メインコンテンツ
Results for
I have written two tools and uploaded fileexchange, which allows us to easily draw chord diagrams:
chord chart 弦图
download:
demo:
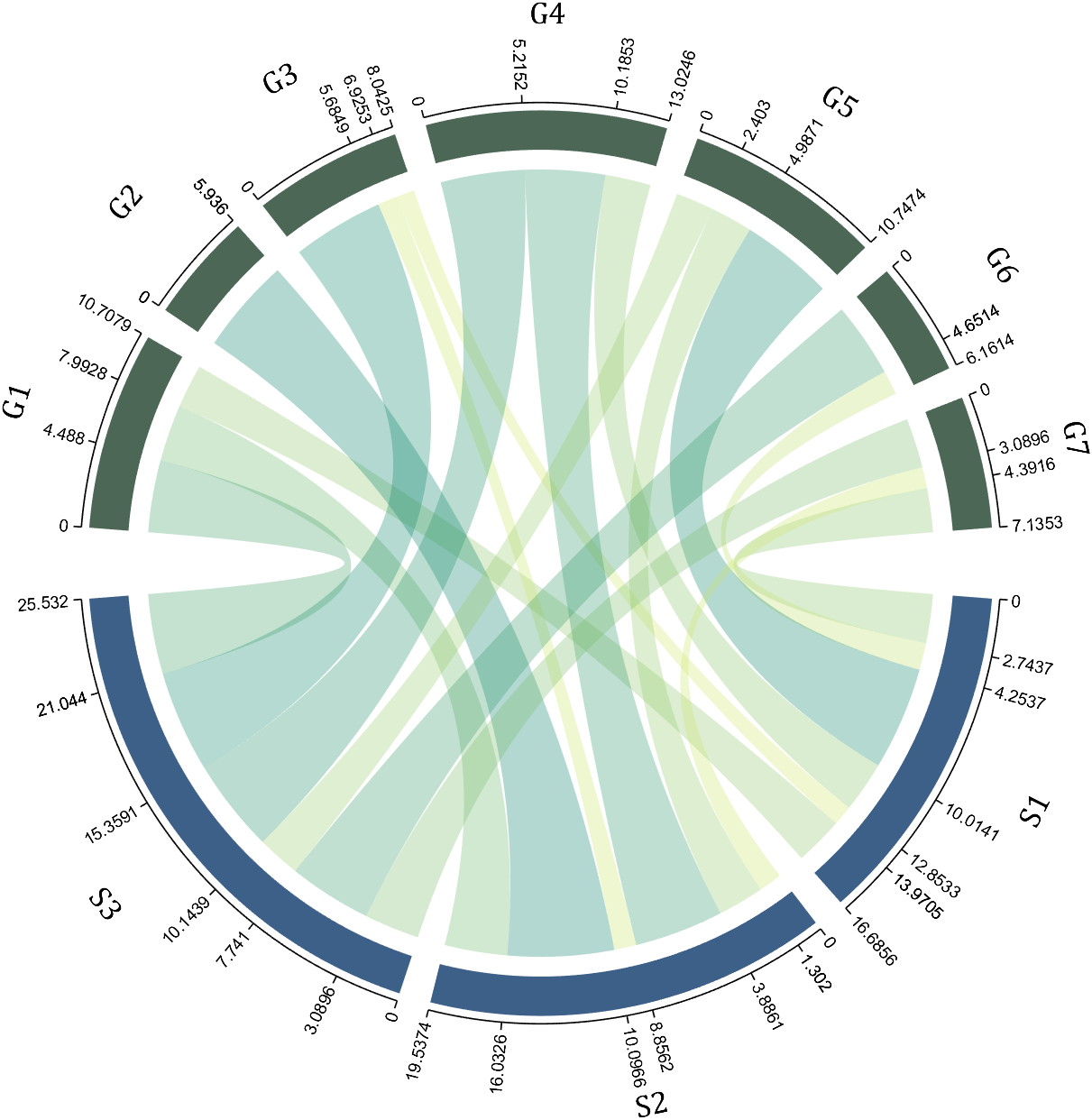
dataMat=[2 0 1 2 5 1 2;
3 5 1 4 2 0 1;
4 0 5 5 2 4 3];
dataMat=dataMat+rand(3,7);
dataMat(dataMat<1)=0;
colName={'G1','G2','G3','G4','G5','G6','G7'};
rowName={'S1','S2','S3'};
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'rowName',rowName,'colName',colName);
CC=CC.draw();
CC.setFont('FontSize',17,'FontName','Cambria')
% 显示刻度和数值
% Displays scales and numeric values
CC.tickState('on')
CC.tickLabelState('on')
% 调节标签半径
% Adjustable Label radius
CC.setLabelRadius(1.4);
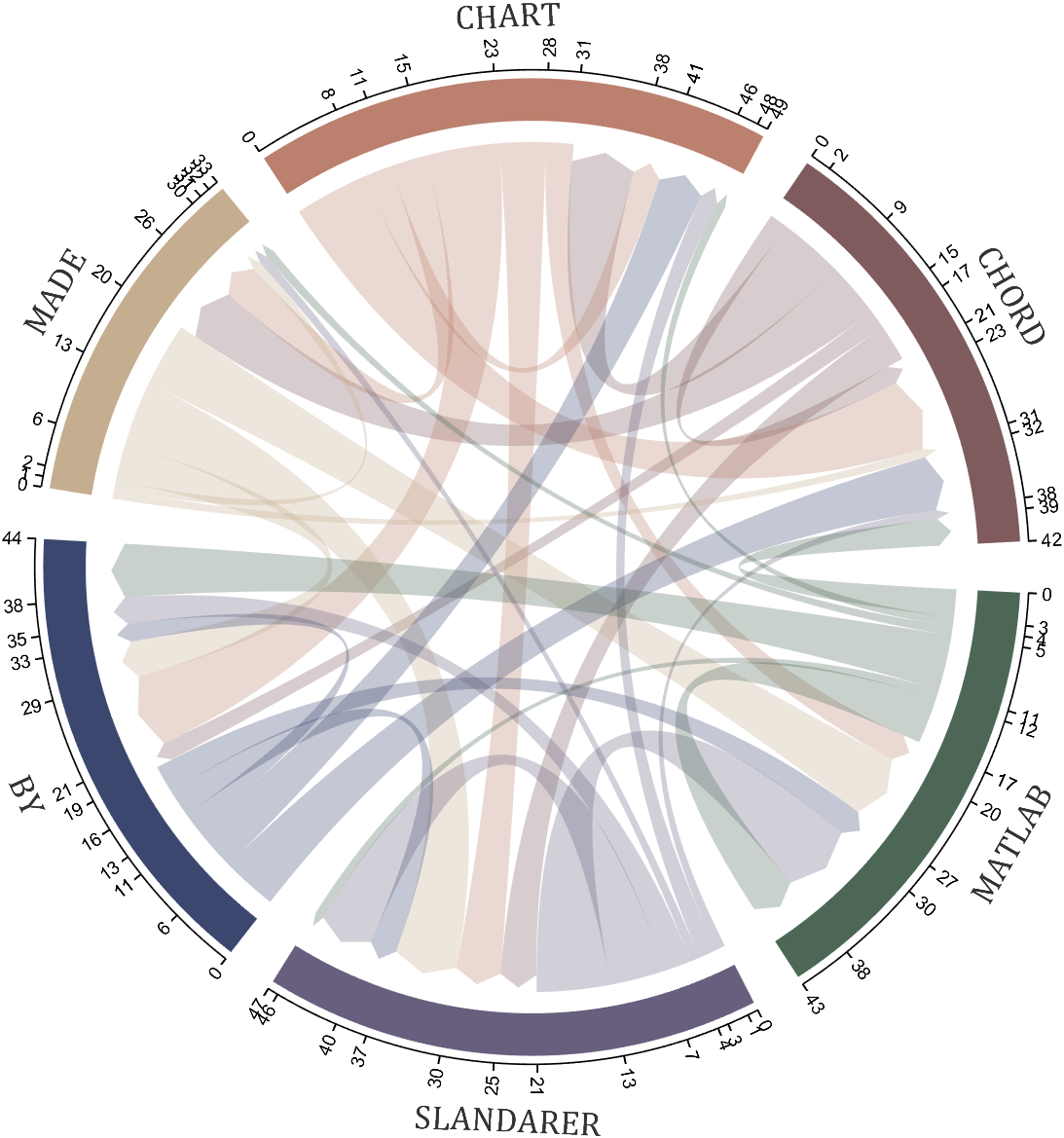
Digraph chord chart 有向弦图
download:
demo:
dataMat=randi([0,8],[6,6]);
% 添加标签名称
NameList={'CHORD','CHART','MADE','BY','SLANDARER','MATLAB'};
