ビームフォーミングおよび到来方向の推定
Phased Array System Toolbox™ には、狭帯域および広帯域のデジタル ビームフォーミング アルゴリズムが含まれています。アルゴリズムはスペクトルベースおよび共分散ベースの手法をカバーしています。ビームフォーマーの位相シフト、Capon、最小分散無歪応答 (MVDR)、および線形制約最小分散 (LCMV) をシミュレーションできます。さらに、ツールボックスには、ESPRIT や MUSIC などの部分空間ベースの到来方向推定法も含まれています。System object は、1 次元および 2 次元の和差モノパルス トラッカーを使用したターゲット トラッキングをサポートします。従来型または適応型の DPCA キャンセラーおよびサンプル行列反転 (SMI) ビームフォーマーを使用して、クラッターや妨害電波の干渉を抑制する手法を採用できます。アルゴリズムの多くはレーダーとソナーの両方をサポートしています。
カテゴリ
注目の例
Acoustic Beamforming Using a Microphone Array
Illustrates microphone array beamforming to extract desired speech signals in an interference-dominant, noisy environment. Such operations are useful to enhance speech signal quality for perception or further processing. For example, the noisy environment can be a trading room, and the microphone array can be mounted on the monitor of a trading computer. If the trading computer must accept speech commands from a trader, the beamformer operation is crucial to enhance the received speech quality and achieve the designed speech recognition accuracy.
Beamforming for MIMO-OFDM Systems
Model a point-to-point MIMO-OFDM system with beamforming. The combination of multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) techniques have been adopted in recent wireless standards, such as 802.11x families, to provide higher data rate. Because MIMO uses antenna arrays, beamforming can be adopted to improve the received signal to noise ratio (SNR) which in turn reduces the bit error rate (BER).
Conventional and Adaptive Beamformers
Apply three beamforming algorithms to narrowband array data: the phase shift beamformer, the minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) beamformer, and the linearly constrained minimum variance (LCMV) beamformer.
Direction of Arrival Estimation with Beamscan, MVDR, and MUSIC
Illustrates using beamscan, MVDR, and MUSIC for direction of arrival (DOA) estimation. Beamscan is a technique that forms a conventional beam and scans it over directions of interest to obtain a spatial spectrum. Minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) is similar to beamscan but uses an MVDR beam. Multiple signal classification (MUSIC) is a subspace method that provides high resolution DOA estimates. For all three methods, the peaks of the output spatial spectrum indicate the DOAs of the received signals. In this example, we illustrate the use of beamscan, MVDR, and MUSIC to estimate broadside angles with a uniform linear array (ULA) and azimuth and elevation angles with a uniform rectangular array (URA).
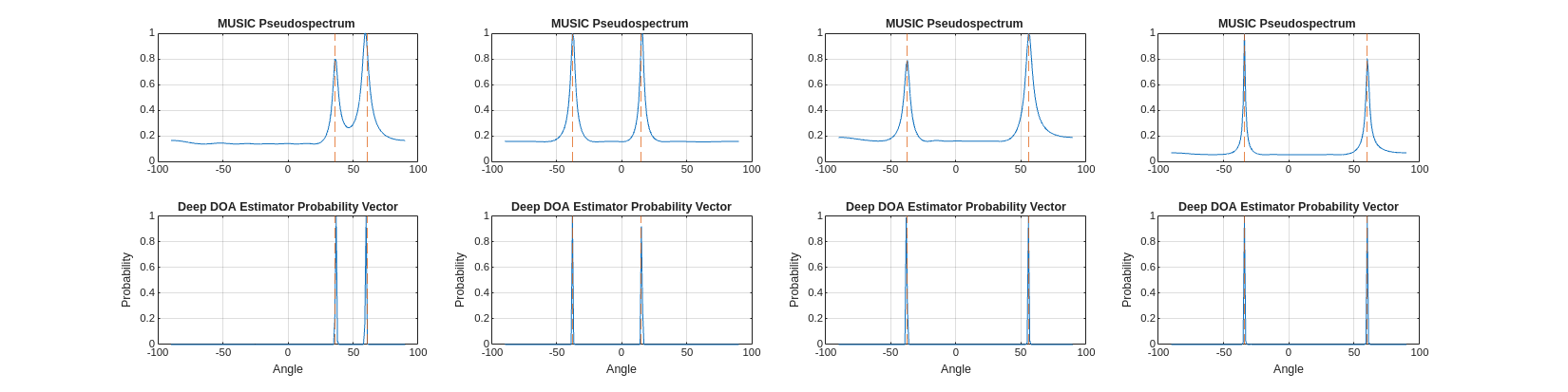
Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Deep Learning
Demonstrates a deep learning approach for Direction-of-Arrival (DOA) estimation.
