Geometry from alphaShape
Create a 3-D geometry using the MATLAB® alphaShape function. First, create an alphaShape object of a block with a cylindrical hole. Then create a geometry from the alphaShape boundary.
Create a 2-D mesh grid.
[xg,yg] = meshgrid(-3:0.25:3); xg = xg(:); yg = yg(:);
Create a unit disk. Remove all the mesh grid points that fall inside the unit disk, and include the unit disk points.
t = (pi/24:pi/24:2*pi)'; x = cos(t); y = sin(t); circShp = alphaShape(x,y,2); in = inShape(circShp,xg,yg); xg = [xg(~in); cos(t)]; yg = [yg(~in); sin(t)];
Create 3-D copies of the remaining mesh grid points, with the z-coordinates ranging from 0 through 1. Combine the points into an alphaShape object.
zg = ones(numel(xg),1); xg = repmat(xg,5,1); yg = repmat(yg,5,1); zg = zg*(0:.25:1); zg = zg(:); shp = alphaShape(xg,yg,zg);
Generate a surface mesh of the alphaShape object.
[elements,nodes] = boundaryFacets(shp);
Create an fegeometry object from the surface mesh.
gm = fegeometry(nodes,elements)
gm =
fegeometry with properties:
NumCells: 1
NumFaces: 7
NumEdges: 14
NumVertices: 10
Vertices: [10×3 double]
Mesh: []
For a 3-D geometry created from the surface mesh, the Mesh property remains empty. To use the geometry in an analysis, generate a mesh.
gm = generateMesh(gm); gm.Mesh
ans =
FEMesh with properties:
Nodes: [3×11247 double]
Elements: [10×6880 double]
MaxElementSize: 0.3418
MinElementSize: 0.1709
MeshGradation: 1.5000
GeometricOrder: 'quadratic'
Plot the geometry with the face labels.
pdegplot(gm,FaceLabels="on",FaceAlpha=0.5);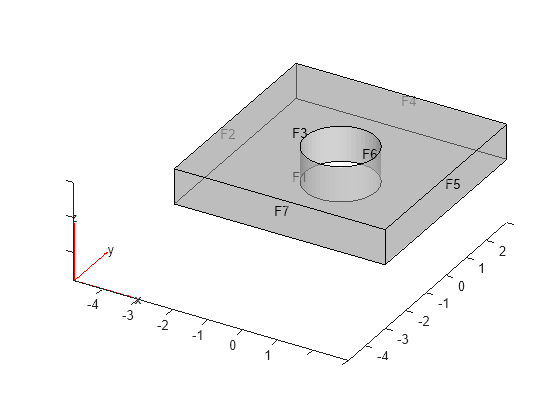
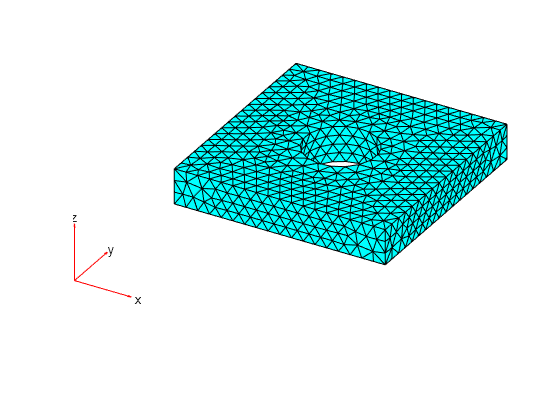
Plot the mesh.
pdemesh(gm);