BCC=biChordChart(dataMat,'Label',NameList,'Arrow','on');
BCC=BCC.draw();
% 添加刻度
BCC.tickState('on')
% 修改字体,字号及颜色
BCC.setFont('FontName','Cambria','FontSize',17,'Color',[.2,.2,.2])
BCC.setLabelRadius(1.3);
BCC.tickLabelState('on')
How to create a legend as follows?
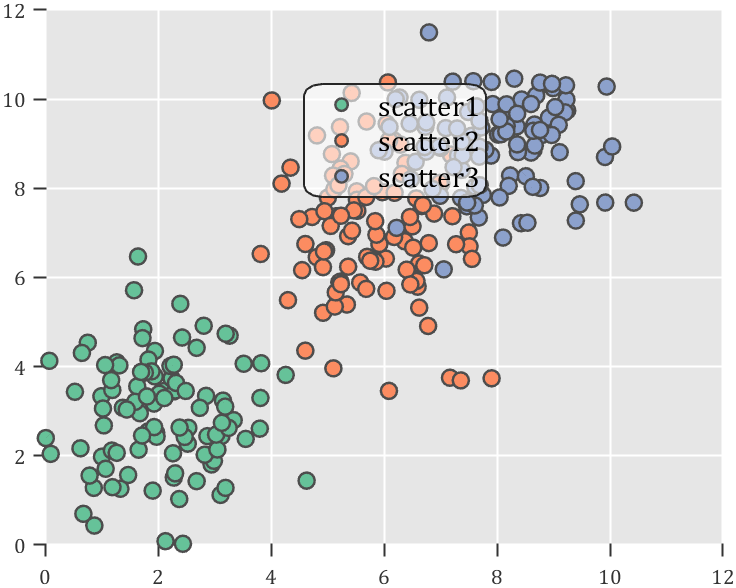
Principle Explanation - Graphic Objects
Hidden Properties of Legend are laid as follows
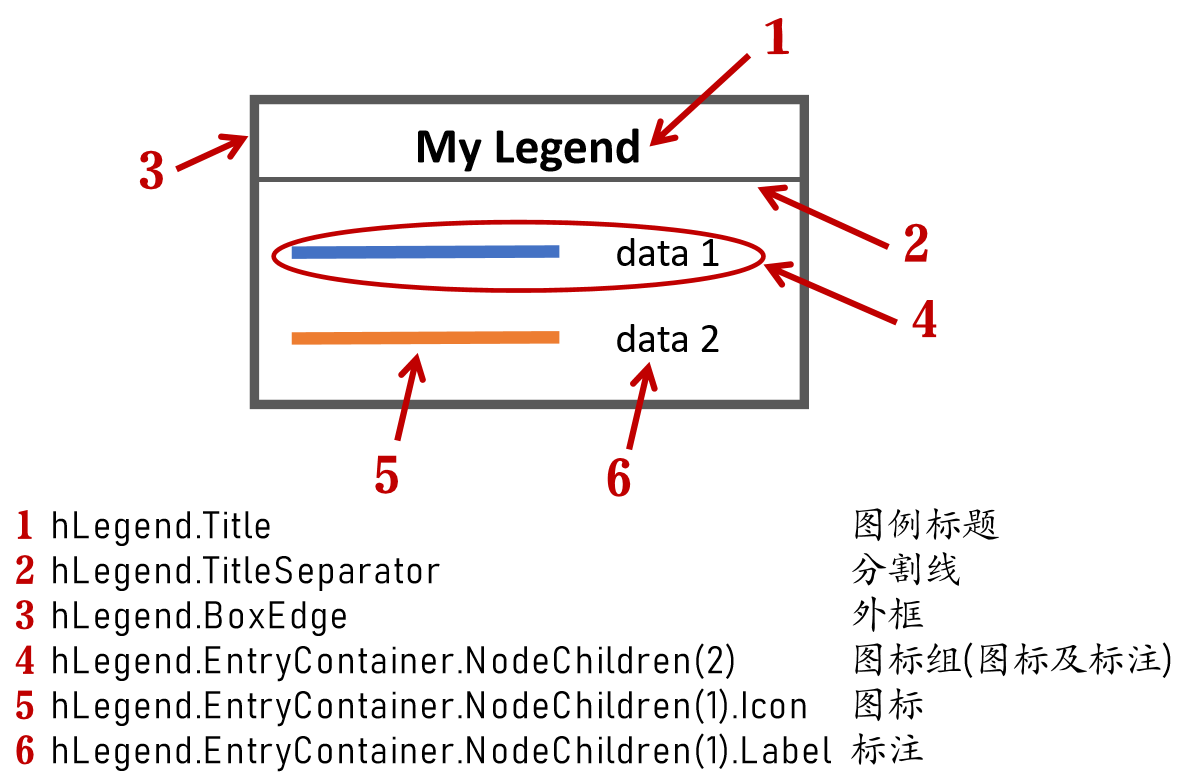
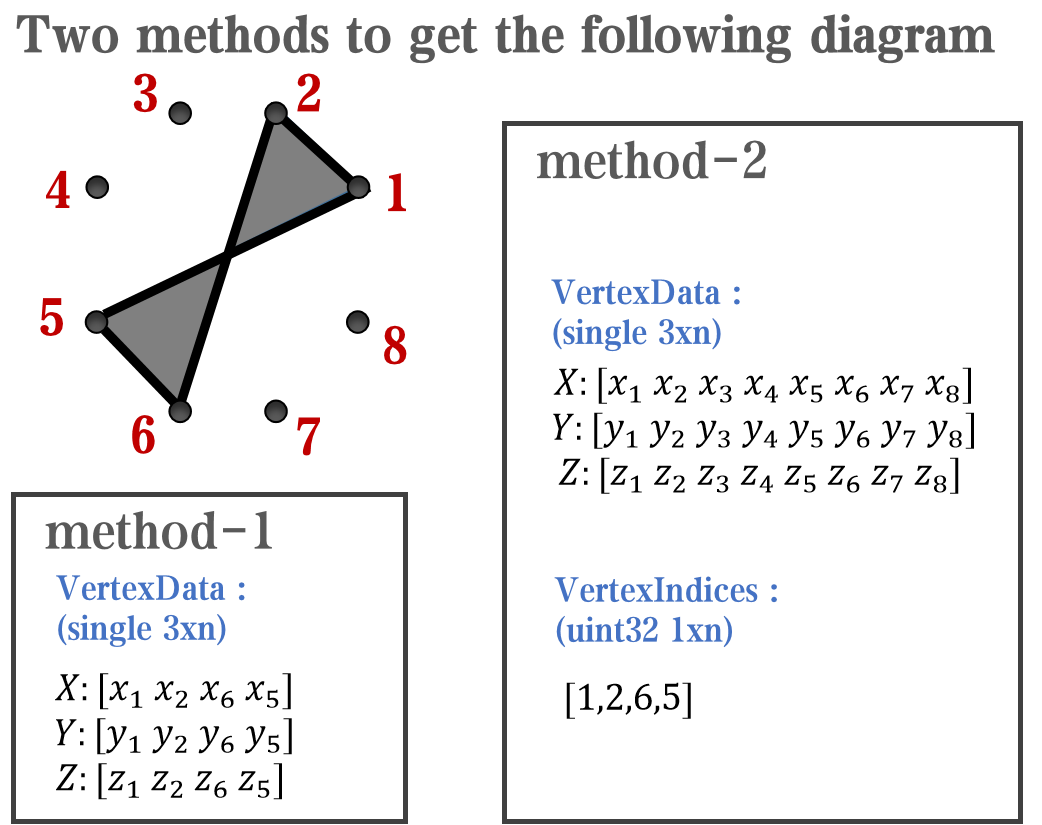
In most cases, legends are drawn using LineLoop and Quadrilateral:
Both of these basic graphic objects are drawn in groups of four points, and the general principle is as follows:
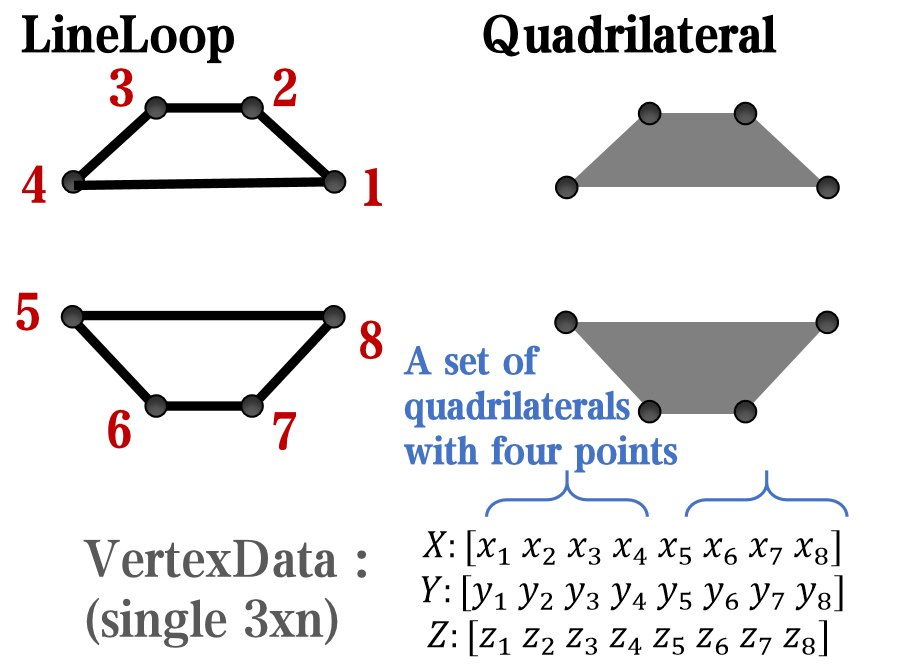
Of course, you can arrange the points in order, or set VertexIndices whitch means the vertex order to obtain the desired quadrilateral shape:
Other objects