- R2025a 以降
- ライブ スクリプトを開く
Direction of Arrival Estimation Using Sparse Arrays
Constructs several popular sparse array architectures and shows how they can be used to estimate more signal sources than the number of elements.
Distributed Beamforming Using 1-Bit Feedback
Synchronize the frequency and phase of distributed nodes to enable beamforming.
High Resolution Direction of Arrival Estimation
Illustrates several high-resolution direction of arrival (DOA) estimation techniques. It introduces variants of the MUSIC, root-MUSIC, ESPRIT and root-WSF algorithms and discusses their respective merits in the context of far-field, narrowband signal sources received by a uniform linear array (ULA) antenna.
Increasing Angular Resolution with Virtual Arrays
Introduces how forming a virtual array in MIMO radars can help increase angular resolution. It shows how to simulate a coherent MIMO radar signal processing chain using Phased Array System Toolbox™.
Introduction to Space-Time Adaptive Processing
Gives a brief introduction to space-time adaptive processing (STAP) techniques and illustrates how to use Phased Array System Toolbox™ to apply STAP algorithms to the received pulses. STAP is a technique used in airborne radar systems to suppress clutter and jammer interference.
Source Localization Using Generalized Cross Correlation
Determine the position of the source of a wideband signal using generalized cross-correlation (GCC) and triangulation. For simplicity, this example is confined to a two-dimensional scenario consisting of one source and two receiving sensor arrays. You can extend this approach to more than two sensors or sensor arrays and to three dimensions.
Acoustic Beamforming Using Microphone Arrays
Beamform signals received by an array of microphones to extract a desired speech signal in a noisy environment. This Simulink® example is based on the MATLAB® example Acoustic Beamforming Using a Microphone Array for System objects.
Conventional and Adaptive Beamformers
Apply conventional and adaptive beamforming in Simulink® to a narrowband signal received by an antenna array. The signal model includes noise and interference. This example is based on the Conventional and Adaptive Beamformers example.
Direction of Arrival with Beamscan and MVDR
Use beamscan and minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) techniques for direction of arrival (DOA) estimation in Simulink®. It is based on the MATLAB® example Direction of Arrival Estimation with Beamscan, MVDR, and MUSIC.
