Poisson’s Equation with Complex 2-D Geometry: PDE Modeler App
This example shows how to solve the Poisson's equation, –Δu = f on a 2-D geometry created as a combination of two rectangles and two circles.
To solve this problem in the PDE Modeler app, follow these steps:
Open the PDE Modeler app by using the
pdeModelercommand.Display grid lines. To do this, select Options > Grid Spacing and clear the Auto checkbox for the x-axis linear spacing. Enter X-axis linear spacing as
-1.5:0.25:1.5. Then select Options > Grid.Align new shapes to the grid lines by selecting Options > Snap.
Draw two circles: one with the radius 0.4 and the center at (-0.5,0) and another with the radius 0.2 and the center at (0.5,0.2). To draw a circle, first click the
 button. Then right-click the origin and drag to draw a circle.
Right-clicking constrains the shape you draw so that it is a circle rather than an
ellipse.
button. Then right-click the origin and drag to draw a circle.
Right-clicking constrains the shape you draw so that it is a circle rather than an
ellipse.Draw two rectangles: one with corners (-1,0.2), (1,0.2), (1,-0.2), and (-1,-0.2) and another with corners (0.5,1), (1,1), (1,-0.6), and (0.5,-0.6). To draw a rectangle, first click the
 button. Then click any corner and drag to draw the
rectangle.
button. Then click any corner and drag to draw the
rectangle.Model the geometry by entering
(R1+C1+R2)-C2in the Set formula field.Save the model to a file by selecting File > Save As.
Remove the subdomain borders. To do this, switch to the boundary mode by selecting Boundary > Boundary Mode. Then select Boundary > Remove All Subdomain Borders.
Specify the boundary conditions for all circle arcs. Using Shift+click, select these borders. Then select Boundary > Specify Boundary Conditions and specify the Neumann boundary condition with g = -5 and q = 0. This boundary condition means that the solution has a slope of –5 in the normal direction for these boundary segments.
For all other boundaries, keep the default Dirichlet boundary condition:
h = 1,r = 0.Specify the coefficients by selecting PDE > PDE Specification or clicking the
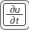 button on the toolbar. Specify
button on the toolbar. Specify c = 1,a = 0, andf = 10.Initialize the mesh by selecting Mesh > Initialize Mesh. Refine the mesh by selecting Mesh > Refine Mesh.

Solve the PDE by selecting Solve > Solve PDE or clicking the
 button on the toolbar. The toolbox assembles the
PDE problem, solves it, and plots the solution.
button on the toolbar. The toolbox assembles the
PDE problem, solves it, and plots the solution.
Plot the solution as a 3-D plot:
Select Plot > Parameters.
In the resulting dialog box, select Height (3-D plot).
Click Plot.