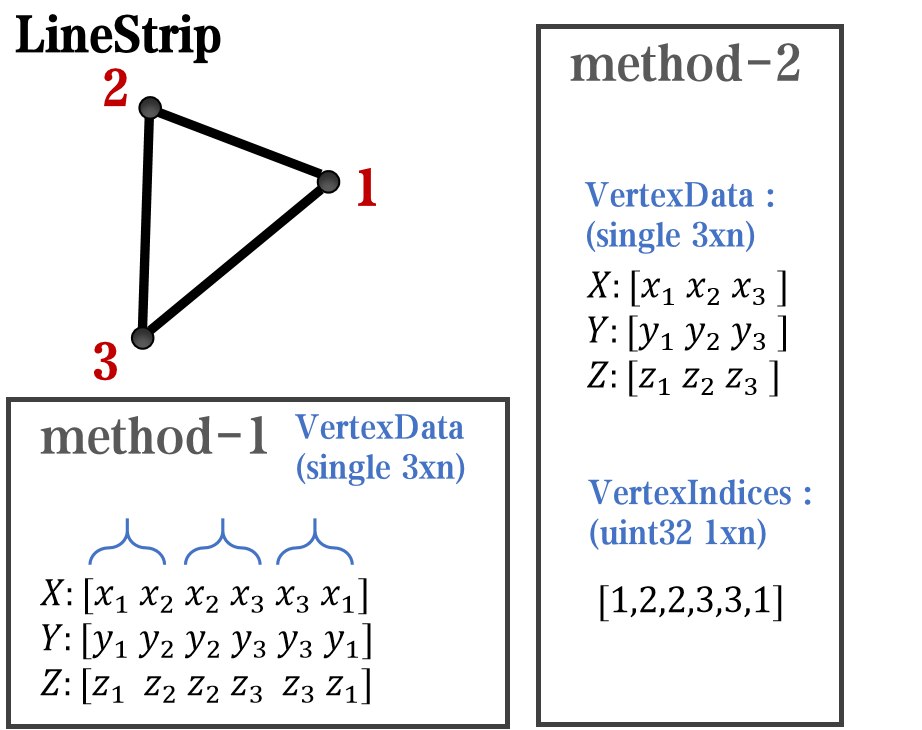
Compared to objects that can only be grouped into four points, we also need to introduce more flexible objects. Firstly, LineStrip, a graphical object that draws lines in groups of two points:
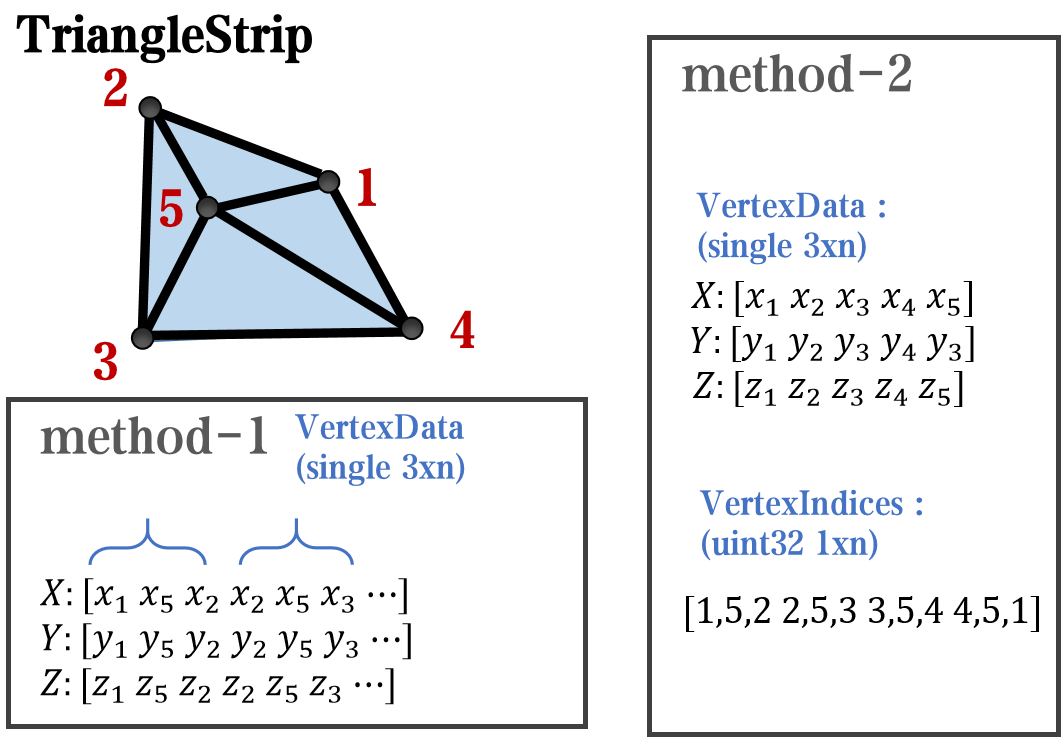
And TriangleStrip is a set of three points that draw objects to fill triangles, for example, complex polygons can be filled with multiple triangles:
Principle Explanation - Create and Replace
Let's talk about how to construct basic graphic objects, which are all constructed using undisclosed and very low-level functions, such as LineStrip, not through:
- LineStrip()
It is built through:
- matlab.graphics.primitive.world.LineStrip()
After building the object, the following properties must be set to make the hidden object visible:
- Layer
- ColorBinding
- ColorData
- VertexData
- PickableParts
The settings of these properties can refer to the original legend to form the object, which will not be elaborated here. You can also refer to the code I wrote.
Afterwards, set the newly constructed object's parent class as the Group parent class of the original component, and then hide the original component
newBoxEdgeHdl.Parent=oriBoxEdgeHdl.Parent;
oriBoxEdgeHdl.Visible='off';
The above is the entire process of component replacement, with two example codes written:
Semi transparent legend
function SPrettyLegend(lgd)
% Semitransparent rounded rectangle legend
% Copyright (c) 2023, Zhaoxu Liu / slandarer
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Zhaoxu Liu / slandarer (2023). pretty legend
% (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/132128-pretty-legend),
% MATLAB Central File Exchange. 检索来源 2023/7/9.