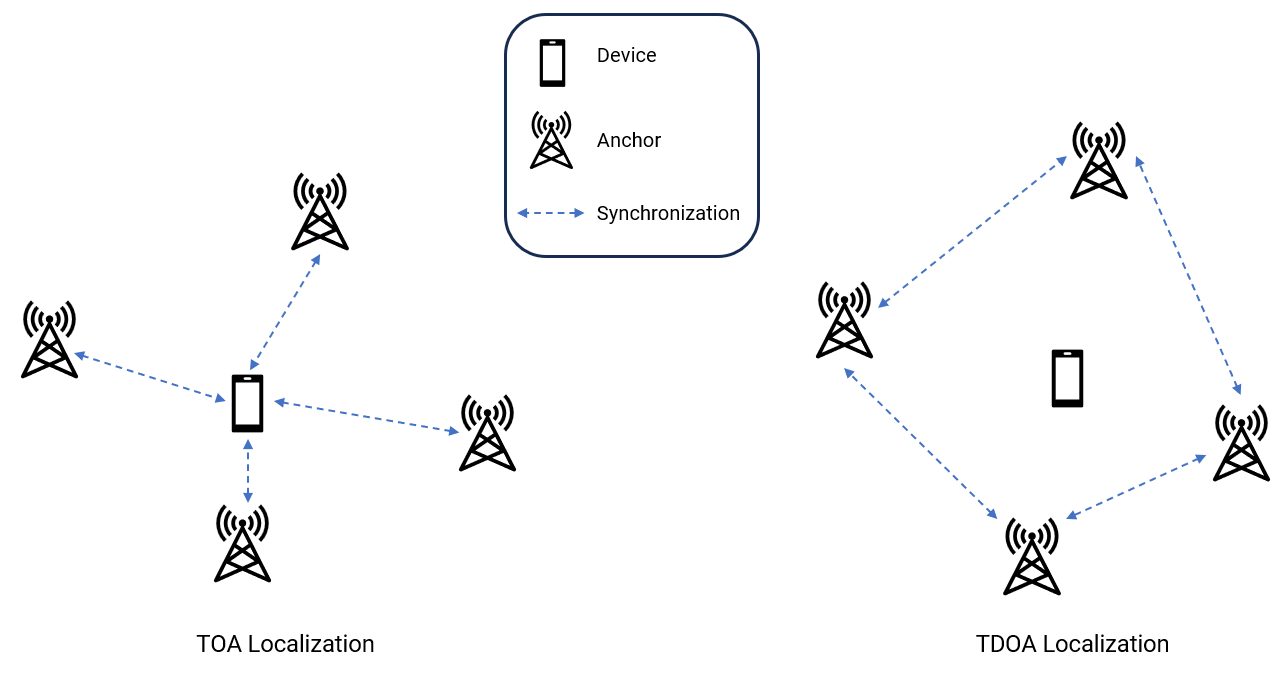
Target Localization in Active and Passive Radars
Model radar networks, configure and propagate radar waveforms, and perform time-of-arrival and time-difference of arrival estimation and localization.
Device Localization in Wireless Systems
Build wireless sensor networks, configure and propagate wireless waveforms, and then perform TOA/TDOA estimation and localization.
Target Tracking Using Sum-Difference Monopulse Radar
Use the sum-difference monopulse tracker to continually estimate signal direction of arrival.
Introduction to Differential Beamforming
Use differential beamforming to form a linear differential microphone array.
Examine the Response of a Focused Phased Array
Use a focused steering vector to generate element weights for a phased array and compute the array response.
Antenna Array Beam Scanning Visualization on a Map
Visualize the changing pattern and coverage map of an antenna array as it scans a sweep of angles. The antenna array is created using Antenna Toolbox™ and Phased Array System Toolbox™. The array is designed to be directional and radiate in the xy-plane to generate a maximum coverage region in the geographic azimuth. Transmitter and receiver sites are created and shown on a map, and the pattern and coverage map are displayed as the antenna array is steered.
802.11az Three-Dimensional Tracking Using Time of Arrival Estimation
Use an IEEE 802.11az Wi-Fi network to track Wi-Fi devices in a three-dimensional space using time of arrival (TOA) estimation.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Web サイトの選択
Web サイトを選択すると、翻訳されたコンテンツにアクセスし、地域のイベントやサービスを確認できます。現在の位置情報に基づき、次のサイトの選択を推奨します:
また、以下のリストから Web サイトを選択することもできます。
最適なサイトパフォーマンスの取得方法
中国のサイト (中国語または英語) を選択することで、最適なサイトパフォーマンスが得られます。その他の国の MathWorks のサイトは、お客様の地域からのアクセスが最適化されていません。
南北アメリカ
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
ヨーロッパ
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)