.IW{1,1},net.b{1},SSE);
これで、元の入力の 1 つである -1.2 でアソシエーターをテストし、ターゲットである 1.0 を返すかどうかを確認できます。
x = -1.2; y = net(x)
y = 1