% =========================================================================
if nargin<1
ax = gca;
lgd = get(ax,'Legend');
end
pause(1e-6)
Ratio = .1;
t1 = linspace(0,pi/2,4); t1 = t1([1,2,2,3,3,4]);
t2 = linspace(pi/2,pi,4); t2 = t2([1,2,2,3,3,4]);
t3 = linspace(pi,3*pi/2,4); t3 = t3([1,2,2,3,3,4]);
t4 = linspace(3*pi/2,2*pi,4); t4 = t4([1,2,2,3,3,4]);
XX = [1,1,1-Ratio+cos(t1).*Ratio,1-Ratio,Ratio,Ratio+cos(t2).*Ratio,...
0,0,Ratio+cos(t3).*Ratio,Ratio,1-Ratio,1-Ratio+cos(t4).*Ratio];
YY = [Ratio,1-Ratio,1-Ratio+sin(t1).*Ratio,1,1,1-Ratio+sin(t2).*Ratio,...
1-Ratio,Ratio,Ratio+sin(t3).*Ratio,0,0,Ratio+sin(t4).*Ratio];
% 圆角边框(border-radius)
oriBoxEdgeHdl = lgd.BoxEdge;
newBoxEdgeHdl = matlab.graphics.primitive.world.LineStrip();
newBoxEdgeHdl.AlignVertexCenters = 'off';
newBoxEdgeHdl.Layer = 'front';
newBoxEdgeHdl.ColorBinding = 'object';
newBoxEdgeHdl.LineWidth = 1;
newBoxEdgeHdl.LineJoin = 'miter';
newBoxEdgeHdl.WideLineRenderingHint = 'software';
newBoxEdgeHdl.ColorData = uint8([38;38;38;0]);
newBoxEdgeHdl.VertexData = single([XX;YY;XX.*0]);
newBoxEdgeHdl.Parent=oriBoxEdgeHdl.Parent;
oriBoxEdgeHdl.Visible='off';
% 半透明圆角背景(Semitransparent rounded background)
oriBoxFaceHdl = lgd.BoxFace;
newBoxFaceHdl = matlab.graphics.primitive.world.TriangleStrip();
Ind = [1:(length(XX)-1);ones(1,length(XX)-1).*(length(XX)+1);2:length(XX)];
Ind = Ind(:).';
newBoxFaceHdl.PickableParts = 'all';
newBoxFaceHdl.Layer = 'back';
newBoxFaceHdl.ColorBinding = 'object';
newBoxFaceHdl.ColorType = 'truecoloralpha';
newBoxFaceHdl.ColorData = uint8(255*[1;1;1;.6]);
newBoxFaceHdl.VertexData = single([XX,.5;YY,.5;XX.*0,0]);
newBoxFaceHdl.VertexIndices = uint32(Ind);
newBoxFaceHdl.Parent = oriBoxFaceHdl.Parent;
oriBoxFaceHdl.Visible = 'off';
end
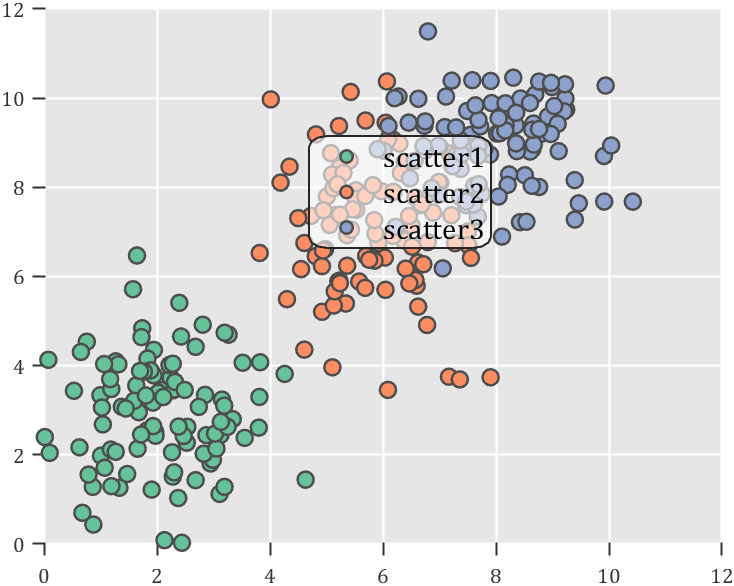
Usage examples
clc; clear; close all
rng(12)
% 生成随机点(Generate random points)
mu = [2 3; 6 7; 8 9];
S = cat(3,[1 0; 0 2],[1 0; 0 2],[1 0; 0 1]);
r1 = abs(mvnrnd(mu(1,:),S(:,:,1),100));
r2 = abs(mvnrnd(mu(2,:),S(:,:,2),100));
r3 = abs(mvnrnd(mu(3,:),S(:,:,3),100));
% 绘制散点图(Draw scatter chart)
hold on
propCell = {'LineWidth',1.2,'MarkerEdgeColor',[.3,.3,.3],'SizeData',60};
scatter(r1(:,1),r1(:,2),'filled','CData',[0.40 0.76 0.60],propCell{:});
scatter(r2(:,1),r2(:,2),'filled','CData',[0.99 0.55 0.38],propCell{:});
scatter(r3(:,1),r3(:,2),'filled','CData',[0.55 0.63 0.80],propCell{:});
% 增添图例(Draw legend)
lgd = legend('scatter1','scatter2','scatter3');
lgd.Location = 'northwest';
lgd.FontSize = 14;
% 坐标区域基础修饰(Axes basic decoration)
ax=gca; grid on
ax.FontName = 'Cambria';
ax.Color = [0.9,0.9,0.9];
ax.Box = 'off';
ax.TickDir = 'out';
ax.GridColor = [1 1 1];
ax.GridAlpha = 1;
ax.LineWidth = 1;
ax.XColor = [0.2,0.2,0.2];
ax.YColor = [0.2,0.2,0.2];
ax.TickLength = [0.015 0.025];
% 隐藏轴线(Hide XY-Ruler)
pause(1e-6)
ax.XRuler.Axle.LineStyle = 'none';
ax.YRuler.Axle.LineStyle = 'none';
SPrettyLegend(lgd)
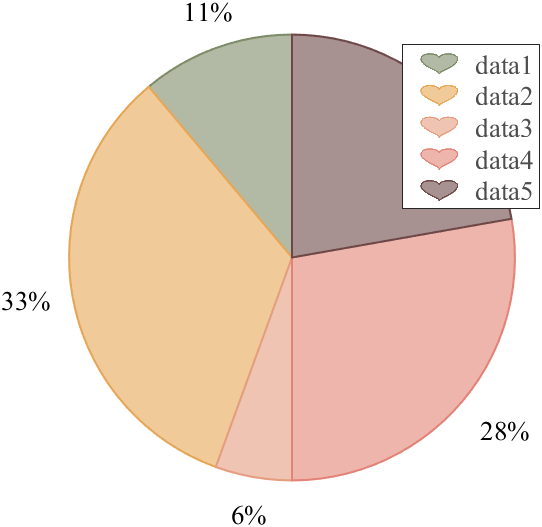
Heart shaped legend (exclusive to pie charts)
function pie2HeartLegend(lgd)
% Heart shaped legend for pie chart
% Copyright (c) 2023, Zhaoxu Liu / slandarer
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Zhaoxu Liu / slandarer (2023). pretty legend
% (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/132128-pretty-legend),
% MATLAB Central File Exchange. 检索来源 2023/7/9.
% =========================================================================
if nargin<1
ax = gca;
lgd = get(ax,'Legend');
end
pause(1e-6)
% 心形曲线(Heart curve)
x = -1:1/100:1;
y1 = 0.6 * abs(x) .^ 0.5 + ((1 - x .^ 2) / 2) .^ 0.5;
y2 = 0.6 * abs(x) .^ 0.5 - ((1 - x .^ 2) / 2) .^ 0.5;
XX = [x, flip(x),x(1)]./3.4+.5;
YY = ([y1, y2,y1(1)]-.2)./2+.5;
Ind = [1:(length(XX)-1);2:length(XX)];
Ind = Ind(:).';
% 获取图例图标(Get Legend Icon)
lgdEntryChild = lgd.EntryContainer.NodeChildren;
iconSet = arrayfun(@(lgdEntryChild)lgdEntryChild.Icon.Transform.Children.Children,lgdEntryChild,UniformOutput=false);
% 基础边框句柄(Base Border Handle)
newEdgeHdl = matlab.graphics.primitive.world.LineStrip();
newEdgeHdl.AlignVertexCenters = 'off';
newEdgeHdl.Layer = 'front';
newEdgeHdl.ColorBinding = 'object';
newEdgeHdl.LineWidth = .8;
newEdgeHdl.LineJoin = 'miter';
newEdgeHdl.WideLineRenderingHint = 'software';
newEdgeHdl.ColorData = uint8([38;38;38;0]);
newEdgeHdl.VertexData = single([XX;YY;XX.*0]);
newEdgeHdl.VertexIndices = uint32(Ind);
% 基础多边形面句柄(Base Patch Handle)
newFaceHdl = matlab.graphics.primitive.world.TriangleStrip();
Ind = [1:(length(XX)-1);ones(1,length(XX)-1).*(length(XX)+1);2:length(XX)];
Ind = Ind(:).';
newFaceHdl.PickableParts = 'all';
newFaceHdl.Layer = 'middle';
newFaceHdl.ColorBinding = 'object';
newFaceHdl.ColorType = 'truecoloralpha';
newFaceHdl.ColorData = uint8(255*[1;1;1;.6]);
newFaceHdl.VertexData = single([XX,.5;YY,.5;XX.*0,0]);
newFaceHdl.VertexIndices = uint32(Ind);
% 替换图例图标(Replace Legend Icon)
for i = 1:length(iconSet)
oriEdgeHdl = iconSet{i}(1);
tNewEdgeHdl = copy(newEdgeHdl);
tNewEdgeHdl.ColorData = oriEdgeHdl.ColorData;
tNewEdgeHdl.Parent = oriEdgeHdl.Parent;
oriEdgeHdl.Visible = 'off';
oriFaceHdl = iconSet{i}(2);
tNewFaceHdl = copy(newFaceHdl);
tNewFaceHdl.ColorData = oriFaceHdl.ColorData;
tNewFaceHdl.Parent = oriFaceHdl.Parent;
oriFaceHdl.Visible = 'off';
end
end
Usage examples
clc; clear; close all
% 生成随机点(Generate random points)
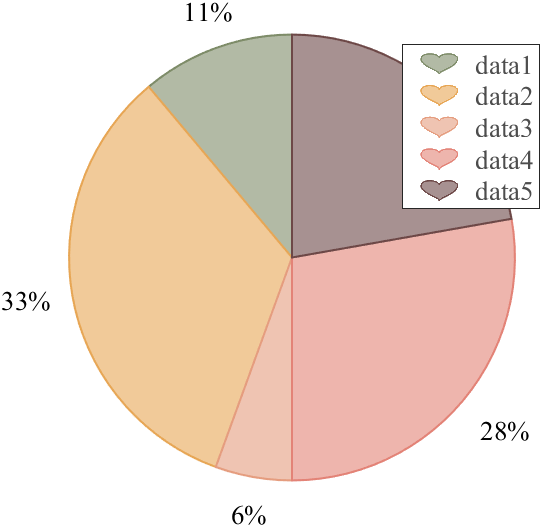
X = [1 3 0.5 2.5 2];
pieHdl = pie(X);
% 修饰饼状图(Decorate pie chart)
colorList=[0.4941 0.5490 0.4118
0.9059 0.6510 0.3333
0.8980 0.6157 0.4980
0.8902 0.5137 0.4667
0.4275 0.2824 0.2784];
for i = 1:2:length(pieHdl)
pieHdl(i).FaceColor=colorList((i+1)/2,:);
pieHdl(i).EdgeColor=colorList((i+1)/2,:);
pieHdl(i).LineWidth=1;
pieHdl(i).FaceAlpha=.6;
end
for i = 2:2:length(pieHdl)
pieHdl(i).FontSize=13;
pieHdl(i).FontName='Times New Roman';
end
lgd=legend('FontSize',13,'FontName','Times New Roman','TextColor',[1,1,1].*.3);
pie2HeartLegend(lgd)
I found this list on Book Authority about the top MATLAB books: https://bookauthority.org/books/best-matlab-books
My favorite book is Accelerating MATLAB Performance - 1001 tips to speed up MATLAB programs. I always pick something up from the book that helps me out.
A key aspect to masting MATLAB Graphics is getting a hang of the MATLAB Graphics Object Hierarchy which is essentially the structure of MATLAB figures that is used in the rendering pipeline. The base object is the Graphics Root (see groot) which contains the Figure. The Figure contains Axes or other containers such as a Tiled Chart Layout (see tiledlayout). Then these Axes can contain graphics primatives (the objects that contain data and get rendered) such as Lines or Patches.
Every graphics object has two important properties, the "Parent" and "Children" properties which can be used to access other objects in the tree. This can be very useful when trying to customize a pre-built chart (such as adding grid lines to both axes in an eye diagram chart) or when trying to access the axes of a non-current figure via a primative (so "gca" doesn't help out).
One last Tip and Trick with this is that you can declare graphics primatives without putting them on or creating an Axes by setting the first input argument to "gobjects(0)" which is an empty array of placeholder graphics objects. Then, when you have an Axes to plot the primitive on and are ready to render it, you can set the "Parent" of the object to your new Axes.
For Example:
l = line(gobjects(0), 1:10, 1:10);
...
...
...
l.Parent = gca;
Practicing navigating and exploring this tree will help propel your understanding of plotting in MATLAB.
spy
Over at Reddit, a MATLAB user asked about when to use a script vs. a live script. How would you answer this?
Starting with MATLAB can be daunting, but the right resources make all the difference. In my experience, the combination of MATLAB Onramp and Cody offers an engaging start.
MATLAB Onramp introduces you to MATLAB's basic features and workflows. Then practice your coding skill on Cody. Challenge yourself to solve 1 basic problem every day for a month! This consistent practice can significantly enhance your proficiency.
What other resources have helped you on your MATLAB journey? Share your recommendations and let's create a comprehensive learning path for beginners!

I'm having problem in its test 6 ... passing 5/6 what would be the real issue..
am wring Transformation matrix correct.. as question said SSW should be 202.5 degree...
so what is the issue..
I would tell myself to understand vectorization. MATLAB is designed for operating on whole arrays and matrices at once. This is often more efficient than using loops.

how can I do to get those informations?
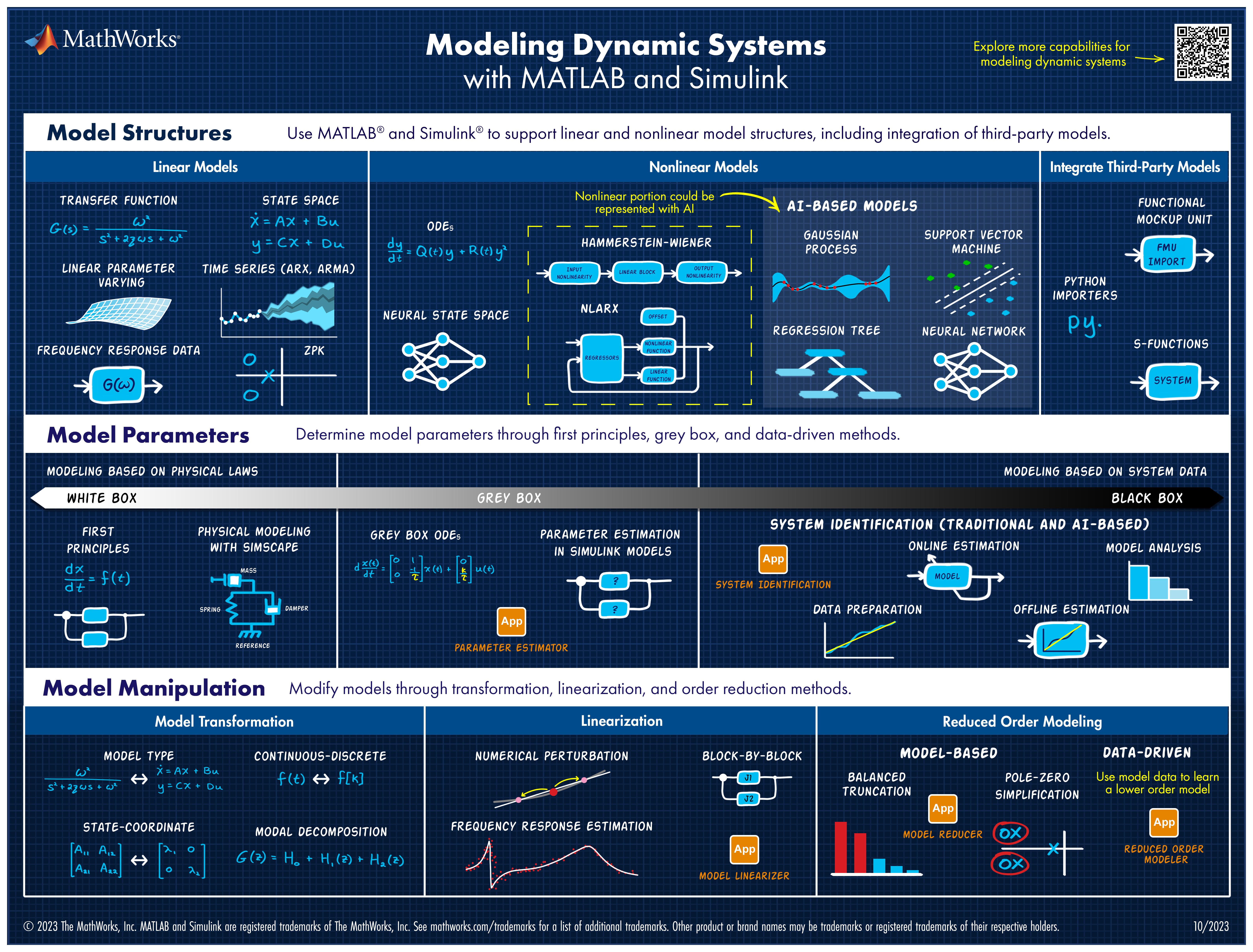
Explore all the capabilities for Modeling Dynamic Systems while keeping them handy with this Cheat Sheet - Download Now.
Here's a MATLAB class I wrote that leverages the MATLAB Central Interface for MATLAB toolbox, which in turn uses the publicy available Community API. Using this class, I've created a few Favorites that show me what's going on in MATLAB Central - without having to leave MATLAB 🙂
The class has a few convenient queries:
- Results for the last 7 days
- Results for the last 30 days
- Results for the current month
- Results for today
And supporting a bunch of different content scopes:
- All MATLAB Central
- MATLAB Answers
- Blogs
- Cody
- Contests
- File Exchange
- Exclude Answers content
The results are displayed in the command window (which worked best for me) and link to each post. Here's what that looks like for this command
>> CommunityFeed.thisMonth("app designer", CommunityFeed.Scope.ExcludeAnswers)

Let me know if you find this class useful and feel free to suggest changes.
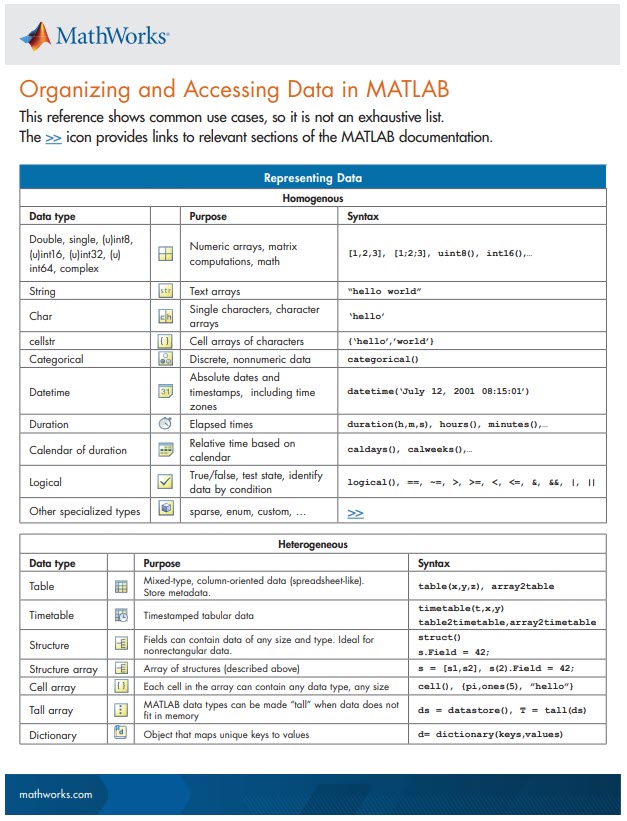
New Cheat Sheet Alert!
Level up your data organization and access skills in MATLAB with our latest cheat sheet! Download the full cheat sheet on MATLAB GitHub for Students here.
Calling all students! New to MATLAB or need helpful resources? Check out our MATLAB GitHub for Students repository! Find MATLAB examples, videos, cheat sheets, and more!
Visit the repository here: MATLAB GitHub for Students
Imagine x is a large vector and you want the smallest 10 elements. How might you do it?

Thats the task:
Given a square cell array:
x = {'01', '56'; '234', '789'};
return a single character array:
y = '0123456789'
I wrote a code that passes Test 1 and 2 and one that passes Test 3 but I'm searching a condition so that the code for Test 3 runs when the cell array only contains letters and the one for Test 1 and 2 in every other case. Can somebody help me?
This is my code:
y = []
[a,b]=size(x)
%%TEST 3
delimiter=zeros(1,a)
delimiter(end)=1
delimiter=repmat(delimiter,1,b)
delimiter(end)=''
delimiter=string(delimiter)
y=[]
for i=1:a*b
y = string([y x(i)])
end
y=join(y,delimiter)
y=erase(y,'0')
y=regexprep(y,'1',' ')
%%TEST 1+2
for i=1:a*b
y = string([y x(i)])
y=join(y)
end
y=erase(y,' ' )
That's the question: Given four different positive numbers, a, b, c and d, provided in increasing order: a < b < c < d, find if any three of them comprise sides of a right-angled triangle. Return true if they do, otherwise return false .
I wrote this code but it doesn't pass test 7. I don't really understand why it isn't working. Can somebody help me?
function flag = isTherePythagoreanTriple(a, b, c, d)
a2=a^2
b2=b^2
c2=c^2
d2=d^2
format shortG
if a2+b2==c2
flag=true
else if a2+b2==d2
flag=true
else if a2+c2==d2
flag=true
else if c2+b2==d2
flag=true
else flag=false
end
end
end
end
end
That's the question:
The file cars.mat contains a table named cars with variables Model, MPG, Horsepower, Weight, and Acceleration for several classic cars.
Load the MAT-file. Given an integer N, calculate the output variable mpg.
Output mpg should contain the MPG of the top N lightest cars (by Weight) in a column vector.
I wrote this code and the resulting column vector has the right values but it doesn't pass the tests. What's wrong?
function mpg = sort_cars(N)
load cars.mat
sorted=sortrows(cars,4)
mpg = sorted(1:N,2)
end
I recently have found that I am no longer able to give my difficulty rating for questions on Cody after sucessfully completing a question. This is obviously not a big deal, I was just wondering if this was an issue on my end or if there was some change that I was not aware of.
The option to rate does not pop up after solving a problem, and the rating in general does not even show up anymore when answering questions (though it is visible from problem groups).
When solving problems over on Cody, I can almost always view all solutions to a problem after submitting a correct solution of my own. Very rarely, however, this is not the case, and I instead get the following message:
This solution is locked. To view this solution, you need to provide a solution of the same size or smaller.
You may solve another problem from Community group to unlock all the solutions to this problem.
If this happens, then again, I can almost always rectify this by submitting a (correct) solution to a different problem (I take it that the Community group is the implicit group of all problems on Cody --- is it?). But sometimes that, too, fails.
So my question is, why? What are the criteria that determine when all solutions are, in fact, unlocked?
